What is Complera?
Complera is a prescription medicine that is used to treat Human Immunodeficiency Virus-1 (HIV-1) in people weighing at least 77 lb (35 kg) who:
- have never taken HIV-1 medicines before, and who have an amount of HIV-1 in their blood (this is called 'viral load') that is no more than 100,000 copies/mL before they start taking Complera,
or - in certain people who have a viral load that is less than 50 copies/mL when they start taking Complera, to replace their current HIV-1 medicines.
HIV-1 is the virus that causes AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). Complera does not cure HIV-1 or AIDS.
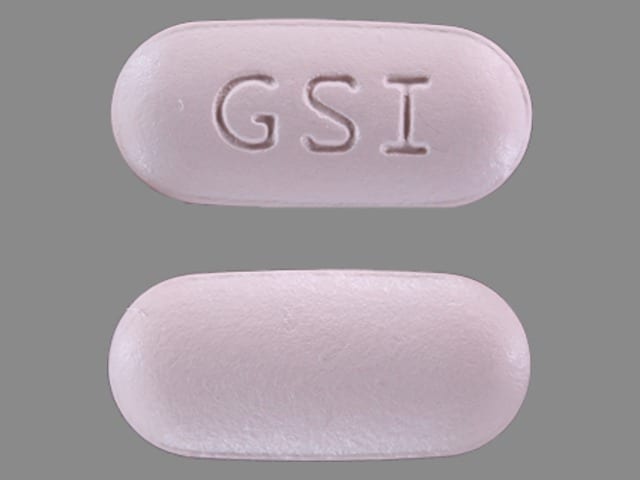
Complera contains 3 medicines (emtricitabine, rilpivirine, tenofovir disoproxil fumarate) combined in one tablet. Emtricitabine (Emtriva) and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (Viread) are HIV-1 nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). Rilpivirine (Edurant) is an HIV-1 non-nucleoside analog reverse transcriptase inhibitor (NNRTI).
It is not known if Complera is safe and effective in children less than 12 years of age or who weigh less than 77 lb (35 kg).
What is the most important information I should know about Complera?
Important: Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about medicines that should not be taken with Complera. For more information, see the section "What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Complera?".
Complera can cause serious side effects, including:
Worsening of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Your healthcare provider will test you for HBV before starting treatment with Complera. If you have HBV infection and take Complera, your HBV may get worse (flare-up) if you stop taking Complera. A "flare-up" is when your HBV infection suddenly returns in a worse way than before.
- Do not stop taking Complera without first talking to your healthcare provider.
- Do not run out of Complera. Refill your prescription or talk to your healthcare provider before your Complera is all gone.
- If you stop taking Complera, your healthcare provider will need to check your health often and do blood tests regularly for several months to check your HBV infection. Tell your healthcare provider about any new or unusual symptoms you may have after you stop taking Complera.
For more information about side effects, see the section “What are the possible side effects of Complera?”.
Who should not take Complera?
Do not take Complera if you also take:
- anti-seizure medicines:
- carbamazepine
- oxcarbazepine
- phenobarbital
- phenytoin
- anti-tuberculosis (anti-TB) medicines:
- rifampin
- rifapentine
- proton pump inhibitor (PPI) medicine for certain stomach or intestinal problems:
- dexlansoprazole
- esomeprazole
- lansoprazole
- omeprazole
- pantoprazole sodium
- rabeprazole
- more than 1 dose of the steroid medicine dexamethasone or dexamethasone sodium phosphate
- St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Complera?
Before taking Complera, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver problems, including hepatitis B or C virus infection
- have kidney problems
- have a history of depression or suicidal thoughts
- have bone problems
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Complera can harm your unborn child. Tell your healthcare provider if you become pregnant during treatment with Complera.
Pregnancy Registry. There is a pregnancy registry for those who take Complera during pregnancy. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the health of you and your baby. Talk with your healthcare provider about how you can take part in this registry. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. Do not breastfeed if you are taking Complera.
- You should not breastfeed if you have HIV-1 because of the risk of passing HIV-1 to your baby.
- At least two of the medicines contained in Complera can be passed to your baby in your breast milk.
- Talk with your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with Complera.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Some medicines interact with Complera. Keep a list of your medicines to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
- You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines that can interact with Complera.
- Do not start taking a new medicine without telling your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider can tell you if it is safe to take Complera with other medicines.
How should I take Complera?
