Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Solution, oral:
Kaletra: Lopinavir 80 mg and ritonavir 20 mg per 1 mL (160 mL) [contains ethanol 42.4%, menthol, propylene glycol; cotton candy flavor]]
Tablet:
Kaletra:
Lopinavir 100 mg and ritonavir 25 mg
Lopinavir 200 mg and ritonavir 50 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
A coformulation of lopinavir and ritonavir. The lopinavir component binds to the site of HIV-1 protease activity and inhibits the cleavage of viral Gag-Pol polyprotein precursors into individual functional proteins required for infectious HIV. This results in the formation of immature, noninfectious viral particles. The ritonavir component inhibits the CYP3A metabolism of lopinavir, allowing increased plasma levels of lopinavir.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Lopinavir: Hepatic via CYP3A4; 13 metabolites identified; may induce its own metabolism
Excretion
Lopinavir: Feces (83%, 20% as unchanged drug); urine (10%; <3% as unchanged drug)
Clearance: (Apparent oral): 6 to 7 L/hour
Time to Peak
Lopinavir: ~4 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Lopinavir: 5 to 6 hours
Protein Binding
Lopinavir: 98% to 99%; binds to both alpha-1 acid glycoprotein and albumin; higher affinity for alpha-1 acid glycoprotein; decreased with mild-to-moderate hepatic dysfunction
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
Lopinavir is principally metabolized and eliminated by the liver. Multiple dosing of lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily to patients coinfected with HIV-1 and hepatitis C virus with mild to moderate hepatic impairment resulted in a 30% increase in lopinavir AUC and a 20% increase in Cmax compared with patients infected with HIV-1 with normal hepatic function.
Use: Labeled Indications
HIV-1 infection: Treatment of HIV-1 infection in adults and pediatric patients 14 days and older in combination with other antiretroviral agents
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (eg, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, urticaria, angioedema) to lopinavir, ritonavir, or any component of the formulation; coadministration with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening reactions or with potent CYP3A inducers where significantly decreased lopinavir levels may be associated with a potential for loss of virologic response and resistance and cross-resistance to develop (eg, alfuzosin, apalutamide, dronedarone, cisapride, colchicine [patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment], elbasvir/grazoprevir, ergot derivatives [eg, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine], lomitapide, lovastatin, lurasidone, oral midazolam, pimozide, ranolazine, rifampin, sildenafil [when used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension], simvastatin, St John's wort, triazolam).
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling):
Tablets, oral solution: Coadministration with apalutamide, astemizole (not available in Canada), fusidic acid, salmeterol, terfenadine (not available in Canada), vardenafil, venetoclax (during dose initiation and the ramp-up phase)
Oral solution: Pregnancy; hepatic or renal failure; coadministration with disulfiram or metronidazole
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
HIV-1 infection, treatment (as a component of combination therapy): Oral:
Patients receiving concomitant antiretroviral therapy without efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine:
Twice-daily dosing: Therapy-naive or therapy-experienced: Lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily.
Once-daily dosing: Therapy-naive or experienced patients with <3 lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions: Lopinavir 800 mg/ritonavir 200 mg once daily. Once-daily dosing is not recommended in those receiving efavirenz, fosamprenavir, nevirapine, nelfinavir, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin.
Pregnant women (with no lopinavir-resistance-associated amino acid substitutions): Lopinavir 400 mg/ritonavir 100 mg twice daily. Once-daily dosing is not recommended. Tablets are recommended; avoid use of the oral solution. Alternately, the HHS perinatal guidelines recommend an increased dose of lopinavir 600 mg/ritonavir 150 mg twice daily, or lopinavir 500 mg/ritonavir 125 mg twice daily, during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, especially in PI-experienced pregnant women and women with a baseline viral load >50 copies/mL. If standard doses are used, close monitoring is recommended (HHS [perinatal] 2019).
Dosage adjustment for combination therapy with efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine: Oral:
Twice-daily dosing: Therapy-naive and therapy-experienced patients:
Solution: Lopinavir 520 mg/ritonavir 130 mg (6.5 mL) twice daily
Tablet: Lopinavir 500 mg/ritonavir 125 mg twice daily
Once-daily dosing: Once-daily dosing not recommended.
Dosage adjustment for combination therapy with carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin: Once-daily dosing not recommended
Dosing: Pediatric
HIV-1 infection, treatment: Oral: Use in combination with other antiretroviral agents: Note: Pediatric dosage is based on patient body weight or surface area and is presented here based on lopinavir component. Do not exceed recommended adult dose. Use of tablets in patients <15 kg or <0.6 m2 is not recommended (use oral solution). Once daily dosing in pediatric patients is not recommended; in a study of treatment-experienced children, once daily dosing resulted in a lower trough concentration and less virological control (Foissac 2011)
Infants ≥42 weeks postmenstrual age (HHS [pediatric] 2016):
Patients receiving concomitant antiretroviral therapy without efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine: Lopinavir 16 mg/kg/dose or 300 mg/m2/dose twice daily. Note: Infants who receive 300 mg/m2/dose twice daily may have lower trough concentrations compared to adults; evaluate infants and adjust dose for incremental growth at frequent intervals.
Patients receiving concomitant antiretroviral therapy with efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine: Dosage information does not exist; lopinavir/ritonavir is not recommended in infants who are receiving these agents.
Children and Adolescents:
Patients receiving concomitant antiretroviral therapy without efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine:
Antiretroviral naïve: Note: Higher dose (see below) recommended in antiretroviral-experienced patients who may have decreased sensitivity to lopinavir; some clinicians choose to initiate therapy with the higher dose in all patients due to lower trough concentrations observed with the lower dose (HHS [pediatric] 2016):
BSA-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Lopinavir 230 mg/m2/dose (maximum dose: 400 mg/dose) twice daily; others have suggested 300 mg/m2/dose twice daily if the oral solution is used. Note: For patients already receiving lopinavir and ritonavir, an immediate dosage reduction at 12 months of age is not recommended; patients are allowed to "grow into" the 230 mg/m2/dose dosage as they gain weight over time.
