Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Suspension, Oral:
Generic: 125 mg/5 mL (118 mL [DSC], 120 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Gris-PEG: 125 mg [DSC], 250 mg [DSC] [scored]
Generic: 125 mg, 250 mg, 500 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Inhibits fungal cell mitosis at metaphase; binds to human keratin making it resistant to fungal invasion
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Ultramicrosize griseofulvin absorption is almost complete; absorption of microsize griseofulvin is variable (27% to 72% of an oral dose); enhanced by ingestion of a fatty meal (GI absorption of ultramicrosize is ~1.5 times that of microsize); absorbed from the duodenum
Distribution
Deposited in the keratin layer of skin, hair, and nails; concentrates in liver, fat, and skeletal muscles; Vd: ~1.5 L (Vozeh 1988)
Metabolism
Extensively hepatic
Excretion
Urine (<1% as unchanged drug); feces (~33%); perspiration
Time to Peak
Serum: 4 hours
Half-Life Elimination
9 to 24 hours
Use: Labeled Indications
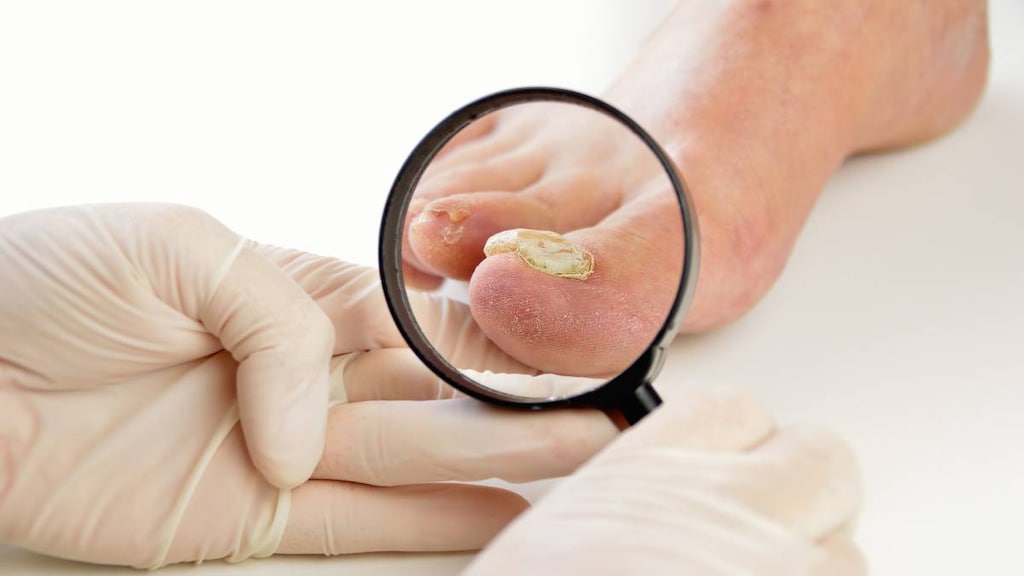
Dermatophyte infections: Treatment of the following dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails not adequately treated by topical therapy: Tinea corporis, tinea pedis, tinea cruris, tinea barbae, tinea capitis, tinea unguium (onychomycosis) when caused by one or more of the following species of fungi: Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton tonsurans, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, Trichophyton interdigitalis, Trichophyton verrucosum, Trichophyton megnini, Trichophyton gallinae, Trichophyton crateriform, Trichophyton sulphureum, Trichophyton schoenleini, Microsporum audouini, Microsporum canis, Microsporum gypseum, and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Limitations of use: Use for the prophylaxis of fungal infections has not been established; not effective for the treatment of tinea versicolor.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to griseofulvin or any component of the formulation; hepatic failure; porphyria; pregnancy
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Dermatophyte infections: Oral:
Microsize: 500 mg/day in single or divided doses; for more widespread lesions initial doses of 750 to 1,000 mg/day in single or divided doses may be needed; may decrease gradually to 500 mg/day or less if patient responds to higher dose.
Ultramicrosize: 375 mg daily in single or divided doses; doses up to 750 mg/day in divided doses have been used for infections more difficult to eradicate such as tinea unguium and tinea pedis
Duration of therapy depends on the site of infection:
Tinea corporis: 2 to 4 weeks
Tinea cruris: Duration not specified in manufacturer’s labeling; in pediatric patients 6 weeks has been recommended (Red Book, 2015)
Tinea capitis: 4 to 6 weeks
Tinea pedis: 4 to 8 weeks
Tinea unguium: 4 to 6 months or longer
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
General dosing; susceptible infection (Bradley 2018; Red Book [AAP 2018]): Children >2 years and Adolescents:
Microsize: Oral: 20 to 25 mg/kg/day in single or 2 divided doses; maximum daily dose: 1,000 mg/day
Ultramicrosize: Oral: 10 to 15 mg/kg/day once daily; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Tinea capitis: Note: Preferred therapy for Microsporum canis infection; may be used in combination with adjunctive topical therapy (eg, selenium or antifungal shampoo) (Red Book [AAP 2018]). Patients receiving doses on the lower end of the dose range may require longer durations of treatment for fungal eradication (Shemer 2013).
