Boxed Warning
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis:
Severe acute exacerbations of hepatitis have been reported in patients who have discontinued anti–hepatitis B therapy, including adefovir. Closely monitor hepatic function with both clinical and laboratory follow-up for at least several months in patients who discontinue anti–hepatitis B therapy. If appropriate, resumption of anti–hepatitis B therapy may be warranted.
Nephrotoxicity:
In patients at risk of or having underlying renal dysfunction, long-term administration of adefovir may result in nephrotoxicity. Closely monitor renal function in these patients; they may require dose adjustment.
HIV resistance:
HIV resistance may emerge in chronic hepatitis B patients with unrecognized or untreated HIV infection treated with anti–hepatitis B therapies that may have activity against HIV (eg, adefovir).
Lactic acidosis/severe hepatomegaly with steatosis:
Lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis, including fatal cases, have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogs alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral, as dipivoxil:
Hepsera: 10 mg
Generic: 10 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Acyclic nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitor (adenosine analog) which interferes with HBV viral RNA-dependent DNA polymerase resulting in inhibition of viral replication.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Distribution
0.35 to 0.39 L/kg
Metabolism
Prodrug; rapidly converted to adefovir (active metabolite) in intestine
Excretion
Urine (45% as active metabolite within 24 hours); Dialysis: ~35% of dose (10 mg) removed during 4 hours hemodialysis session
Time to Peak
Median: 1.75 hours (range: 0.58 to 4 hours)
Half-Life Elimination
7.5 hours; prolonged in renal impairment
Protein Binding
≤4%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Cmax and AUC increased in those with moderate or severe renal function impairment or with end-stage renal disease.
Use: Labeled Indications
Treatment of chronic hepatitis B with evidence of active viral replication (based on persistent elevation of ALT/AST or histologic evidence)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to adefovir or any component of the formulation
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Hepatitis B (chronic): Oral: 10 mg once daily
Treatment duration (AASLD practice guidelines): Treatment duration for nucleos(t)ide analog-based therapy (eg, adefovir) is variable and influenced by HBeAg status, duration of HBV suppression, and presence of cirrhosis/decompensation (AASLD [Terrault 2016):
Patients without cirrhosis:
Hepatitis B e antigen positive (HBeAg-positive) immune-active chronic hepatitis: Treat until HBeAg seroconversion; after seroconversion, prolonged duration of therapy is often required in patients treated with nucleos(t)ide analogues. Optimal duration is unknown; however, consolidation therapy is generally a minimum of 12 months of persistently normal ALT and undetectable serum HBV DNA levels after HBeAg seroconversion.
HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic hepatitis: Indefinite antiviral therapy is suggested unless there is competing rationale for discontinuation (risk/benefit decision); treatment discontinuation may be considered in patients with loss of HBsAg; however, there is insufficient evidence to guide decisions in these patients.
Patients with cirrhosis:
HBeAg-positive immune-active chronic hepatitis: In patients who seroconvert on therapy, continue antiviral therapy indefinitely due to concerns with decompensation and death, unless there is a strong competing rationale for discontinuation.
HBeAg-negative immune-active chronic hepatitis: Treatment discontinuation is not recommended due to potential for decompensation and death (limited data).
Viral breakthrough(AASLD practice guidelines): Patients with confirmed viral breakthrough (HBV DNA ≥100 IU/mL with previously undetectable levels [<10 IU/mL] or >1 log increase in HBV DNA) should either be switched to an alternative antiviral monotherapy agent with a high genetic barrier to resistance or receive a second antiviral agent with a complementary resistance profile; consult current clinical practice guidelines for recommended agents (AASLD [Terrault 2016]).
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Hepatitis B infection, chronic: Note: Optimal duration of treatment not established, continuation of therapy for at least 12 months after seroconversion has been suggested. Prolonged therapy (up to 4 years) has been reported to be safe and well-tolerated in pediatric patients (2 to 18 years). Patients not achieving a <2 log decrease in serum HBV DNA after at least 6 months of therapy should either receive additional treatment or be switched to an alternative therapy (AASLD [Terrault 2016]; Jonas 2012; Lok 2009).
Children 2 to <7 years: Limited data available; efficacy results variable: Oral: 0.3 mg/kg/dose once daily; maximum dose: 10 mg (Jonas 2008; Jonas 2012)
Children ≥7 to <12 years: Limited data available; efficacy results variable: Oral: 0.25 mg/kg/dose once daily; maximum dose: 10 mg (Jonas 2008; Jonas 2012)
Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: Oral: 10 mg once daily; in HIV-exposed/-positive patients not requiring combination antiretroviral therapy or receiving a lamivudine- or emtricitabine-containing HIV-suppressive regimen, adefovir may be considered as HBV alternate therapy (interferon is preferable) (HHS [pediatric 2016])
Administration
May be administered without regard to food.
