Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Capsule, Oral:
Generic: 300 mg
Suspension Reconstituted, Oral:
Generic: 125 mg/5 mL (60 mL, 100 mL); 250 mg/5 mL (60 mL, 100 mL)
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis by binding to one or more of the penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) which in turn inhibits the final transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan synthesis in bacterial cell walls, thus inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis. Bacteria eventually lyse due to ongoing activity of cell wall autolytic enzymes (autolysins and murein hydrolases) while cell wall assembly is arrested.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Distribution
Penetrates into blister fluid, middle ear fluid, tonsils, sinus, and lung tissues. Vd: Children 6 months to 12 years: 0.67 ± 0.38 L/kg; Adults: 0.35 ± 0.29 L/kg
Metabolism
Minimal
Excretion
Primarily urine (~12% to 18% as unchanged drug)
Time to Peak
2 to 4 hours
Half-Life Elimination
1.7 (± 0.6) hours with normal renal function
Protein Binding
60% to 70%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Clearance is reduced.
Use: Labeled Indications
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, exacerbation: Treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis in adults and adolescents caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and Moraxella catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains)
Otitis media, acute: Treatment of acute bacterial otitis media in pediatric patients caused by H. influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), S. pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and M. catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains)
Pneumonia, community-acquired: Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia in adults and adolescents caused by H. influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), H. parainfluenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), S. pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and M. catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains)
Sinusitis, acute: Treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis in adults and adolescents caused by H. influenzae (including beta-lactamase-producing strains), S. pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and M. catarrhalis (including beta-lactamase-producing strains). Note: Limitations of use: According to the IDSA guidelines for acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, cefdinir is no longer recommended as monotherapy for initial empiric treatment (IDSA [Chow 2012]).
Skin and skin structure infections, uncomplicated: Treatment of uncomplicated skin and skin structure infections in adults, adolescents, and pediatric patients caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including beta-lactamase-producing strains) and Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcal pharyngitis (group A): Treatment of pharyngitis/tonsillitis in adults, adolescents, and pediatric patients caused by S. pyogenes
Use: Off Label
Urinary tract infection, complicated, including pyelonephritisc
Clinical experience suggests the utility of cefdinir as an alternative agent in the treatment of acute complicated UTI (including pyelonephritis) after administration of an appropriate parenteral agent Hooton 2018a.
Urinary tract infection, acute uncomplicated cystitis or acute simple cystitiscyes
Clinical experience suggests the utility of cefdinir as an alternative agent in the treatment of acute simple cystitis (infection limited to the bladder and no signs/symptoms of upper tract or systemic infections) Hooton 2018b, Hooton 2018c.
Based on the Infectious Diseases Society of America and European Society for Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (IDSA/ESCMID) international clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acute uncomplicated cystitis and pyelonephritis in women, cefdinir is an effective and recommended alternative agent in the management of acute uncomplicated cystitis ESCMID/IDSA [Gupta 2011].
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to cefdinir, any component of the formulation, or other cephalosporins.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, exacerbation: Oral: 300 mg twice daily or 600 mg once daily for 5 to 7 days (Bartlett 2018; GOLD 2018). Note: Some experts reserve for use in patients with uncomplicated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (eg, age <65 years without major comorbidities, FEV1 >50% predicted, infrequent exacerbations) (Anzueto 2007; Sethi 2008).
Otitis media, acute (alternative agent for mild [non-anaphylactic] penicillin allergy): Limited data available: Oral: 300 mg twice daily or 600 mg once daily; duration of therapy is 5 to 7 days (mild to moderate infection) or 10 days (severe infection) (Limb 2019; manufacturer's labeling)
Pneumonia, community-acquired, pathogen-directed therapy (alternative agent): Note: Use only for community-acquired pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae if the penicillin MIC is <2 mcg/mL (IDSA/ATS [Mandell 2007]).
Oral: 300 mg twice daily (manufacturer's labeling). Duration is for a minimum of 5 days and varies based on disease severity and response to therapy; patients should be afebrile for ≥48 hours and clinically stable before therapy is discontinued (IDSA/ATS [Mandell 2007]).
Streptococcal pharyngitis (group A) (alternative agent for mild [non-anaphylactic] penicillin allergy): Oral: 300 mg twice daily for 5 to 10 days or 600 mg once daily for 10 days (Pichichero 2018; manufacturer's labeling)
Urinary tract infection (UTI) (alternative agent) (off-label use): Note: Use only when preferred agents cannot be used (due to limited evidence and decreased efficacy of oral beta-lactams compared to other agents) (IDSA/ESCMID [Gupta 2011]; Hooton 2018a; Hooton 2018b; Hooton 2018c).
