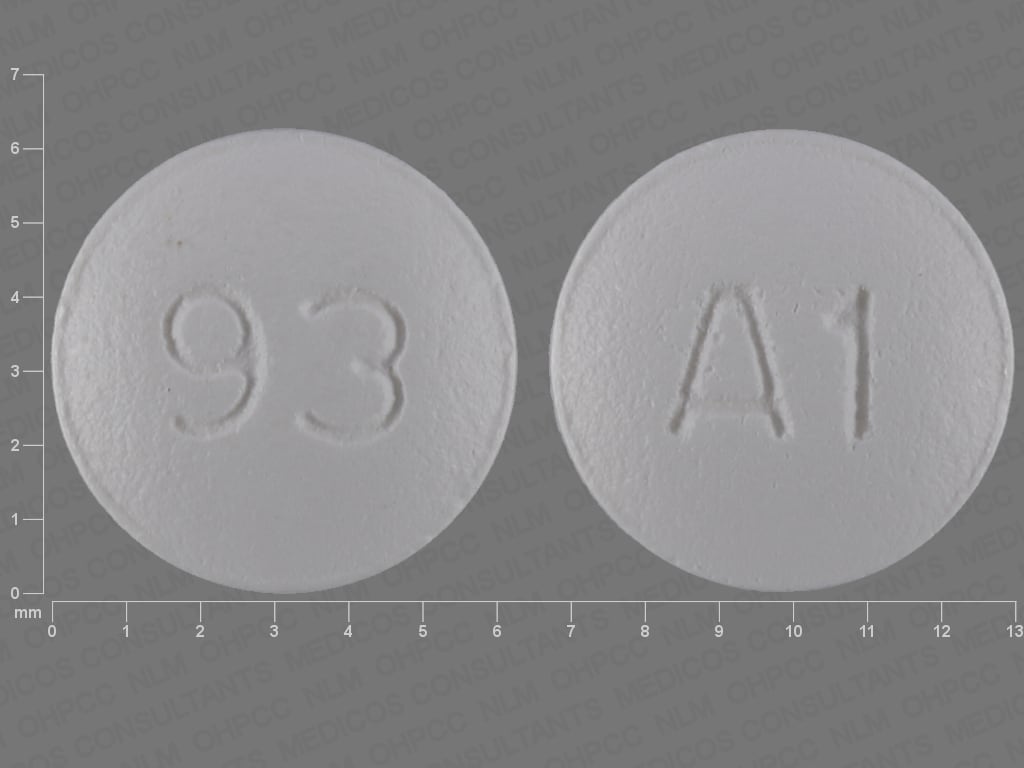
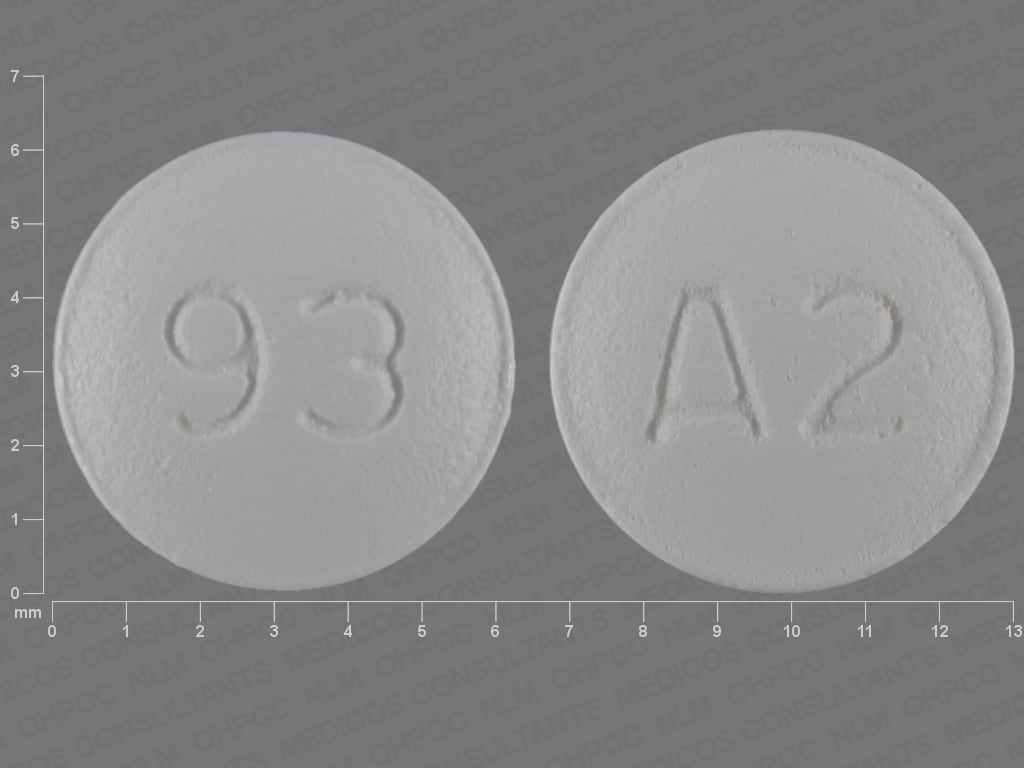
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Tablet, Oral, as maleate:
Axert: 6.25 mg [DSC]
Axert: 12.5 mg [DSC] [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Generic: 6.25 mg, 12.5 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Selective agonist for serotonin (5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors) in cranial arteries; causes vasoconstriction and reduces sterile inflammation associated with antidromic neuronal transmission correlating with relief of migraine
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Well absorbed
Distribution
Vd: ~180 to 200 L
Metabolism
Via MAO type A oxidative deamination (~27% of dose) and CYP3A4 and 2D6 (~12% of dose) to inactive metabolites
Excretion
Urine (~75%; ~40% of total dose as unchanged drug); feces (~13% of total dose as unchanged drug and metabolites)
Time to Peak
Plasma: 1 to 3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Mean: 3 to 5 hours (Baldwin 2004; McEnroe 2005)
Protein Binding
∼35%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Clearance is decreased approximately 65% in those with CrCl 10 to 30 mL/minute and decreased approximately 40% in those with CrCl 31 to 71 mL/minute. Cmax increased approximately 80%.
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
The maximum decrease expected in almotriptan clearance due to hepatic function impairment would be 60%.
Special Populations: Elderly
A longer terminal half-life (3.7 vs 3.2 h) and a 25% higher AUC has been observed in elderly patients.
Use: Labeled Indications
Acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults (with a history of migraine) and adolescents (with a history of migraine lasting ≥4 hours when left untreated)