Storage
Store controlled room temperature of 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
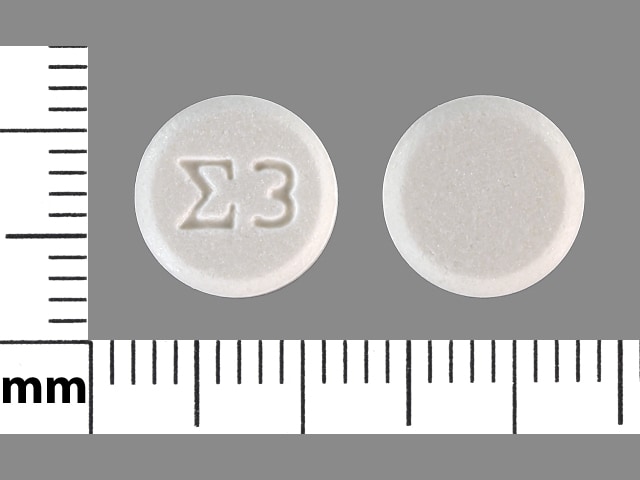
Adefovir Images
Drug Interactions
Ataluren: May increase the serum concentration of Adefovir. Monitor therapy
Cabozantinib: MRP2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Cabozantinib. Monitor therapy
Cladribine: Agents that Undergo Intracellular Phosphorylation may diminish the therapeutic effect of Cladribine. Avoid combination
Nitisinone: May increase the serum concentration of OAT1/3 Substrates. Monitor therapy
Orlistat: May decrease the serum concentration of Antiretroviral Agents. Monitor therapy
Pretomanid: May increase the serum concentration of OAT1/3 Substrates. Monitor therapy
Tenofovir Products: Adefovir may diminish the therapeutic effect of Tenofovir Products. Adefovir may increase the serum concentration of Tenofovir Products. Tenofovir Products may increase the serum concentration of Adefovir. Avoid combination
Teriflunomide: May increase the serum concentration of OAT1/3 Substrates. Monitor therapy
Tolvaptan: May increase the serum concentration of OAT1/3 Substrates. Management: Patients being treated with the Jynarque brand of tolvaptan should avoid concomitant use of OAT1/3 substrates. Concentrations and effects of the OAT1/3 substrate would be expected to increase with any combined use. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
In liver transplant patients with baseline renal dysfunction, frequency of increased serum creatinine has been observed to be as high as 32% to 51% at 48 and 96 weeks post-transplantation, respectively; considering the concomitant use of other potentially nephrotoxic medications, baseline renal insufficiency, and predisposing comorbidities, the role of adefovir in these changes could not be established.
>10%:
Central nervous system: Headache (24% to 25%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain (15%), diarrhea (≤13%)
Genitourinary: Hematuria (grade ≥3: 11%)
Hepatic: Hepatitis (exacerbation; ≤25% within 12 weeks of adefovir discontinuation)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness (≤25%)
1% to 10%:
Dermatologic: Pruritus, skin rash
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypophosphatemia (<2 mg/dL: 1% and 3% in pre-/post-liver transplant patients, respectively)
Gastrointestinal: Flatulence (≤8%), dyspepsia (5% to 9%), nausea, vomiting
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Back pain (≤10%)
Renal: Increased serum creatinine (≥0.5 mg/dL: 2% to 3% in compensated liver disease; incidence may be higher in patients with decompensated cirrhosis or in liver transplant recipients), renal failure
Respiratory: Cough (6% to 8%), rhinitis (≤5%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Fanconi's syndrome, hepatitis, myopathy, nephrotoxicity, osteomalacia, pancreatitis, proximal tubular nephropathy
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Lactic acidosis/hepatomegaly: [US Boxed Warning]: Fatal cases of lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis have been reported with the use of nucleoside analogues alone or in combination with other antiretrovirals; use with caution in patients with risk factors for liver disease (risk may be increased with female gender, obesity, pregnancy or prolonged exposure) and suspend treatment in any patient who develops clinical or laboratory findings suggestive of lactic acidosis or hepatotoxicity (transaminase elevation may/may not accompany hepatomegaly and steatosis).