Acute uncomplicated cystitis or acute simple cystitis (infection limited to bladder and no signs/symptoms of upper tract, prostate, or systemic infection): Oral: 300 mg twice daily for 5 to 7 days (IDSA/ESCMID [Gupta 2011]; Hooton 2018b; Hooton 2018c)
UTI, complicated, including pyelonephritis: Oral: 300 mg twice daily for 10 to 14 days. Note: Oral therapy should follow appropriate parenteral therapy and patients should be monitored closely. For outpatient treatment of mild infection, a single dose of a long-acting parenteral agent is acceptable before transitioning to oral therapy (IDSA/ESCMID [Gupta 2011]; Hooton 2018a).
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
General dosing, susceptible infection (Red Book 2012): Mild to moderate infections: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral: 14 mg/kg/day in divided doses 1 to 2 times daily; maximum daily dose: 600 mg/day
Bronchitis, acute exacerbation: Oral: Adolescents: 300 mg every 12 hours for 5 to 10 days or 600 mg every 24 hours for 10 days
Otitis media, acute: Infants ≥6 months and Children: Oral: 14 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 to 24 hours for 5 to 10 days; maximum daily dose: 600 mg/day. Variable duration of therapy: If <2 years of age or severe symptoms (any age): 10-day course; if 2 to 5 years of age with mild to moderate symptoms: 7-day course; if ≥6 years of age with mild to moderate symptoms: 5- to 7-day course (AAP [Lieberthal 2013]). Note: Recommended by the AAP as an alternative agent for initial treatment in penicillin allergic patients (AAP [Lieberthal 2013]).
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis: Note: Although FDA approved at twice daily dosing, duration <10 days is not recommended (Shulman 2012).
Infants ≥6 months and Children: Oral: 7 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours for 5 to 10 days or 14 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours for 10 days; maximum daily dose: 600 mg/day
Adolescents: Oral: 300 mg every 12 hours for 5 to 10 days or 600 mg every 24 hours for 10 days
Pneumonia, community-acquired: Adolescents: Oral: 300 mg every 12 hours for 10 days
Skin and skin structure infection, uncomplicated:
Infants ≥6 months and Children: Oral: 14 mg/kg/day in divided doses twice daily for 10 days; maximum daily dose: 600 mg/day
Adolescents: Oral: 300 mg every 12 hours for 10 days
Sinusitis, acute maxillary: Note: Due to decreased S. pneumonia sensitivity, cefdinir is no longer recommended as monotherapy for the initial empiric treatment of sinusitis (Chow 2012)
Infants ≥6 months and Children: Oral: 14 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 to 24 hours for 10 days; maximum daily dose: 600 mg/day
Adolescents: Oral: 300 mg every 12 hours or 600 mg every 24 hours for 10 days
Reconstitution
Refer to manufacturer’s product labeling for reconstitution instructions.
Administration
Oral: Twice daily doses should be given every 12 hours. May be administered with or without food. Manufacturer recommends administering at least 2 hours before or after antacids or iron supplements. Shake suspension well before use.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Store reconstituted suspension at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for 10 days.
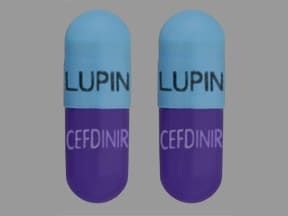
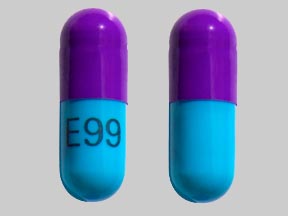
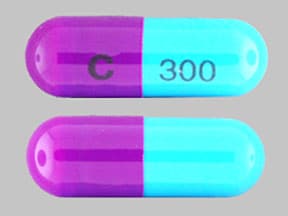
Cefdinir Images
Drug Interactions
Aminoglycosides: Cephalosporins (3rd Generation) may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Aminoglycosides. Monitor therapy
BCG (Intravesical): Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
BCG Vaccine (Immunization): Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG Vaccine (Immunization). Monitor therapy
Cholera Vaccine: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Cholera Vaccine. Management: Avoid cholera vaccine in patients receiving systemic antibiotics, and within 14 days following the use of oral or parenteral antibiotics. Avoid combination
Iron Preparations: May decrease the serum concentration of Cefdinir. Red-appearing, non-bloody stools may also develop due to the formation of an insoluble iron-cefdinir complex. Management: Avoid concurrent cefdinir and oral iron when possible. Separating doses by several hours may minimize interaction. Iron-containing infant formulas do not appear to interact with cefdinir. Exceptions: Ferric Carboxymaltose; Ferric Derisomaltose; Ferric Gluconate; Ferric Hydroxide Polymaltose Complex; Ferric Pyrophosphate Citrate; Ferumoxytol; Iron Dextran Complex; Iron Sucrose. Consider therapy modification
Lactobacillus and Estriol: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus and Estriol. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Minerals (with ADEK, Folate, Iron): May decrease the serum concentration of Cefdinir. Specifically, Iron Salts may decrease the serum concentration of Cefdinir. Red-appearing, non-bloody stools may also develop due to the formation of an insoluble iron-cefdinir complex. Management: Avoid concurrent cefdinir and oral iron-containing multivitamins when possible. Separating doses by several hours may minimize interaction. Iron-containing infant formulas do not appear to interact with cefdinir. Consider therapy modification
Probenecid: May increase the serum concentration of Cephalosporins. Monitor therapy
Sodium Picosulfate: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sodium Picosulfate. Management: Consider using an alternative product for bowel cleansing prior to a colonoscopy in patients who have recently used or are concurrently using an antibiotic. Consider therapy modification
Typhoid Vaccine: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Typhoid Vaccine. Only the live attenuated Ty21a strain is affected. Management: Vaccination with live attenuated typhoid vaccine (Ty21a) should be avoided in patients being treated with systemic antibacterial agents. Use of this vaccine should be postponed until at least 3 days after cessation of antibacterial agents. Consider therapy modification
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Cephalosporins may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
False-positive reaction for urinary ketones may occur with nitroprusside- but not nitroferricyanide-based tests. False-positive urine glucose results may occur when using Clinitest®, Benedict's solution, or Fehling’s solution; glucose-oxidase-based reaction systems (eg, Clinistix®, Tes-Tape®) are recommended. May cause positive direct Coombs’ test.
