Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Solution, Intravenous:
Generic: 5 mg/mL (10 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Persantine: 25 mg [DSC], 50 mg [DSC], 75 mg [DSC] [contains fd&c yellow #10 aluminum lake, methylparaben, propylparaben, sodium benzoate]
Generic: 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits the activity of adenosine deaminase and phosphodiesterase, which causes an accumulation of adenosine, adenine nucleotides, and cyclic AMP; these mediators then inhibit platelet aggregation and may cause vasodilation; may also stimulate release of prostacyclin or PGD2; causes coronary vasodilation
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Readily, but variable
Metabolism
Hepatic to glucuronide conjugate
Excretion
Feces (as glucuronide conjugates and unchanged drug)
Time to Peak
Serum: 2-2.5 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Terminal: 10-12 hours
Protein Binding
91% to 99%
Use: Labeled Indications
Oral: Used with warfarin to decrease thrombosis in patients after artificial heart valve replacement
IV: Diagnostic agent in CAD
Use: Off Label
Stroke (prevention, in combination with aspirin)byes
A meta-analysis of clinical trials conducted using both immediate and extended release formulations of dipyridamole (in combination with immediate release aspirin) demonstrated that the combination of dipyridamole and aspirin is more effective than aspirin alone in preventing recurrent cerebral and systemic vascular events in patients with previous noncardioembolic ischemic stroke or TIA Verro 2008.
Based on the American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines on Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis 9th ed, aspirin/extended-release dipyridamole (eg, Aggrenox) is effective and recommended for the secondary prevention of stroke in patients with a history of noncardioembolic ischemic stroke or TIA.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to dipyridamole or any component of the formulation
According to the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology (ASNC) the following are additional contraindications for dipyridamole stress testing (ASNC [Henzlova 2016]): Bronchospastic lung disease with ongoing wheezing or history of significant reactive airway disease; systolic BP <90 mm Hg; uncontrolled hypertension (systolic BP >200 mm Hg or diastolic BP >110 mm Hg); ingestion of caffeinated foods or beverages within the last 12 hours; unstable angina, acute coronary syndrome, or myocardial infarction within 2 to 4 days. Relative contraindications include: Heart rate <40 beats/minute; second- or third-degree heart block without a pacemaker; severe aortic stenosis; seizure disorder (cannot receive aminophylline)
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Adjunctive therapy for prophylaxis of thromboembolism with cardiac valve replacement: Oral: 75 to 100 mg 4 times/day
Evaluation of coronary artery disease: IV: 0.56 mg/kg over 4 minutes; maximum dose: 70 mg (ASNC [Henzlova 2016])
Following completion of dipyridamole infusion, inject radiotracer (eg, thallium-201) in 3 to 5 minutes (ASNC [Henzlova 2016]). Note: To reverse complications and side effects of dipyridamole, aminophylline (50 to 250 mg IV push over 30 to 60 seconds given at least 1 minute after the radiotracer injection) should be available for urgent/emergent use.
Obesity: Dosing for patients who are obese or morbidly obese is not established; in these patients, it is customary to use doses up to the weight of 125 kg (ASNC [Henzlova 2016]).
Dosing: Geriatric
Oral: Avoid use (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
IV: Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Antiplatelet, general dosing: Limited data available: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral: 2 to 6 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses; usual adult maximum dose: 100 mg/dose (Park 2014)
Antiplatelet, mechanical prosthetic heart valves: Note: Although FDA approved for this indication, expert recommendations do not include dipyridamole as a first-line option for thrombotic prophylaxis for mechanical prosthetic heart valves in pediatric patients; vitamin K antagonists with other antiplatelet agents (eg, low-dose aspirin) are recommended (ACCP [Monagle 2012]; ACCP [Whitlock 2012]). Limited data available: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral: 2 to 5 mg/kg/day in divided doses, most commonly in 3 divided doses (ACCP [Monagle 2012]; Park 2014).
Cardiac perfusion scans: Limited data available: Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: IV: 0.56 mg/kg administered over 4 minutes; maximum adult dose: 70 mg/dose (ASNC [Henzlova 2016]; Vijarnsorn 2017). Note: To reverse complications and side effects of dipyridamole, aminophylline should be available for urgent/emergent use (ASNC [Henzlova 2016]).
