Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Capsule, Oral:
Hectorol: 0.5 mcg [DSC] [contains fd&c red #40]
Hectorol: 1 mcg [DSC] [contains fd&c yellow #6 (sunset yellow)]
Hectorol: 2.5 mcg [DSC]
Generic: 0.5 mcg, 1 mcg, 2.5 mcg
Solution, Intravenous:
Hectorol: 2 mcg/mL (1 mL); 4 mcg/2 mL (2 mL) [contains alcohol, usp, disodium edta]
Generic: 4 mcg/2 mL (2 mL)
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Doxercalciferol is metabolized to the active form of vitamin D. The active form of vitamin D controls the intestinal absorption of dietary calcium, the tubular reabsorption of calcium by the kidneys, and in conjunction with PTH, the mobilization of calcium from the skeleton.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Hepatic via CYP27 to active metabolites, 1α,25-(OH)2D2 (major) and 1α,24-dihydroxyvitamin D2 (minor).
Time to Peak
Major metabolite: 8 hours (injection); 11 to 12 hours (oral).
Half-Life Elimination
Major metabolite: ~32 to 37 hours (range: up to 96 hours)
Use: Labeled Indications
Secondary hyperparathyroidism (patients on dialysis): Injection, oral: Treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis
Secondary hyperparathyroidism (patients not on dialysis): Oral: Treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in patients with stage 3 or 4 CKD
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to doxercalciferol or any component of the formulation; hypercalcemia; vitamin D toxicity
Documentation of allergenic cross-reactivity for vitamin D analogues is limited. However, because of similarities in chemical structure and/or pharmacologic actions, the possibility of cross-sensitivity cannot be ruled out with certainty.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Secondary hyperparathyroidism:
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients on dialysis:
Note: KDIGO guidelines recommend maintaining intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels in the range of ~2 to 9 times the upper normal limit for the assay. Caution is advised to avoid hypercalcemia or elevated phosphate levels (KDIGO 2017)
Initial:
Oral: 10 mcg 3 times/week at dialysis (no more frequently than every other day)
IV: 4 mcg 3 times/week at the end of dialysis (no more frequently than every other day)
Dose titration: Ensure serum calcium is within normal limits prior to increasing the dose.
Oral: Titrate the dose by 2.5 mcg/dose at 8-week intervals to achieve target plasma PTH level. Maximum: 20 mcg 3 times/week at dialysis (60 mcg weekly). Hold therapy or decrease dose if PTH is persistently and abnormally low or if corrected serum calcium is consistently above normal range; if doxercalciferol is held, may restart 1 week later at a dose that is at least 2.5 mcg lower than the previous dose.
IV: Titrate the dose by 1 to 2 mcg/dose at 8-week intervals if plasma PTH is not lowered by 50% and to achieve target plasma PTH level. Maximum: 18 mcg weekly. Hold therapy or decrease dose if PTH is persistently and abnormally low or if corrected serum calcium is consistently above normal range; if doxercalciferol is held, may restart 1 week later at a dose that is at least 1 mcg lower than the previous dose.
CKD patients not on dialysis (CKD stage ≥G3):
Note: KDIGO guidelines do not recommend routine use of vitamin D analogs (eg, doxercalciferol) in patients not on dialysis with CKD stages G3 to G5; it may be reasonable to reserve use for patients with CKD stages G4 or G5 and with severe and progressive hyperparathyroidism. Caution is advised to avoid hypercalcemia or elevated phosphate levels (KDIGO 2017).
Initial: Oral: 1 mcg once daily
Dose titration: Oral: Titrate the dose by 0.5 mcg/dose at 2-week intervals to achieve target plasma PTH level. Maximum: 3.5 mcg once daily. Ensure serum calcium is within normal limits prior to increasing the dose. Hold therapy or decrease dose if PTH is persistently and abnormally low or if corrected serum calcium is consistently above normal range; if doxercalciferol is held, may restart 1 week later at a dose that is at least 0.5 mcg lower than the previous dose.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
Injection: Administer as an IV bolus.
Dietary Considerations
Based on serum levels, dietary phosphate may be restricted and/or controlled with phosphate-lowering agents. The daily combined elemental calcium intake (dietary and calcium based phosphate-lowering agents) should not exceed 2 g. Additional vitamin D supplements and magnesium-containing antacids should be avoided. Capsules contain coconut oil.
Storage
Capsules: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Injection, single use vial: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Protect from light.