Alternate fixed dosing for patients weighing ≥15 kg who are able to swallow tablets: Dosing approximates lopinavir 230 mg/m2/dose:
BSA ≥0.6 to <0.9 m2: Lopinavir 200 mg twice daily
BSA ≥0.9 to <1.4 m2: Lopinavir 300 mg twice daily
BSA ≥1.4 m2: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Weight-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Dosing approximates lopinavir 230 mg/m2/dose:
<15 kg: Lopinavir 12 mg/kg/dose twice daily
15 to 40 kg: Lopinavir 10 mg/kg/dose twice daily
>40 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Alternate fixed dosing for patients weighing ≥15 kg and able to swallow tablets: Dosing approximates lopinavir 230 mg/m2/dose:
≥15 to 25 kg: Lopinavir 200 mg twice daily
>25 to 35 kg: Lopinavir 300 mg twice daily
>35 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Antiretroviral-experienced or suspected decreased sensitivity to lopinavir; Note: This dose is also used by some clinicians for initial therapy in all patients (HHS [pediatric] 2016):
BSA-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Lopinavir 300 mg/m2/dose (maximum dose: 400 mg/dose) twice daily
Weight-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Dosing approximates lopinavir 300 mg/m2/dose:
<15 kg: Lopinavir 13 mg/kg/dose twice daily
15 to 45 kg: Lopinavir 11 mg/kg/dose twice daily
>45 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Weight band dosing for patients weighing ≥15 kg and able to swallow tablets: Dosing approximates lopinavir 300 mg/m2/dose:
15 to 20 kg: 200 mg twice daily
>20 to 30 kg: 300 mg twice daily
>30 kg: 400 mg twice daily
Patients receiving concomitant antiretroviral therapy with efavirenz, nelfinavir, or nevirapine (or treatment-experienced patients not receiving these agents who have suspected decreased susceptibility to lopinavir):
BSA-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Lopinavir 300 mg/m2/dose twice daily; maximum dose: Oral solution: 520 mg/dose; Tablet: 500 mg/dose
Alternate fixed dosing for patients who are able to swallow tablets: Dosing approximates lopinavir 300 mg/m2/dose:
BSA ≥0.6 to <0.8 m2: Lopinavir 200 mg twice daily
BSA ≥0.8 to < 1.2 m2: Lopinavir 300 mg twice daily
BSA ≥1.2 to < 1.7 m2: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
BSA ≥1.7 m2: Lopinavir 500 mg twice daily
Weight-directed dosing: Children and Adolescents: Dosing approximates lopinavir ~300 mg/m2/dose:
<15 kg: Lopinavir 13 mg/kg/dose twice daily
≥15 to 45 kg: Lopinavir 11 mg/kg/dose twice daily
>45 kg:
Oral solution: Lopinavir 520 mg (6.5 mL) twice daily
Tablets: Lopinavir 500 mg twice daily
Fixed dosing for patients weighing ≥15 kg who are able to swallow tablets:
≥15 to 20 kg: Lopinavir 200 mg twice daily
>20 to 30 kg: Lopinavir 300 mg twice daily
>30 to 45 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
>45 kg: Lopinavir 500 mg twice daily; Note: Alternatively, lopinavir 600 mg twice daily (3 tablets of the 200/50 mg lopinavir/ritonavir) can be used for ease of dosing (HHS [pediatric] 2016).
HIV-1 nonoccupational postexposure prophylaxis (nPEP) (HHS [nPEP] 2016): Note: Initiate therapy within 72 hours of exposure and continue for 28 days; use in combination with other antiretroviral agents. Oral:
Infants (at least 42 weeks postmenstrual age): Oral solution: 300 mg/m2/dose or 16 mg/kg/dose twice daily
Children:
Weight-directed dosing: Oral solution:
<15 kg: Lopinavir 12 mg/kg/dose twice daily
15 to 40 kg: Lopinavir 10 mg/kg/dose twice daily
>40 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Fixed dosing: Patients weighing ≥15 kg and able to swallow tablets: Tablets:
≥15 to 25 kg: Lopinavir 200 mg twice daily
>25 to 35 kg: Lopinavir 300 mg twice daily
>35 kg: Lopinavir 400 mg twice daily
Adolescents: Not recommended; other antiretroviral agents should be used
Administration
Solution: Must be administered with food; if using didanosine, take didanosine 1 hour before or 2 hours after lopinavir/ritonavir. Administer using calibrated dosing cup or syringe. Contains ethanol and propylene glycol; not recommended for use with polyurethane feeding tubes (potential incompatibility); silicone and polyvinyl chloride feeding tubes may be used.
Tablet: May be taken with or without food. Swallow whole, do not break, crush, or chew. May be taken with didanosine when taken without food.
Dietary Considerations
Solution must be taken with food. Tablet may be taken with or without food
Storage
Oral solution: Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Avoid exposure to excessive heat. If stored at 25°C or 77°F, use within 2 months.
Tablet: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Exposure to high humidity outside of the original container or USP equivalent tight container for >2 weeks is not recommended.