Proteinuria (IgA nephropathy, Henoch-Schönlein purpura), adjunct therapy: Limited data available: Children ≥7 years and Adolescents: Oral: Initial: 3 to 5 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses; may titrate to reported range: 5 to 6 mg/kg/day in 3 divided doses; maximum daily dose: 400 mg/day; in trials dipyridamole was given as part of a 3 or 4 drug combination therapy (eg, immunosuppressant agents, antihypertensive agents, and an anticoagulant) (Kamei 2011; Kano 2003; Ninchoji 2011; Yoshikawa 2008). Note: Antiplatelet therapy is not recommended by national guidelines because efficacy results in trials cannot be directly associated with dipyridamole as opposed to the other agents in the drug regimen (KDIGO 2012).
Dosing: Obesity
Refer to indication-specific dosing for obesity-related information (may not be available for all indications).
Reconstitution
Prior to administration, dilute solution for injection to a ≥1:2 ratio in NS, 1/2NS, or D5W. Total volume should be ~20-50 mL.
Extemporaneously Prepared
10 mg/mL Oral Suspension
A 10 mg/mL oral suspension may be made with tablets and one of three different vehicles (cherry syrup, a 1:1 mixture of Ora-Sweet and Ora-Plus, or a 1:1 mixture of Ora-Sweet SF and Ora-Plus). Crush twenty-four 50 mg tablets in a mortar and reduce to a fine powder. Add 20 mL of the chosen vehicle and mix to a uniform paste; mix while adding the vehicle in incremental proportions to almost 120 mL; transfer to a calibrated bottle, rinse mortar with vehicle, and add quantity of vehicle sufficient to make 120 mL. Label "shake well" and "protect from light". Stable for 60 days when stored in amber plastic prescription bottles in the dark at room temperature or refrigerated.
Allen LV and Erickson III MA, "Stability of Baclofen, Captopril, Diltiazem, Hydrochloride, Dipyridamole, and Flecainide Acetate in Extemporaneously Compounded Oral Liquids," Am J Health Syst Pharm, 1996, 53:2179-84.8879325
Administration
IV: Infuse diluted solution over 4 minutes.
Storage
IV: Store between 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F); do not freeze. Protect from light.
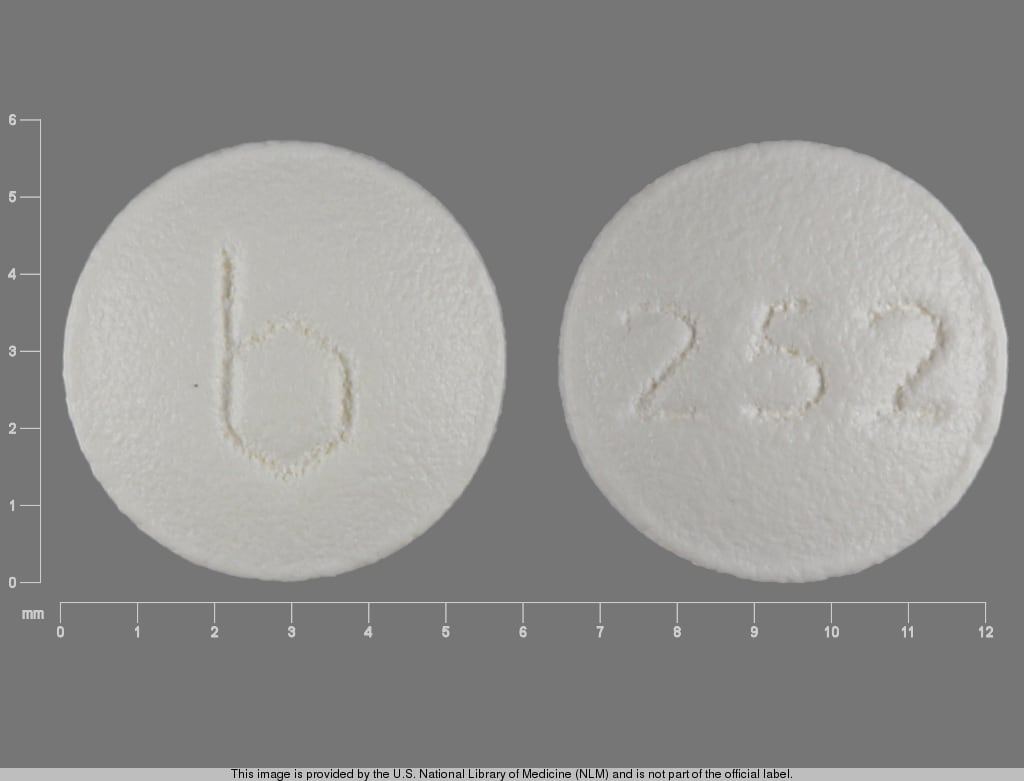
Dipyridamole Images
Drug Interactions
Acalabrutinib: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: Dipyridamole may diminish the therapeutic effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Adenosine: Dipyridamole may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Adenosine. Specifically, cardiovascular effects of adenosine may be enhanced. Adenosine dose reduction may be needed. Management: For patients requiring pharmacologic stress testing with adenosine, hold dipyridamole for 48 hours prior to testing. Consider therapy modification
Agents with Antiplatelet Properties (e.g., P2Y12 inhibitors, NSAIDs, SSRIs, etc.): May enhance the antiplatelet effect of other Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Anticoagulants: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Anticoagulants. Exceptions: Bemiparin; Enoxaparin; Heparin. Monitor therapy
Apixaban: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Apixaban. Specifically, the risk for bleeding may be increased. Management: Carefully consider risks and benefits of this combination and monitor closely. Monitor therapy
Bemiparin: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Bemiparin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of bemiparin with antiplatelet agents. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor closely for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Consider therapy modification
Beta-Blockers: Dipyridamole may enhance the bradycardic effect of Beta-Blockers. Exceptions: Levobunolol; Metipranolol. Monitor therapy
Cephalothin: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Cephalothin. Specifically, the risk for bleeding may be increased. Monitor therapy
Cladribine: Inhibitors of Equilibrative Nucleoside (ENT1) and Concentrative Nucleoside (CNT3) Transport Proteins may increase the serum concentration of Cladribine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitors during the 4 to 5 day oral cladribine treatment cycles whenever possible. If combined, consider an ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitor dose reduction and separation in the timing of administration. Consider therapy modification
Collagenase (Systemic): Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Collagenase (Systemic). Specifically, the risk of injection site bruising and/or bleeding may be increased. Monitor therapy