Infants >1 month to Children ≤2 years: Limited data available: Oral: Microsize: 15 to 25 mg/kg/day in single or 2 divided doses (maximum daily dose: 1,000 mg/day) until resolution; usually 6 to 8 weeks duration, although resistant cases may require longer duration; tinea capitis is rare in ages <1 year, infant dosing based on small case-series/reports (Atanasovski 2011; Fuller 2014; Gupta 2017; Lorch Dauk 2010; Michaels 2012)
Children >2 years and Adolescents:
Microsize: Oral: 20 to 25 mg/kg/day in single daily dose or in 2 divided doses (maximum daily dose: 1,000 mg/day) for 6 to 8 weeks or until fungal cultures clear; in some cases, treatment up to 12 to 18 weeks may be necessary (Ely 2014; Fuller 2014; Gupta 2017; Kakourou 2010; Red Book [AAP 2018]). Although lower doses (10 to 15 mg/kg/day) have been suggested previously by experts (Higgins 2000) and by the manufacturer, they are associated with extended treatment durations and/or potentially lower cure rates and have fallen out of favor (Bradley 2018; Red Book [AAP 2018]).
Ultramicrosize: Oral: 10 to 15 mg/kg/day once daily (maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day) for 6 to 8 weeks or until fungal cultures clear; in some cases, treatment up to 12 to 18 weeks may be necessary (Ali 2007; Ely 2014; Kakourou 2010; Red Book [AAP 2018])
Administration
Oral: Administer with a fatty meal to increase absorption (Red Book [AAP 2015])
Gris-PEG tablets: May be swallowed whole or crushed and sprinkled onto 1 tablespoonful of applesauce and swallowed immediately without chewing.
Suspension: Shake well before use.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from light.
Griseofulvin Images
Drug Interactions
Alcohol (Ethyl): Griseofulvin may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Alcohol (Ethyl). A disulfiram-like reaction may occur. Monitor therapy
Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic). Avoid combination
Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical). Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May decrease the serum concentration of Griseofulvin. Exceptions: Methohexital; Thiopental. Monitor therapy
Carbocisteine: Griseofulvin may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Carbocisteine. Specifically, griseofulvin may enhance adverse effects of alcohol that is present in liquid formulations of carbocisteine-containing products. Monitor therapy
CycloSPORINE (Systemic): Griseofulvin may decrease the serum concentration of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Estrogen Derivatives (Contraceptive): Griseofulvin may increase the metabolism of Estrogen Derivatives (Contraceptive). Contraceptive failure is possible. Management: Use an alternative, nonhormonal form of contraception, or use an alternative to griseofulvin. Consider therapy modification
Porfimer: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Porfimer. Monitor therapy
Progestins (Contraceptive): Griseofulvin may diminish the therapeutic effect of Progestins (Contraceptive). Contraceptive failure is possible. Avoid combination
Saccharomyces boulardii: Antifungal Agents (Systemic, Oral) may diminish the therapeutic effect of Saccharomyces boulardii. Avoid combination
Ulipristal: Griseofulvin may decrease the serum concentration of Ulipristal. Avoid combination
Verteporfin: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Verteporfin. Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Griseofulvin may decrease the serum concentration of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
False-positive urinary VMA levels (Rampini 1989)
Adverse Reactions
Frequency not defined.
Central nervous system: Confusion, dizziness, fatigue, headache, insomnia
Dermatologic: Dermatological reaction (erythema multiforme-like drug reaction), skin photosensitivity, skin rash (most common), urticaria (most common)
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, epigastric distress, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, nausea, oral candidiasis, vomiting
Genitourinary: Nephrosis
Hematologic & oncologic: Granulocytopenia
Hepatic: Hepatotoxicity
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Angioedema, increased serum bilirubin, increased serum transaminases, leukopenia, lupus-like syndrome, paresthesia, proteinuria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Hematologic effects: Leukopenia has been reported (rare); discontinue therapy if granulocytopenia occurs.
- Hepatic effects: May cause jaundice and elevated liver function tests or bilirubin (may be serious or even fatal); monitor hepatic function and discontinue therapy if necessary.
- Penicillin allergy: Hypersensitivity cross reaction between penicillins and griseofulvin is possible, however, known penicillin-sensitive patients have been treated successfully without complications.
- Photosensitivity: Avoid exposure to intense sunlight to prevent photosensitivity reactions.
- Skin reactions: Severe skin reactions (eg, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme) have been reported (may be serious or even fatal); discontinue use if severe skin reactions occur.
Disease-related concerns:
- Lupus erythematosus: Development of lupus erythematosus, lupus-like syndromes or exacerbation of existing lupus erythematosus has been reported.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Use for the prophylaxis of fungal infections has not been established; not effective for the treatment of tinea versicolor.
Monitoring Parameters
Periodic renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic function tests especially with long-term use
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
X
Pregnancy Considerations
Griseofulvin crosses the placenta (Pacifici 2006). Adverse events have been observed in humans (two cases of conjoined twins); therefore, use during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Females of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during therapy (estrogen containing contraceptives may be less effective). Men should avoid fathering a child for at least 6 months after therapy.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat fungal infections.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of strength and energy
- Trouble sleeping
- Diarrhea
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Lupus like rash on the cheeks or other body parts, sunburn easy, muscle or joint pain, chest pain or shortness of breath, or swelling in the arms or legs
- Liver problems like dark urine, feeling tired, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin or eyes
- Confusion
- Burning or numbness feeling
- Redness or white patches in mouth or throat
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in mouth, throat, nose, or eyes
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.