- Take Complera exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take Complera with food. Taking Complera with food is important to help get the right amount of medicine in your body. A protein drink does not replace food. If your healthcare provider decides to stop Complera and you are switched to new medicines to treat HIV-1 that include rilpivirine tablets, the rilpivirine tablets should be taken only with a meal.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking Complera without first talking with your healthcare provider. Stay under the care of your healthcare provider during treatment with Complera.
- If you miss a dose of Complera within 12 hours of the time you usually take it, take your dose of Complera with food as soon as possible. Then, take your next dose of Complera at the regularly scheduled time. If you miss a dose of Complera by more than 12 hours of the time you usually take it, wait and then take the next dose of Complera at the regularly scheduled time.
- Do not take more than your prescribed dose to make up for a missed dose.
- If you take too much Complera, contact your local poison control center or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
- When your Complera supply starts to run low, get more from your healthcare provider or pharmacy. It is very important not to run out of Complera. The amount of virus in your blood may increase if the medicine is stopped for even a short time.
What are the possible side effects of Complera?
Complera can cause serious side effects, including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about Complera?"
- Severe skin rash and allergic reactions. Skin rash is a common side effect of Complera. Rash can be serious. Call your healthcare provider right away if you get a rash. In some cases, rash and allergic reaction may need to be treated in a hospital. If you get a rash with any of the following symptoms, stop taking Complera and call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away:
- fever
- skin blisters
- mouth sores
- redness or swelling of the eyes (conjunctivitis)
- swelling of the face, lips, mouth, tongue or throat
- trouble breathing or swallowing
- pain on the right side of the stomach (abdominal) area
- dark or "tea colored" urine
- Severe liver problems. In rare cases, severe liver problems can happen that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: skin or the white part of your eyes turns yellow, dark "tea-colored" urine, light-colored stools, loss of appetite for several days or longer, nausea, or stomach-area pain.
- Change in liver enzymes. People with a history of hepatitis B or C virus infection or who have certain liver enzyme changes may have an increased risk of developing new or worsening liver problems during treatment with Complera. Liver problems can also happen during treatment with Complera in people without a history of liver disease. Your healthcare provider may need to do tests to check your liver enzymes before and during treatment with Complera.
- Depression or mood changes. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- feel sad or hopeless
- feel anxious or restless
- have thoughts of hurting yourself (suicide) or have tried to hurt yourself
- New or worse kidney problems, including kidney failure, can happen in some people who take Complera. Your healthcare provider should do blood tests to check your kidneys before starting treatment with Complera. If you have had kidney problems in the past or need to take another medicine that can cause kidney problems, your healthcare provider may need to do blood tests to check your kidneys during your treatment with Complera.
- Bone problems can happen in some people who take Complera. Bone problems include bone pain, softening, or thinning (which may lead to fractures). Your healthcare provider may need to do additional tests to check your bones.
- Too much lactic acid in your blood (lactic acidosis). Too much lactic acid is a serious but rare medical emergency that can lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get these symptoms: weakness or being more tired than usual, unusual muscle pain, being short of breath or fast breathing, stomach pain with nausea and vomiting, cold or blue hands and feet, feel dizzy or lightheaded, or a fast or abnormal heartbeat.
- Changes in your immune system (Immune Reconstitution Syndrome) can happen when you start taking HIV-1 medicines. Your immune system may get stronger and begin to fight infections that have been hidden in your body for a long time. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you start having new symptoms after starting your HIV-1 medicine.
The most common side effects of rilpivirine, one of the medicines in Complera, include:
- depression
- trouble sleeping
- headache
The most common side effects of emtricitabine and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, two of the medicines in Complera, include:
- diarrhea
- nausea
- tiredness
- headache
- dizziness
- depression
- trouble sleeping
- abnormal dreams
- rash
These are not all the possible side effects of Complera.
Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to US FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Complera Images
General information about the safe and effective use of Complera
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Complera for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Complera to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Complera that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.COMPLERA.com.
How should I store Complera?
- Store Complera at room temperature below 30 °C (86 °F).
- Keep Complera in its original container and keep the container tightly closed.
- Do not use Complera if the seal over the bottle opening is broken or missing.
Keep Complera and all other medicines out of reach of children.
What are the ingredients in Complera?
Active ingredients: emtricitabine, rilpivirine hydrochloride, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate.
Inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 20, povidone, pregelatinized starch. The tablet film coating contains hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide, triacetin.