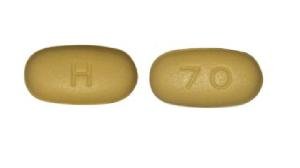
Lopinavir and Ritonavir Images
Drug Interactions
Abacavir: Protease Inhibitors may decrease the serum concentration of Abacavir. Monitor therapy
Abemaciclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Abemaciclib. Management: In patients taking abemaciclib at a dose of 200 mg or 150 mg twice daily, reduce the dose to 100 mg twice daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. In patients taking abemaciclib 100 mg twice daily, decrease the dose to 50 mg twice daily. Consider therapy modification
Acalabrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Acalabrutinib. Avoid combination
Acenocoumarol: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Acenocoumarol. Monitor therapy
Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ado-Trastuzumab Emtansine. Specifically, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase concentrations of the cytotoxic DM1 component. Avoid combination
Afatinib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Afatinib. Management: Reduce afatinib by 10 mg if not tolerated. Some non-US labeling recommends avoiding combination if possible. If used, administer the P-gp inhibitor simultaneously with or after the dose of afatinib. Consider therapy modification
Albendazole: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Albendazole. Monitor therapy
Alfuzosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alfuzosin. Avoid combination
Alfuzosin: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Alfuzosin. Avoid combination
Alitretinoin (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alitretinoin (Systemic). Management: Consider reducing the alitretinoin dose to 10 mg when used together with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor for increased alitretinoin effects/toxicities if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Almotriptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Almotriptan. Management: Limit initial almotriptan adult dose to 6.25 mg and maximum adult dose to 12.5 mg/24-hrs when used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Avoid concurrent use in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Consider therapy modification
Alosetron: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Alosetron. Monitor therapy
Alpelisib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Alpelisib. Management: Avoid coadministration of BCRP/ABCG2 inhibitors and alpelisib due to the potential for increased alpelisib concentrations and toxicities. If coadministration cannot be avoided, closely monitor for increased alpelisib adverse reactions. Consider therapy modification
ALPRAZolam: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of ALPRAZolam. Management: Consider using an alternative agent that is less likely to interact. If combined, monitor for increased therapeutic/toxic effects of alprazolam if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Amiodarone: Lopinavir may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Amiodarone. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Amiodarone. More specifically, Lopinavir/Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Amiodarone. Management: If this combination cannot be avoided, monitor for increased amiodarone serum concentrations and effects as well as for evidence of QT interval prolongation. Avoid combination
Amiodarone: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Amiodarone. Management: Ritonavir US prescribing information lists this combination as contraindicated. Amiodarone use should be avoided with lopinavir/ritonavir, but if the combination must be used, monitor closely for increased amiodarone serum concentrations and effects. Avoid combination
AmLODIPine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of AmLODIPine. Monitor therapy
Antidiabetic Agents: Hyperglycemia-Associated Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Antidiabetic Agents. Monitor therapy
Antihepaciviral Combination Products: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Antihepaciviral Combination Products. Specifically, the serum concentrations of the paritaprevir component may increase significantly. Avoid combination
Apalutamide: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Avoid combination
Apixaban: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Apixaban. Management: US labeling recommends a 50% apixaban dose reduction in patients who would otherwise receive 5 or 10 mg twice daily, and avoiding in patients who would otherwise receive 2.5 mg twice daily. Canadian labeling lists any combined use as contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Aprepitant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Aprepitant. Avoid combination
ARIPiprazole: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ritonavir. The risk of metabolic disturbances (e.g. hyperglycemia, weight gain, hyperlipidemia) may be increased. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of ARIPiprazole. Management: See full interaction monograph. Aripiprazole dose adjustment may not be required when used as adjunctive therapy for major depressive disorder. Consider therapy modification
ARIPiprazole Lauroxil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of ARIPiprazole Lauroxil. Management: Please refer to the full interaction monograph for details concerning the recommended dose adjustments. Consider therapy modification
Artesunate: Ritonavir may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Artesunate. Monitor therapy
Astemizole: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Astemizole. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
Asunaprevir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Asunaprevir. Avoid combination
Asunaprevir: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Asunaprevir. Avoid combination
AtorvaSTATin: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of AtorvaSTATin. Management: See full monograph for recommended dose limits. Avoid atorvastatin with tipranavir/ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Atovaquone: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Atovaquone. Monitor therapy
Avanafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Avanafil. Avoid combination
Avapritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Avapritinib. Avoid combination
Axitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Axitinib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of axitinib with any strong CYP3A inhibitor whenever possible. If a strong CYP3A inhibitor must be used with axitinib, a 50% axitinib dose reduction is recommended. Consider therapy modification
Barnidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Barnidipine. Avoid combination
Bedaquiline: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Bedaquiline. Management: Consider alternatives to this combination. Concomitant use should only occur if the benefit of coadministration outweighs the risk. If combined, monitor for increased bedaquiline effects/toxicities (eg, QTc interval prolongation). Consider therapy modification
Benperidol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Benperidol. Monitor therapy
Benzhydrocodone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Benzhydrocodone. Specifically, the concentration of hydrocodone may be increased. Monitor therapy
Betamethasone (Ophthalmic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Betamethasone (Ophthalmic). Monitor therapy
Betrixaban: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Betrixaban. Management: Decrease the adult betrixaban dose to an initial single dose of 80 mg followed by 40 mg once daily if combined with a P-glycoprotein inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Bictegravir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bictegravir. Monitor therapy
Bilastine: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Bilastine. Management: Consider alternatives when possible; bilastine should be avoided in patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency who are receiving p-glycoprotein inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Blonanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Blonanserin. Avoid combination
Bortezomib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bortezomib. Monitor therapy
Bosentan: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Bosentan. Management: Use bosentan 62.5 mg daily or every other day in adult patients who have been on ritonavir for at least 10 days. Temporarily stop bosentan (for at least 36 hrs) before starting ritonavir; wait until at least 10 days on ritonavir before restarting. Consider therapy modification
Bosentan: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Bosentan. Bosentan may decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Management: Use bosentan 62.5 mg/day or every other day in adult patients taking lopinavir/ritonavir for at least 10 days. Temporarily stop bosentan (for at least 36 hrs) before starting lopinavir/ritonavir; wait at least 10 days before restarting bosentan. Consider therapy modification
Bosutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bosutinib. Avoid combination
Brentuximab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brentuximab Vedotin. Specifically, concentrations of the active monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) component may be increased. Monitor therapy
Brentuximab Vedotin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Brentuximab Vedotin. Specifically, concentrations of the active monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) component may be increased. Monitor therapy
Brexpiprazole: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brexpiprazole. Management: Reduce brexpiprazole dose 50% with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors; reduce to 25% of usual if used with both a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor and a CYP2D6 inhibitor in patients not being treated for MDD, or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor used in a CYP2D6 poor metabolizer. Consider therapy modification
Brigatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brigatinib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of brigatinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combination cannot be avoided, reduce the brigatinib dose by approximately 50%, rounding to the nearest tablet strength (ie, from 180 mg to 90 mg, or from 90 mg to 60 mg). Consider therapy modification
Brinzolamide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Brinzolamide. Monitor therapy
Bromocriptine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Bromocriptine. Avoid combination
Budesonide (Nasal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Nasal). Monitor therapy
Budesonide (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Oral Inhalation). Monitor therapy
Budesonide (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Systemic). Avoid combination
Budesonide (Topical): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Budesonide (Topical). Management: Per US prescribing information, avoid this combination. Canadian product labeling does not recommend strict avoidance. If combined, monitor for excessive glucocorticoid effects as budesonide exposure may be increased. Consider therapy modification
Buprenorphine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Buprenorphine. Monitor therapy
BuPROPion: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of BuPROPion. Mixed effects on concentrations of the active hydroxybupropion metabolite have been reported. Management: Monitor for decreased bupropion effects. Significant bupropion dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain adequate response. Avoid the use of naltrexone/bupropion for weight management in patients receiving ritonavir. Monitor therapy
BuPROPion: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of BuPROPion. Concentrations of the active metabolite, hydroxybupropion, may also be decreased. Management: Monitor bupropion response closely. Significant bupropion dose adjustments may be necessary to maintain adequate response. Avoid the use of naltrexone/bupropion for weight management in patients receiving lopinavir. Monitor therapy
BusPIRone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of BusPIRone. Management: Limit the buspirone dose to 2.5 mg daily and monitor patients for increased buspirone effects/toxicities if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Cabazitaxel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cabazitaxel. Management: Concurrent use of cabazitaxel with strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 should be avoided when possible. If such a combination must be used, consider a 25% reduction in the cabazitaxel dose. Consider therapy modification
Cabozantinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cabozantinib. Management: Avoid use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with cabozantinib if possible. If combined, cabozantinib dose adjustments are recommended and vary based on the cabozantinib product used and the indication for use. See monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Calcifediol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Calcifediol. Monitor therapy
Calcium Channel Blockers (Nondihydropyridine): Protease Inhibitors may decrease the metabolism of Calcium Channel Blockers (Nondihydropyridine). Increased serum concentrations of the calcium channel blocker may increase risk of AV nodal blockade. Management: Avoid concurrent use when possible. If used, monitor for CCB toxicity. The manufacturer of atazanavir recommends a 50% dose reduction for diltiazem be considered. Saquinavir, tipranavir, and darunavir/cobicistat use with bepridil is contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Canagliflozin: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Canagliflozin. Management: Consider increasing canagliflozin dose to 200 mg/day in patients tolerating 100 mg/day. A further increase to 300 mg/day can be considered in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater. Consider therapy modification
Cannabidiol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Cannabis: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cannabis. More specifically, tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol serum concentrations may be increased. Monitor therapy
CarBAMazepine: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Management: Increased doses of lopinavir may be necessary when using these agents in combination. Do not use a once daily lopinavir/ritonavir regimen together with carbamazepine. Increase monitoring of therapeutic response in all patients using this combination. Consider therapy modification
Cariprazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cariprazine. Management: Cariprazine dose reductions of 50% are required; specific recommended management varies slightly for those stable on cariprazine versus those just starting cariprazine. See prescribing information or full interaction monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Cat's Claw: May increase the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Monitor therapy
Celiprolol: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Celiprolol. Monitor therapy
Ceritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ceritinib. Management: If such combinations cannot be avoided, the ceritinib dose should be reduced by approximately one-third (to the nearest 150 mg). Resume the prior ceritinib dose after cessation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Exceptions discussed in separate monographs. Consider therapy modification
Cilostazol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cilostazol. Management: Consider reducing the cilostazol dose to 50 mg twice daily in adult patients who are also receiving strong inhibitors of CYP3A4. Consider therapy modification
Cinacalcet: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cinacalcet. Monitor therapy
Cisapride: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Cisapride. This may result in QTc prolongation and malignant cardiac arrhythmias. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
Cladribine: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Cladribine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of BCRP inhibitors during the 4 to 5 day oral cladribine treatment cycles whenever possible. If combined, consider dose reduction of the BCRP inhibitor and separation in the timing of administration. Consider therapy modification
Cladribine: Inhibitors of Equilibrative Nucleoside (ENT1) and Concentrative Nucleoside (CNT3) Transport Proteins may increase the serum concentration of Cladribine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitors during the 4 to 5 day oral cladribine treatment cycles whenever possible. If combined, consider an ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitor dose reduction and separation in the timing of administration. Consider therapy modification
Clarithromycin: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may diminish the therapeutic effect of Clarithromycin. Specifically, lopinavir may decrease the formation of the active 14-hydroxy-clarithromycin metabolite, which may negatively impact clarithromycin effectiveness. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Clarithromycin. Clarithromycin may increase the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Avoid combination
Clobetasone: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Clobetasone. Avoid combination
Clopidogrel: Ritonavir may diminish the antiplatelet effect of Clopidogrel. Ritonavir may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Clopidogrel. Monitor therapy
Clorazepate: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Clorazepate. Monitor therapy