Disease-related concerns:
- Chronic hepatitis B: [US Boxed Warning]: Severe, acute exacerbation of hepatitis B may occur upon discontinuation. Exacerbations may occur in up to 25% of patients and usually within 12 weeks and may be self-limited or resolve upon resuming treatment; risk may be increased with advanced liver disease or cirrhosis. Monitor liver function several months after stopping treatment; reinitiation of antihepatitis B therapy may be required. Ethanol should be avoided in hepatitis B infection due to potential hepatic toxicity.
- HIV: [US Boxed Warning]: May cause the development of HIV resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients with unrecognized or untreated HIV infection. Determine HIV status prior to initiating treatment with adefovir.
- Renal impairment: [US Boxed Warning]: Use with caution in patients with renal dysfunction or in patients at risk of renal toxicity (including concurrent nephrotoxic agents or NSAIDs). Chronic administration may result in nephrotoxicity. Dosage adjustment is required in adult patients with renal dysfunction or in patients who develop renal dysfunction during therapy; no data available for use in children ≥12 years or adolescents with renal impairment. Calculation of creatinine clearance in all patients is recommended prior to initiating therapy.
Concurrent drug therapy:
- Tenofovir: Do not use concurrently with tenofovir (Viread®) or any product containing tenofovir (eg, Truvada, Atripla, Complera).
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Current clinical hepatitis B practice guidelines do not recommend adefovir for initial use in the management of chronic HBV due to high rate of resistance with long-term use; other antiviral agents with a high barrier to drug resistance are preferred (eg, tenofovir or entecavir). In the setting of lamivudine-resistant HBV, adefovir (including when combined with lamivudine) is also not a preferred strategy to manage antiviral resistance; consult current clinical practice guidelines for recommendations (AASLD [Terrault 2016]). If used, combination therapy with lamivudine should be used to decrease the risk of resistance in patients with lamivudine-resistant HBV.
Monitoring Parameters
Manufacturer's labeling: HIV status (prior to initiation of therapy); renal function (prior to initiation and during therapy, especially in patients with risk factors for renal impairment or pre-existing renal impairment); following discontinuation, closely monitor hepatic function with both clinical and laboratory follow-up at repeated intervals for several months following discontinuation of adefovir.
Alternate recommendations: Chronic Hepatitis B: HBV DNA and ALT (HBV DNA usually done every 3 months until undetectable and then every 3 to 6 months thereafter); HBeAg; anti-HBe (in patients who are HBeAg-positive to monitor for seroconversion); HBsAg; creatinine clearance (baseline); if at risk for renal impairment, creatinine clearance, serum phosphate, urine glucose, and urine protein at baseline and at least annually; consider monitoring bone density in patients with risk factors for osteopenia or fracture history (study prior to initiation and during therapy); lactic acid levels (if clinical concern); following discontinuation, monitor for recurrent viremia, ALT flares, seroreversion, and clinical decompensation every 3 months for at least 1 year (AASLD [Terrault 2016]). As antivirals do not eliminate the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, continued monitoring for this complication is recommended in at-risk patients.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Information related to the use of adefovir in pregnancy is limited (Yi 2012); use of other agents is recommended (AASLD [Terrault 2016]).
Health care providers are encouraged to enroll women exposed to adefovir during pregnancy in the Hepsera pregnancy registry (800-258-4263).
Patient Education
- Discuss specific use of drug and side effects with patient as it relates to treatment. (HCAHPS: During this hospital stay, were you given any medicine that you had not taken before? Before giving you any new medicine, how often did hospital staff tell you what the medicine was for? How often did hospital staff describe possible side effects in a way you could understand?)
- Patient may experience headache, diarrhea, passing gas, abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, or loss of strength and energy. Have patient report immediately to prescriber signs of kidney problems (unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain), signs of liver problems (dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin), signs of lactic acidosis (fast breathing, fast heartbeat, abnormal heartbeat, vomiting, fatigue, shortness of breath, severe loss of strength and energy, severe dizziness, feeling cold, or muscle pain or cramps), or signs of low phosphate (vision changes, confusion, mood changes, muscle pain, muscle weakness, shortness of breath, difficulty breathing, or difficulty swallowing) (HCAHPS).
- Educate patient about signs of a significant reaction (eg, wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat). Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Patient should consult prescriber for additional questions.
Intended Use and Disclaimer: Should not be printed and given to patients. This information is intended to serve as a concise initial reference for healthcare professionals to use when discussing medications with a patient. You must ultimately rely on your own discretion, experience and judgment in diagnosing, treating and advising patients.