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to almotriptan or any component of the formulation; hemiplegic or basilar migraine; known or suspected ischemic heart disease (eg, angina pectoris, MI, documented silent ischemia, coronary artery vasospasm, Prinzmetal's variant angina); cerebrovascular syndromes (eg, stroke, transient ischemic attacks); peripheral vascular disease (eg, ischemic bowel disease); uncontrolled hypertension; use within 24 hours of another 5-HT1 agonist; use within 24 hours of ergotamine derivatives and/or ergotamine-containing medications (eg, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine)
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Migraine: Oral: Initial: 6.25-12.5 mg in a single dose; if the headache returns, repeat the dose after 2 hours; no more than 2 doses (maximum daily dose: 25 mg)
Note: The safety of treating more than 4 migraines/month has not been established.
Dosage adjustment with concomitant use of an enzyme inhibitor:
Patients receiving a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Initial: 6.25 mg in a single dose; maximum daily dose: 12.5 mg
Patients with renal impairment and concomitant use of a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Avoid use
Patients with hepatic impairment and concomitant use of a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Avoid use
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Migraine: Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: Oral: Initial: 6.25 to 12.5 mg in a single dose; if headache returns, may repeat the dose after 2 hours; maximum 2 doses/day; maximum daily dose: 25 mg/day. Note: The safety of treating >4 migraines/month has not been established.