CloZAPine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of CloZAPine. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Monitor therapy
CloZAPine: CYP1A2 Inducers (Weak) may decrease the serum concentration of CloZAPine. Monitor therapy
Cobicistat: May enhance the therapeutic effect of Ritonavir. Specifically, cobicistat and ritonavir have overlapping effects on the CYP3A4-mediated metabolism of other drugs. Avoid combination
Cobimetinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Cobimetinib. Avoid combination
Codeine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Codeine. Monitor therapy
Colchicine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Colchicine. Management: Colchicine is contraindicated in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function who are also receiving a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. In those with normal renal and hepatic function, reduce colchicine dose as directed. See full monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Colchicine: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Colchicine. Colchicine distribution into certain tissues (e.g., brain) may also be increased. Management: Colchicine is contraindicated in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function who are also receiving a p-glycoprotein inhibitor. In those with normal renal and hepatic function, reduce colchicine dose as directed. See full monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Conivaptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Conivaptan. Avoid combination
Copanlisib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Copanlisib. Management: If concomitant use of copanlisib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce the copanlisib dose to 45 mg. Monitor patients for increased copanlisib effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Corticosteroids (Orally Inhaled): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Corticosteroids (Orally Inhaled). Management: Orally inhaled fluticasone propionate with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is not recommended. Exceptions: Beclomethasone (Oral Inhalation); Triamcinolone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Corticosteroids (Systemic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Corticosteroids (Systemic). Exceptions: MethylPREDNISolone; PrednisoLONE (Systemic); PredniSONE. Monitor therapy
Crizotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Crizotinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of crizotinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors whenever possible. If combined use cannot be avoided, decrease the crizotinib dose to 250 mg daily. Exceptions are discussed in separate monographs. Consider therapy modification
Cyclophosphamide: Protease Inhibitors may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Cyclophosphamide. Specifically, the incidences of neutropenia, infection, and mucositis may be increased. Monitor therapy
CycloSPORINE (Systemic): Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Management: Consider empiric cyclosporine dose reductions and monitor cyclosporine serum concentrations closely if ritonavir is initiated. Consider therapy modification
CYP2B6 Substrates (High risk with Inducers): CYP2B6 Inducers (Moderate) may decrease the serum concentration of CYP2B6 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Moderate): May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May increase the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Consider an alternative for one of the interacting drugs. Some combinations may be specifically contraindicated. Consult appropriate manufacturer labeling. Consider therapy modification
CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Exceptions: Alitretinoin (Systemic); AmLODIPine; Benzhydrocodone; Buprenorphine; Gefitinib; HYDROcodone; Mirtazapine; Praziquantel; Telithromycin; Vinorelbine. Consider therapy modification
Dabrafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dabrafenib. Avoid combination
Daclatasvir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Daclatasvir. Management: Decrease the daclatasvir dose to 30 mg once daily if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. No dose adjustment is needed when daclatasvir is used with darunavir/cobicistat. Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dapoxetine. Avoid combination
Darolutamide: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Darolutamide. Monitor therapy
Darunavir: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Darunavir. Darunavir may increase the serum concentration of lopinavir Avoid combination
Dasatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dasatinib. Management: This combination should be avoided if possible. If combined, dasatinib dose reductions are recommended. See full monograph for details. Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Consider therapy modification
Deferasirox: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Deferasirox. Management: Avoid combination when possible; if the combination must be used, consider a 50% increase in initial deferasirox dose, with monitoring of serum ferritin concentrations and clinical responses to guide further dosing. Consider therapy modification
Deflazacort: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Deflazacort. Management: Administer one third of the recommended deflazacort dose when used together with a strong or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Delamanid: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Delamanid. Management: Increase ECG monitoring frequency if delamanid is combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors due to the risk for QTc interval prolongation. Continue frequent ECG assessments throughout full delamanid treatment period. Exceptions discussed separately. Consider therapy modification
Delavirdine: Protease Inhibitors may decrease the serum concentration of Delavirdine. Delavirdine may increase the serum concentration of Protease Inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
DexAMETHasone (Ophthalmic): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of DexAMETHasone (Ophthalmic). Monitor therapy
Didanosine: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Didanosine. This interaction refers only to lopinavir/ritonavir oral solution, which must be taken with food, and is principally the result of a food-didanosine interaction. Management: Didanosine should be administered 1 hour prior to or 2 hours after administration of lopinavir/ritonavir oral solution (which must be taken with food). Didanosine and lopinavir/ritonavir tablets can be administered together. Consider therapy modification
Digoxin: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Digoxin. Consider therapy modification
Disulfiram: Lopinavir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Disulfiram. Specifically, the combination of lopinavir/ritonavir solution, which contains 42% alcohol, may result in a disulfiram-alcohol reaction if combined. Avoid combination
Disulfiram: Ritonavir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Disulfiram. Specifically, the combination of ritonavir oral solution, which contains 43% alcohol, may result in a disulfiram-alcohol reaction if combined. Avoid combination
DOCEtaxel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of DOCEtaxel. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of docetaxel and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined use is unavoidable, consider a 50% docetaxel dose reduction and monitor for increased docetaxel toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Dofetilide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dofetilide. Monitor therapy
Domperidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Domperidone. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
Doxercalciferol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Doxercalciferol. Monitor therapy
DOXOrubicin (Conventional): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of DOXOrubicin (Conventional). Management: Seek alternatives to strong CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients treated with doxorubicin whenever possible. One U.S. manufacturer (Pfizer Inc.) recommends that these combinations be avoided. Consider therapy modification
DOXOrubicin (Conventional): P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of DOXOrubicin (Conventional). Management: Seek alternatives to P-glycoprotein inhibitors in patients treated with doxorubicin whenever possible. One U.S. manufacturer (Pfizer Inc.) recommends that these combinations be avoided. Consider therapy modification
Dronabinol: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Dronabinol. Monitor therapy
Dronedarone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dronedarone. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