Injection, multi-dose use vial: Store intact vial at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). After initial entry, unused portion may be stored at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 3 days. Protect from light.
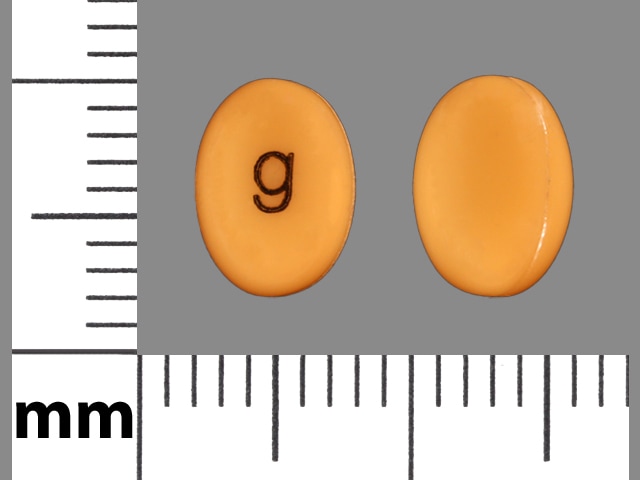
Doxercalciferol Images
Drug Interactions
Aluminum Hydroxide: Vitamin D Analogs may increase the serum concentration of Aluminum Hydroxide. Specifically, the absorption of aluminum may be increased, leading to increased serum aluminum concentrations. Avoid combination
Bile Acid Sequestrants: May decrease the serum concentration of Vitamin D Analogs. More specifically, bile acid sequestrants may impair absorption of Vitamin D Analogs. Management: Avoid concomitant administration of vitamin D analogs and bile acid sequestrants (eg, cholestyramine). Separate administration of these agents by several hours to minimize the potential risk of interaction. Monitor plasma calcium concentrations. Consider therapy modification
Burosumab: Vitamin D Analogs may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Burosumab. Avoid combination
Calcium Salts: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Monitor therapy
Cardiac Glycosides: Vitamin D Analogs may enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Cardiac Glycosides. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Doxercalciferol. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Doxercalciferol. Monitor therapy
Danazol: May enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: Serum Phosphate Level-Altering Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Erdafitinib. Management: Avoid coadministration of serum phosphate level-altering agents with erdafitinib before initial dose increase period based on serum phosphate levels (Days 14 to 21). Consider therapy modification
Magnesium Salts: Doxercalciferol may enhance the hypermagnesemic effect of Magnesium Salts. Management: Consider using a non-magnesium-containing antacid or phosphate-binding product in patients also receiving doxercalciferol. If magnesium-containing products must be used with doxercalciferol, serum magnesium concentrations should be monitored closely. Consider therapy modification
Mineral Oil: May decrease the serum concentration of Vitamin D Analogs. More specifically, mineral oil may interfere with the absorption of Vitamin D Analogs. Management: Avoid concomitant, oral administration of mineral oil and vitamin D analogs. Consider separating the administration of these agents by several hours to minimize the risk of interaction. Monitor plasma calcium concentrations. Consider therapy modification
Multivitamins/Fluoride (with ADE): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Avoid combination
Multivitamins/Minerals (with ADEK, Folate, Iron): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Avoid combination
Orlistat: May decrease the serum concentration of Vitamin D Analogs. More specifically, orlistat may impair absorption of Vitamin D Analogs. Management: Monitor clinical response (including serum calcium) to oral vitamin D analogs closely if used with orlistat. If this combination must be used, consider giving the vitamin D analog at least 2 hrs before or after orlistat. Consider therapy modification
Sucralfate: Vitamin D Analogs may increase the serum concentration of Sucralfate. Specifically, the absorption of aluminum from sucralfate may be increased, leading to an increase in the serum aluminum concentration. Avoid combination
Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics: May enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Monitor therapy
Vitamin D Analogs: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Vitamin D Analogs. Avoid combination
Adverse Reactions
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Edema (7% to 34%)
Central nervous system: Headache (28%), malaise (28%), insomnia (15%), paresthesia (15%), dizziness (12%), hypertonia (11%)
Gastrointestinal: Constipation (26%), nausea and vomiting (21%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia (19%)
Infection: Infection (30%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Asthenia (15%)
Respiratory: Rhinitis (22%), cough (19%), dyspnea (12% to 19%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Angina pectoris (8%), bradycardia (7%), chest pain (7%)
Central nervous system: Depression (7%), sleep disorder (3%)
Dermatologic: Pruritus (7% to 8%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Dehydration (7%), weight gain (5%)
Gastrointestinal: Dyspepsia (5% to 7%), anorexia (5%)
Genitourinary: Urinary tract infection (7%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Leukopenia (7%)
Infection: Abscess (3%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia (5%)
Respiratory: Sinusitis (7%)
Frequency not defined:
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypercalcemia, hyperphosphatemia
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, burning sensation of skin, chest discomfort, hypersensitivity reaction, hypotension, unresponsive to stimuli
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Excessive vitamin D: Excessive vitamin D administration may lead to over suppression of parathyroid hormone (PTH), progressive or acute hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, hyperphosphatemia, and adynamic bone disease.