Dosage adjustment with concomitant use of an enzyme inhibitor: Children ≥12 years and Adolescents:
Patients receiving a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Initial: 6.25 mg in a single dose; maximum daily dose: 12.5 mg/day
Patients with renal impairment and concomitant use of a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Avoid use
Patients with hepatic impairment and concomitant use of a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor: Avoid use
Administration
Administer without regard to meals.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Almotriptan Images
Drug Interactions
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May increase the serum concentration of Almotriptan. Management: Limit initial almotriptan adult dose to 6.25 mg and maximum adult dose to 12.5 mg/24-hrs when used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Avoid concurrent use in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Exceptions: Nefazodone. Consider therapy modification
Droxidopa: Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans) may enhance the hypertensive effect of Droxidopa. Monitor therapy
Ergot Derivatives: May enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans). Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans) may enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Ergot Derivatives. Exceptions: Nicergoline. Avoid combination
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans) may enhance the serotonergic effect of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans). Exceptions: Rasagiline; Safinamide; Selegiline. Avoid combination
Nefazodone: Almotriptan may enhance the serotonergic effect of Nefazodone. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Nefazodone may increase the serum concentration of Almotriptan. Management: Limit the initial almotriptan dose to 6.25 mg when combined with nefazodone, and do not exceed 12.5 mg in any 24-hour period. Avoid concomitant use in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Monitor for serotonin syndrome. Consider therapy modification
Serotonergic Agents (High Risk): Almotriptan may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Isocarboxazid; Linezolid; Methylene Blue; Moclobemide; Nefazodone; Phenelzine; Tranylcypromine. Monitor therapy
SUMAtriptan: Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of SUMAtriptan. Avoid combination
Adverse Reactions
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Drowsiness (≤5%), dizziness (≤4%), headache (≤2%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (1% to 3%), vomiting (≤2%), xerostomia (1%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Paresthesia (≤1%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abdominal cramps, abdominal discomfort, abdominal pain, abnormal dreams, altered sense of smell, anaphylactic shock, anaphylaxis, angina pectoris, angioedema, anxiety, arthralgia, arthritis, ataxia, back pain, blepharospasm, blurred vision, bronchitis, central nervous system stimulation, chest pain, chills, cold extremities, colitis, confusion, conjunctivitis, coronary artery vasospasm, decreased visual acuity, depression, dermatitis, diaphoresis, diarrhea, diplopia, dry eye syndrome, dysgeusia, dysmenorrhea, dyspepsia, dyspnea, epistaxis, erythema, euphoria, eye irritation, eye pain, fatigue, fever, gastritis, gastroenteritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, hemiplegia, hyperacusis, hypercholesterolemia, hyperglycemia, hyperhidrosis, hyperreflexia, hypersensitivity reaction, hypertension, hypertonia, hyperventilation, hypoesthesia, increased creatine phosphokinase, increased gamma-glutamyl transferase, increased thirst, insomnia, ischemic heart disease, lack of concentration, laryngismus, laryngitis, limb pain, malaise, mastalgia, myalgia, myasthenia, myocardial infarction, myopathy, neck pain, neck stiffness, nervousness, neuropathy, nightmares, nystagmus, otalgia, otitis media, palpitations, pharyngitis, pruritus, restlessness, rhinitis, scotoma, seizure, shakiness, sialorrhea, sinusitis, skin photosensitivity, skin rash, sneezing, syncope, tachycardia, tinnitus, tremor, vasodilation, ventricular fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, vertigo, weakness
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Cardiac events: Coronary artery vasospasm, transient ischemia, myocardial infarction, ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation, cardiac arrest, and death have been reported with 5-HT1 agonist administration. Patients who experience sensations of chest pain/pressure/tightness or symptoms suggestive of angina following dosing should be evaluated for coronary artery disease or Prinzmetal's angina before receiving additional doses; if dosing is resumed and similar symptoms recur, monitor with ECG.
- Cerebrovascular events: Cerebral/subarachnoid hemorrhage and stroke have been reported with 5-HT1 agonist administration.
- Elevated blood pressure: Significant elevation in blood pressure, including hypertensive crisis, has been reported on rare occasions following 5-HT1 agonist administration in patients with and without a history of hypertension.