Drospirenone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Drospirenone. Management: Drospirenone use is contraindicated specifically when the strong CYP3A4 inhibitors atazanavir and cobicistat are administered concurrently. Caution should be used when drospirenone is coadministered with other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Dutasteride: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Dutasteride. Monitor therapy
Duvelisib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Duvelisib. Management: Reduce the dose of duvelisib to 15 mg twice a day when used together with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Edoxaban: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Edoxaban. Management: See full monograph for details. Reduced doses are recommended for patients receiving edoxaban for venous thromboembolism in combination with certain P-gp inhibitors. Similar dose adjustment is not recommended for edoxaban use in atrial fibrillation. Consider therapy modification
Efavirenz: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Management: Avoid once daily use of lopinavir/ritonavir with efavirenz. Avoid use of this combination in patients less than 6 months of age. See lopinavir/ritonavir prescribing information for specific recommended dose increases in particular patient populations. Consider therapy modification
Elagolix: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Elagolix. Avoid combination
Eletriptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eletriptan. Avoid combination
Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor, and Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor, and Ivacaftor. Management: When combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, administer two elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor tablets (100 mg/50 mg/75 mg) in the morning, twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening doses of ivacaftor (150 mg) alone should be administered. Consider therapy modification
Eliglustat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eliglustat. Management: Use should be avoided under some circumstances. See full drug interaction monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Eluxadoline: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Eluxadoline. Management: Decrease the eluxadoline dose to 75 mg twice daily if combined with lopinavir and monitor patients for increased eluxadoline effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Eluxadoline: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Eluxadoline. Management: Decrease the eluxadoline dose to 75 mg twice daily if combined with ritonavir and monitor patients for increased eluxadoline effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Elvitegravir: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Elvitegravir. Specifically, lopinavir/ritonavir may increase the concentration of elvitegravir. Management: When elvitegravir is combined with lopinavir/ritonavir, the dose of elvitegravir should be reduced to 85 mg once daily and the dose of lopinavir/ritonavir should be 400 mg/100 mg twice daily. Consider therapy modification
Encorafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Encorafenib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of encorafenib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors whenever possible. If concomitant administration is unavoidable, decrease the encorafenib dose. See monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Enfortumab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Enfortumab Vedotin. Specifically, concentrations of the active monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) component may be increased. Monitor therapy
Enfuvirtide: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Enfuvirtide. Enfuvirtide may increase the serum concentration of Protease Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Entrectinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Entrectinib. Management: Avoid strong CYP3A4 inhibitors during treatment with entrectinib. Reduce dose to 100 mg/day if combination cannot be avoided in adults and those 12 yrs of age or older with a BSA of at least 1.5 square meters. No alternative dosing provided for others. Consider therapy modification
Enzalutamide: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Concurrent use of enzalutamide with CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided. Use of enzalutamide and any other CYP3A4 substrate should be performed with caution and close monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Eplerenone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eplerenone. Avoid combination
Erdafitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Erdafitinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of erdafitinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If combined, monitor closely for erdafitinib adverse reactions and consider dose modifications accordingly. Consider therapy modification
Ergot Derivatives: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Exceptions: Cabergoline; Nicergoline; Pergolide. Avoid combination
Erlotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Erlotinib. Management: Avoid use of this combination when possible. When the combination must be used, monitor the patient closely for the development of severe adverse reactions, and if such severe reactions occur, reduce the erlotinib dose (in 50 mg decrements). Consider therapy modification
Estriol (Systemic): Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Estriol (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Estriol (Topical): Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Estriol (Topical). Monitor therapy
Estrogen Derivatives: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Estrogen Derivatives. Monitor therapy
Estrogen Derivatives (Contraceptive): Protease Inhibitors may decrease the serum concentration of Estrogen Derivatives (Contraceptive). Management: Use oral contraceptives containing at least 35mcg ethinyl estradiol with atazanavir/ritonavir, or no more than 30mcg in patients receiving atazanavir alone. Use of an alternative, non-hormonal contraceptive is recommended with other protease inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Eszopiclone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Eszopiclone. Management: Limit the eszopiclone dose to 2 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and monitor for increased eszopiclone effects and toxicities (eg, somnolence, drowsiness, CNS depression). Consider therapy modification
Etizolam: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Etizolam. Management: Consider use of lower etizolam doses when using this combination; specific recommendations concerning dose adjustment are not available. Monitor clinical response to the combination closely. Consider therapy modification
Etravirine: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Etravirine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of etravirine with antiviral doses of ritonavir; use with ritonavir-boosted fosamprenavir or with ritonavir-boosted tipranavir is also not recommended. Consider therapy modification
Everolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Everolimus. Avoid combination
Evogliptin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Evogliptin. Monitor therapy
Fedratinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fedratinib. Management: Consider alternatives when possible. If used together, decrease fedratinib dose to 200 mg/day. After the inhibitor is stopped, increase fedratinib to 300 mg/day for the first 2 weeks and then to 400 mg/day as tolerated. Consider therapy modification
FentaNYL: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of FentaNYL. Management: Monitor patients closely for several days following initiation of this combination, and adjust fentanyl dose as necessary. Consider therapy modification
Fesoterodine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Fesoterodine. Management: Avoid fesoterodine doses greater than 4 mg daily in adult patients who are also receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Flecainide: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Flecainide. Avoid combination
Flibanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Flibanserin. Avoid combination
Fluticasone (Nasal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fluticasone (Nasal). Avoid combination
Fluticasone (Oral Inhalation): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fluticasone (Oral Inhalation). Management: Use of orally inhaled fluticasone propionate with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is not recommended. Use of orally inhaled fluticasone furoate with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be done with caution. Monitor patients using such a combination more closely. Consider therapy modification