Dabigatran Etexilate: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Dabigatran Etexilate. Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may increase the serum concentration of Dabigatran Etexilate. This mechanism applies specifically to clopidogrel. Management: Carefully consider risks and benefits of this combination and monitor closely; Canadian labeling recommends avoiding prasugrel or ticagrelor. Monitor therapy
Dasatinib: May enhance the anticoagulant effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Monitor therapy
Deoxycholic Acid: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Deoxycholic Acid. Specifically, the risk for bleeding or bruising in the treatment area may be increased. Monitor therapy
Edoxaban: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Edoxaban. Specifically, the risk of bleeding may be increased. Monitor therapy
Enoxaparin: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Enoxaparin. Management: Discontinue antiplatelet agents prior to initiating enoxaparin whenever possible. If concomitant administration is unavoidable, monitor closely for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Consider therapy modification
Fat Emulsion (Fish Oil Based): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Glucosamine: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Heparin: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Heparin. Management: Decrease the dose of heparin or agents with antiplatelet properties if coadministration is required. Consider therapy modification
Herbs (Anticoagulant/Antiplatelet Properties) (eg, Alfalfa, Anise, Bilberry): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Bleeding may occur. Management: Avoid combination when possible. If used, monitor more closely for evidence of bleeding. Discontinue herbal products with anticoagulant or antiplatelet actions 2 weeks prior to surgical, dental, or invasive procedures. Consider therapy modification
Ibritumomab Tiuxetan: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ibritumomab Tiuxetan. Both agents may contribute to impaired platelet function and an increased risk of bleeding. Monitor therapy
Ibrutinib: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Inotersen: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Limaprost: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Fluoride (with ADE): May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Minerals (with ADEK, Folate, Iron): May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Minerals (with AE, No Iron): May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Obinutuzumab: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Obinutuzumab. Specifically, the risk of serious bleeding-related events may be increased. Monitor therapy
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Specifically, the risk of bleeding may be increased by concurrent use of these agents. Monitor therapy
Pentoxifylline: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Prostacyclin Analogues: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Regadenoson: Dipyridamole may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Regadenoson. Specifically, adenosine mediated effects may be enhanced. Management: Avoid dipyridamole for 48 hours prior to the administration of regadenoson when possible. Consider therapy modification
Riociguat: Dipyridamole may enhance the hypotensive effect of Riociguat. Avoid combination
Rivaroxaban: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Rivaroxaban. Management: Carefully consider risks and benefits of this combination and monitor closely; Canadian labeling recommends avoiding prasugrel or ticagrelor. Monitor therapy
Salicylates: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Salicylates. Increased risk of bleeding may result. Monitor therapy
Thrombolytic Agents: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Thrombolytic Agents. Monitor therapy
Tipranavir: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Urokinase: Agents with Antiplatelet Properties may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Urokinase. Avoid combination
Vitamin E (Systemic): May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Zanubrutinib: May enhance the antiplatelet effect of Agents with Antiplatelet Properties. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
Concurrent caffeine or theophylline use may demonstrate a false-negative result with dipyridamole-thallium myocardial imaging.