- Headaches: Acute migraine agents (eg, triptans, opioids, ergotamine, or a combination of the agents) used for 10 or more days per month may lead to worsening of headaches (medication overuse headache); withdrawal treatment may be necessary in the setting of overuse.
- Ocular effects: Transient and permanent blindness and partial vision loss have been reported (rare) with 5-HT1 agonist administration.
- Sulfonamide allergy: Almotriptan contains a sulfonyl group which is structurally different from a sulfonamide. Cross-reactivity in patients with sulfonamide allergy has not been evaluated; however, the manufacturer recommends that caution be exercised in this patient population.
- Vasospasm-related events: Peripheral vascular ischemia and colonic ischemia have been reported with 5-HT1 agonist administration.
Disease-related concerns:
- Coronary artery disease: Almotriptan should not be given to patients with documented ischemic or vasospastic CAD. Patients with risk factors for CAD (eg, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, smoker, obesity, diabetes, strong family history of CAD, menopause, male >40 years of age) should undergo adequate cardiac evaluation prior to administration; if the cardiac evaluation is “satisfactory,” first dose should be given in the healthcare provider's office (consider ECG monitoring). All patients should undergo periodic evaluation of cardiovascular status during treatment.
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment. Drug clearance may be reduced leading to increased plasma concentrations; dosage reduction is recommended.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with moderate-to-severe renal failure. Drug clearance may be reduced leading to increased plasma concentrations; dosage reduction is recommended for severe renal impairment.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Serotonin syndrome: Symptoms of agitation, confusion, hallucinations, hyper-reflexia, myoclonus, shivering, and tachycardia may occur with concomitant proserotonergic drugs (ie, SSRIs/SNRIs or triptans) or agents which reduce almotriptan's metabolism. Concurrent use of serotonin precursors (eg, tryptophan) is not recommended. If concomitant administration with SSRIs is warranted, monitor closely, especially at initiation and with dose increases.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Only indicated for treatment of acute migraine; it is not indicated for migraine prophylaxis, or for the treatment of cluster headaches, hemiplegic migraine, or basilar migraine. If a patient does not respond to the first dose, the diagnosis of acute migraine should be reconsidered.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
C
Pregnancy Considerations
Adverse events were observed in animal reproduction studies. Information related to almotriptan use in pregnancy is limited (Källén, 2011; Nezvalová-Henriksen, 2010; Nezvalová-Henriksen, 2012). Until additional information is available, other agents are preferred for the initial treatment of migraine in pregnancy (Da Silva, 2012; MacGregor, 2012; Williams, 2012).
Patient Education
- Discuss specific use of drug and side effects with patient as it relates to treatment. (HCAHPS: During this hospital stay, were you given any medicine that you had not taken before? Before giving you any new medicine, how often did hospital staff tell you what the medicine was for? How often did hospital staff describe possible side effects in a way you could understand?)
- Patient may experience fatigue or dry mouth. Have patient report immediately to prescriber severe headache, severe dizziness, passing out, constipation, diarrhea, severe nausea, severe vomiting, severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea, burning or numbness feeling, weight loss, leg cramps, feeling of heaviness in legs, leg pain, sensation of cold, burning or aching pain in feet or toes, shortness of breath, vision changes, blindness, abnormal heartbeat, signs of serotonin syndrome (dizziness, severe headache, agitation, sensing things that seem real but are not, fast heartbeat, abnormal heartbeat, flushing, tremors, sweating a lot, change in balance, severe nausea, or severe diarrhea), signs of a heart attack (chest pain; pain in arms, back, neck, jaw, or abdomen; shortness of breath; cold sweats; severe dizziness; passing out; or severe nausea or vomiting), or signs of severe cerebrovascular disease (change in strength on one side is greater than the other, difficulty speaking or thinking, change in balance, or vision changes) (HCAHPS).
- Educate patient about signs of a significant reaction (eg, wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat). Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Patient should consult prescriber for additional questions.
Intended Use and Disclaimer: Should not be printed and given to patients. This information is intended to serve as a concise initial reference for health care professionals to use when discussing medications with a patient. You must ultimately rely on your own discretion, experience, and judgment in diagnosing, treating, and advising patients.