Fosamprenavir: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Specifically, amprenavir (the active metabolite of fosamprenavir) may decrease the serum concentration of lopinavir. Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Fosamprenavir. Specifically, lopinavir/ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of amprenavir (the active metabolite of fosamprenavir) Avoid combination
Fosaprepitant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Fosaprepitant. Avoid combination
Fosphenytoin: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Fosphenytoin. Management: The manufacturer of lopinavir/ritonavir recommends avoiding once-daily administration if used together with phenytoin. Consider therapy modification
Fosphenytoin: May decrease the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Fosphenytoin. Consider therapy modification
Fostamatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Fostamatinib. Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Fusidic Acid (Systemic). Fusidic Acid (Systemic) may increase the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Avoid combination
Galantamine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Galantamine. Monitor therapy
Garlic: May decrease the serum concentration of Protease Inhibitors. Management: Concurrent use of garlic supplements with protease inhibitors is not recommended. If this combination is used, monitor closely for altered serum concentrations/effects of protease inhibitors, and particularly for signs/symptoms of therapeutic failure. Consider therapy modification
Gefitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Gefitinib. Monitor therapy
Gilteritinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Gilteritinib. Management: Consider alternatives to the use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with gilteritinib. If the combination cannot be avoided, monitor more closely for evidence of gilteritinib toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Glasdegib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Glasdegib. Management: Consider alternatives to this combination when possible. If the combination must be used, monitor closely for evidence of QT interval prolongation and other adverse reactions to glasdegib. Consider therapy modification
Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir. Avoid combination
Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Glecaprevir and Pibrentasvir. Avoid combination
Grazoprevir: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Grazoprevir. Avoid combination
GuanFACINE: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of GuanFACINE. Management: Reduce the guanfacine dose by 50% when initiating this combination. Consider therapy modification
Halofantrine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Halofantrine. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
HYDROcodone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of HYDROcodone. Monitor therapy
Ibrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ibrutinib. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ibrutinib and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor must be used short-term (eg, anti-infectives for 7 days or less), interrupt ibrutinib therapy until the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is discontinued. Avoid combination
Idelalisib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Idelalisib. Monitor therapy
Ifosfamide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ifosfamide. Monitor therapy
Iloperidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Iloperidone. Specifically, concentrations of the metabolites P88 and P95 may be increased. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Iloperidone. Management: Reduce iloperidone dose by half when administered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Imatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Imatinib. Monitor therapy
Imidafenacin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Imidafenacin. Monitor therapy
Irinotecan Products: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Irinotecan Products. Specifically, serum concentrations of SN-38 may be increased. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Irinotecan Products. Avoid combination
Isavuconazonium Sulfate: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Isavuconazonium Sulfate. Specifically, CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase isavuconazole serum concentrations. Management: Combined use is considered contraindicated per US labeling. Lopinavir/ritonavir (and possibly other uses of ritonavir doses less than 400 mg every 12 hours) is treated as a possible exception to this contraindication despite strongly inhibiting CYP3A4. Avoid combination
Istradefylline: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Istradefylline. Management: Limit the maximum istradefylline dose to 20 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and monitor for increased istradefylline effects/toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Itraconazole: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Itraconazole. Management: Limit the adult maximum itraconazole dose to 200 mg/day in patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Itraconazole: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Itraconazole. Management: Limit the adult maximum itraconazole dose to 200 mg/day in patients receiving ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Ivabradine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivabradine. Avoid combination
Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivacaftor. Management: Ivacaftor dose reductions are required; consult full monograph content for age- and weight-specific recommendations. Consider therapy modification
Ivosidenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ivosidenib. Management: Avoid use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor with ivosidenib whenever possible. When combined use is required, reduce the ivosidenib dose to 250 mg once daily. Drugs listed as exceptions are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Consider therapy modification
Ixabepilone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ixabepilone. Consider therapy modification
Ketoconazole (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Ketoconazole (Systemic). Management: Limit the adult maximum ketoconazole dose to 200 mg/day in patients receiving lopinavir/ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Ketoconazole (Systemic): Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Ketoconazole (Systemic). Management: Limit the adult maximum ketoconazole dose to 200 mg/day in patients receiving ritonavir. Consider therapy modification
Lacosamide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lacosamide. Monitor therapy
LamoTRIgine: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of LamoTRIgine. Consider therapy modification
Lapatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lapatinib. Management: If an overlap in therapy cannot be avoided, consider reducing lapatinib adult dose to 500 mg/day during, and within 1 week of completing, treatment with the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Avoid combination
Larotrectinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Larotrectinib. Management: Avoid use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with larotrectinib. If this combination cannot be avoided, reduce the larotrectinib dose by 50%. Increase to previous dose after stopping the inhibitor after a period of 3 to 5 times the inhibitor half-life. Consider therapy modification
Lasmiditan: May increase the serum concentration of P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Substrates. Avoid combination
Lefamulin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lefamulin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of lefamulin tablets and strong inhibitors of CYP3A4. Avoid combination
Lemborexant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lemborexant. Avoid combination
Lercanidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lercanidipine. Avoid combination
Levamlodipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levamlodipine. Monitor therapy
Levobupivacaine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levobupivacaine. Monitor therapy
Levomethadone: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Levomethadone. Monitor therapy
Levomethadone: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Levomethadone. Monitor therapy
Levomilnacipran: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Levomilnacipran. Management: Do not exceed a maximum adult levomilnacipran dose of 80 mg/day in patients also receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
LinaGLIPtin: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of LinaGLIPtin. Monitor therapy