Adverse Reactions
>10%: Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (8% to 15%)
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Headache (2%)
Dermatologic: Skin rash (≤3%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Decreased serum bicarbonate (≤1%), glycosuria (≤1%), hyperglycemia (≤1%), hyperphosphatemia (≤1%), increased gamma-glutamyl transferase (≤1%), increased lactate dehydrogenase (≤1%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (≤3%), abdominal pain (≤1%), vomiting (≤1%)
Genitourinary: Vulvovaginal candidiasis (≤4%), urine abnormality (increased leukocytes: ≤2%), proteinuria (1% to 2%), occult blood in urine (≤1%), vaginitis (≤1%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Lymphocytosis (≤2%), eosinophilia (1%), lymphocytopenia (1%), abnormal neutrophils (functional disorder of polymorphonuclear neutrophils: ≤1%), thrombocythemia (≤1%), change in WBC count (≤1%)
Hepatic: Increased serum alkaline phosphatase (≤1%), increased serum ALT (≤1%)
Renal: Increased urine pH (≤1%), increased urine specific gravity (≤1%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormal stools, anaphylaxis, anorexia, asthma, blood coagulation disorder, bloody diarrhea, candidiasis, cardiac failure, chest pain, cholestasis, conjunctivitis, constipation, cutaneous candidiasis, decreased hemoglobin, decreased urine specific gravity, disseminated intravascular coagulation, dizziness, drowsiness, dyspepsia, enterocolitis (acute), eosinophilic pneumonitis, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, exfoliative dermatitis, facial edema, fever, flatulence, fulminant hepatitis, granulocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhagic colitis, hemorrhagic diathesis, hepatic failure, hepatitis (acute), hyperkalemia, hyperkinesia, hypersensitivity angiitis, hypertension, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, immune thrombocytopenia, increased amylase, increased blood urea nitrogen, increased monocytes, increased serum AST, increased serum bilirubin, insomnia, interstitial pneumonitis (idiopathic), intestinal obstruction, involuntary body movements, jaundice, laryngeal edema, leukopenia, leukorrhea, loss of consciousness, maculopapular rash, melena, myocardial infarction, pancytopenia, peptic ulcer, pneumonia (drug-induced), pruritus, pseudomembranous colitis, renal disease, renal failure (acute), respiratory failure (acute), rhabdomyolysis, serum sickness, shock, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia, toxic epidermal necrolysis, upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage, weakness, xerostomia
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Penicillin allergy: Use with caution in patients with a history of penicillin allergy, especially IgE-mediated reactions (eg, anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria).
- Superinfection: Prolonged use may result in fungal or bacterial superinfection, including C. difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) and pseudomembranous colitis; CDAD has been observed >2 months postantibiotic treatment.
Disease-related concerns:
- Colitis: Use with caution in patients with a history of colitis.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment (CrCl <30 mL/minute); dosage adjustment may be required.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
- Iron-containing products: Cases of reddish stools have been reported with concomitant use of cefdinir and iron-containing products due to the formation of a nonabsorbable complex in the GI tract.
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor renal function. Observe for signs and symptoms of anaphylaxis during first dose.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
B
Pregnancy Considerations
Teratogenic events have not been observed in animal reproduction studies. An increase in most types of birth defects was not found following first trimester exposure to cephalosporins.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat bacterial infections.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Diarrhea
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Not able to pass urine
- Change in amount of urine passed
- Dark urine
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Seizures
- Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile (C. diff)-associated diarrhea like abdominal pain or cramps, severe diarrhea or watery stools, or bloody stools
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.