Adverse Reactions
Oral: Frequency not always defined.
Cardiovascular: Angina pectoris, flushing
Central nervous system: Dizziness (14%), headache (2%)
Dermatologic: Skin rash (2%), pruritus
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal distress (6%), diarrhea, vomiting
Hepatic: Hepatic insufficiency
Postmarketing and/or case reports: Alopecia, arthritis, cholelithiasis, dyspepsia, fatigue, hepatitis, hypersensitivity reaction, hypotension, laryngeal edema, malaise, myalgia, nausea, palpitations, paresthesia, tachycardia, thrombocytopenia
IV:
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Exacerbation of angina pectoris (20%)
Central nervous system: Dizziness (12%), headache (12%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: ECG abnormality (5% to 8%; ST-T changes, extrasystoles), hypotension (5%), flushing (3%), tachycardia (3%), altered blood pressure (2%), hypertension (2%)
Central nervous system: Pain (3%), fatigue (1%), paresthesia (1%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (5%)
Respiratory: Dyspnea (3%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports (Limited to important or life-threatening): Abdominal pain, arthralgia, ataxia, back pain, bronchospasm, cardiac arrhythmia (ventricular tachycardia, bradycardia, AV block, SVT, atrial fibrillation, asystole), cardiomyopathy, cough, depersonalization, diaphoresis, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, dysphagia, ECG abnormality (unspecified), edema, eructation, flatulence, hypersensitivity reaction, hypertonia, hyperventilation, increased appetite, increased thirst, injection site reaction, leg cramps (intermittent claudication), malaise, mastalgia, muscle rigidity, myalgia, myocardial infarction, orthostatic hypotension, otalgia, palpitations, perineal pain, pharyngitis, pleuritic chest pain, pruritus, renal pain, rhinitis, skin rash, syncope, tenesmus, tinnitus, tremor, urticaria, vertigo, visual disturbance, vomiting, weakness, xerostomia
Warnings/Precautions
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with hypotension, unstable angina, and/or recent myocardial infarction; may enhance exercise induced myocardial ischemia in patients with chronic stable angina.
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Antiplatelet agents/anticoagulants: Use with caution in patients on other antiplatelet agents or anticoagulation.
- Pharmacologic stress testing: Interrupt oral dipyridamole therapy for 48 hours prior to stress testing with adenosine, IV dipyridamole, or regadenoson; may increase risk for cardiovascular adverse effects and impair the test sensitivity.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Injection: Severe adverse reactions have occurred rarely with IV administration. Use the IV form with caution in patients with bronchospastic disease or unstable angina. Have aminophylline ready in case of urgency or emergency with IV use.
Monitoring Parameters
IV: During stress perfusion imaging, monitor blood pressure, heart rate, ECG, respiration. Monitor for signs of poor perfusion (pallor, cyanosis, cold skin) (ASNC [Henzlova 2016])
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Adverse events have not been observed in animal reproduction studies.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used with a blood thinner to prevent clots after a heart valve is replaced.
- It is used during a stress test of the heart.
- It may be given for other reasons. Talk with the doctor
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Headache
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin or eyes
- Severe cerebrovascular disease like change in strength on one side is greater than the other, difficulty speaking or thinking, change in balance, or vision changes
- Chest pain
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Seizures
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.