- Hypercalcemia: Monitor calcium levels closely; patients with chronic renal failure are at an increased risk for hypercalcemia. Avoid use in patients with a recent history of hypercalcemia. Risk of hypercalcemia may be increased by concomitant use of calcium-containing supplements and/or medications that increase serum calcium (eg, thiazide diuretics). Patients with high calcium levels (>10.5 mg/dL) prior to treatment are more likely to develop hypercalcemia. Progressive and/or acute hypercalcemia may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias and seizures; chronic hypercalcemia may lead to generalized vascular and other soft-tissue calcification, including the heart and arteries, exacerbate nephrolithiasis, and has been associated with increased mortality in adults with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Reduce dose or discontinue therapy if hypercalcemia occurs.
- Hypersensitivity: Serious hypersensitivity reactions (some fatal), including anaphylaxis with angioedema, dyspnea, hypotension, chest discomfort, cardiopulmonary arrest, and unresponsiveness, have been reported with IV doxercalciferol. Monitor for hypersensitivity when initiating IV treatment; discontinue if such reaction occurs.
Disease-related concerns:
- Hepatic impairment: Patients with hepatic insufficiency may not appropriately metabolize doxercalciferol. Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment; may require more frequent iPTH, calcium, and phosphate monitoring.
- Hyperphosphatemia: Patients with high phosphate levels (>6.9 mg/dL) prior to treatment are more likely to develop hyperphosphatemia. Correct before initiating therapy; exacerbates secondary hyperparathyroidism, diminishing the effect of doxercalciferol.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Doxercalciferol is not for initial treatment of nutritional vitamin D deficiency. Other forms of vitamin D should be discontinued when doxercalciferol is started. Do not administer doxercalciferol to patients with a recent history of hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia, or evidence of vitamin D toxicity (may have increased risk of hypercalcemia or hyperphosphatemia).
Monitoring Parameters
Serum calcium, phosphate, and parathyroid hormone (PTH): Frequency of measurement may be dependent upon the presence and magnitude of abnormalities, the rate of progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD), and the use of treatments for chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) (KDIGO 2017):
CKD stage G3a to G3b: Serum calcium and phosphate: Every 6 to 12 months; PTH: Frequency based on baseline level and progression of CKD
CKD stage G4: Serum calcium and phosphate: Every 3 to 6 months; PTH: Every 6 to 12 months
CKD stage G5 and G5D: Serum calcium and phosphate: Every 1 to 3 months; PTH: Every 3 to 6 months
In dialysis patients, iPTH, serum calcium and phosphate should be determined prior to initiation of therapy and weekly thereafter for the first 12 weeks. For predialysis patients, serum calcium and phosphate and plasma levels of iPTH should be monitored at least every two weeks for 3 months after initiation of therapy or following dose adjustments, then monthly for 3 months, and every 3 months thereafter.
Periodic 24-hour urinary calcium and phosphate; magnesium; alkaline phosphatase every 12 months or more frequently in the presence of elevated PTH; creatinine, BUN, albumin; intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) every 3 to 12 months depending on CKD severity; signs/symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions (upon IV initiation)
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Adverse events have not been observed in animal reproduction studies
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat high parathyroid hormone levels in certain patients.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Joint pain
- Runny nose
- Cough
- Trouble sleeping
- Weight gain
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- High calcium like weakness, confusion, fatigue, headache, nausea and vomiting, constipation, or bone pain
- Dehydration like dry skin, dry mouth, dry eyes, increased thirst, fast heartbeat, dizziness, fast breathing, or confusion
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Chills
- Burning or numbness feeling
- Stiff muscles
- Depression
- Increased thirst
- Passing a lot of urine
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Chest pain
- Weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Lack of appetite
- Seizures
- Slow heartbeat
- Swelling
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.