Lomitapide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lomitapide. Avoid combination
Lorlatinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lorlatinib. Management: Avoid use of lorlatinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If the combination cannot be avoided, reduce the lorlatinib dose from 100 mg once daily to 75 mg once daily, or from 75 mg once daily to 50 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
Lorlatinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Avoid concurrent use of lorlatinib with any CYP3A4 substrates for which a minimal decrease in serum concentrations of the CYP3A4 substrate could lead to therapeutic failure and serious clinical consequences. Consider therapy modification
Lovastatin: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Lovastatin. Avoid combination
Lovastatin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lovastatin. Avoid combination
Lumacaftor and Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lumacaftor and Ivacaftor. Management: When initiating or resuming lumacaftor/ivacaftor after a therapy interruption of 7 days or more, reduce the lumacaftor/ivacaftor dose to 1 tablet daily or 1 packet of oral granules every other day for the first week, and then resume the standard dose. Consider therapy modification
Lumateperone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lumateperone. Avoid combination
Lumefantrine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lumefantrine. Monitor therapy
Lurasidone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Lurasidone. Avoid combination
Macitentan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Macitentan. Avoid combination
Manidipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Manidipine. Management: Consider avoiding concomitant use of manidipine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If combined, monitor closely for increased manidipine effects and toxicities. Manidipine dose reductions may be required. Consider therapy modification
Maraviroc: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Maraviroc. Management: Reduce the adult dose of maraviroc to 150 mg twice daily when used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Do not use maraviroc with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients with Clcr less than 30 mL/min. Consider therapy modification
Mebendazole: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Mebendazole. Monitor therapy
Meperidine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Meperidine. Monitor therapy
Meptazinol: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Meptazinol. Avoid combination
Methadone: Lopinavir may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Methadone. Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Methadone. More specifically, the combination of Lopinavir and Ritonavir may decrease Methadone serum concentrations. Monitor therapy
Methadone: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Methadone. Monitor therapy
MethylPREDNISolone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of MethylPREDNISolone. Management: Consider methylprednisolone dose reduction in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors and monitor for increased steroid related adverse effects. Consider therapy modification
MetroNIDAZOLE (Systemic): Ritonavir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of MetroNIDAZOLE (Systemic). Specifically, the combination of ritonavir oral solution or ritonavir soft gelatin capsule, both of which contain alcohol, and metronidazole may result in a disulfiram-like reaction. Avoid combination
MetroNIDAZOLE (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Lopinavir. Specifically, the use of topical metronidazole with lopinavir/ritonavir solution (which contains 42% alcohol) may result in a disulfiram-like reaction. Monitor therapy
Midazolam: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Midazolam. Management: Oral midazolam contraindicated with all protease inhibitors. IV midazolam contraindicated with fosamprenavir and nelfinavir; other protease inhibitors recommend caution, close monitoring, and consideration of lower IV midazolam doses with concurrent use. Avoid combination
Midostaurin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Midostaurin. Management: Seek alternatives to the concomitant use of midostaurin and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors if possible. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, monitor patients for increased risk of adverse reactions. Exceptions are discussed in separate monographs. Consider therapy modification
MiFEPRIStone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of MiFEPRIStone. Management: Limit mifepristone adult dose, when used for treatment of hyperglycemia in Cushing's syndrome, to a maximum of 900 mg/day when combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor for increased mifepristone toxicity regardless of dose or indication. Consider therapy modification
Mirodenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Mirodenafil. Management: Consider using a lower dose of mirodenafil when used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Monitor for increased mirodenafil effects/toxicities with the use of this combination. Consider therapy modification
Mirtazapine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Mirtazapine. Monitor therapy
Mitotane: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Doses of CYP3A4 substrates may need to be adjusted substantially when used in patients being treated with mitotane. Consider therapy modification
Naldemedine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Naldemedine. Monitor therapy
Naldemedine: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Naldemedine. Monitor therapy
Nalfurafine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nalfurafine. Monitor therapy
Naloxegol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Naloxegol. Avoid combination
Nefazodone: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Nefazodone. Management: Consider alternatives to, or reduced doses of, nefazodone in patients treated with HIV protease inhibitors. Monitor patients receiving these combinations closely for toxic effects of nefazodone. Consider therapy modification
Nelfinavir: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Nelfinavir. Concentrations of the nelfinavir M8 metabolite may also be increased. Management: Avoid once daily use of lopinavir/ritonavir with nelfinavir. Avoid use of this combination in patients less than 6 months of age. See lopinavir/ritonavir prescribing information for recommended dose increases in other patients. Consider therapy modification
Neratinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Neratinib. Avoid combination
Nevirapine: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Management: Avoid once daily use of lopinavir/ritonavir with nevirapine. Avoid use of this combination in patients less than 6 months of age. See lopinavir/ritonavir prescribing information for recommended dose increases in other patients. Consider therapy modification
Nilotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nilotinib. Management: Avoid if possible. If combination needed, decrease nilotinib to 300 mg once/day for patients with resistant or intolerant Ph+ CML or to 200 mg once/day for patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML in chronic phase. Exceptions discussed in separate monograph. Consider therapy modification
NiMODipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
Nintedanib: Combined Inhibitors of CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Nintedanib. Monitor therapy
Nisoldipine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Nisoldipine. Avoid combination
OLANZapine: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of OLANZapine. Monitor therapy
Olaparib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Olaparib. Management: Avoid use of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors in patients being treated with olaparib, if possible. If such concurrent use cannot be avoided, the dose of olaparib should be reduced to 100 mg twice daily. Consider therapy modification
Orlistat: May decrease the serum concentration of Antiretroviral Agents. Monitor therapy
Ospemifene: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ospemifene. Monitor therapy
Oxybutynin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Oxybutynin. Monitor therapy
OxyCODONE: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of OxyCODONE. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of OxyCODONE. Serum concentrations of the active metabolite oxymorphone may also be increased. Consider therapy modification
Palbociclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Palbociclib. Avoid combination
Panobinostat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Panobinostat. Management: Reduce the panobinostat dose to 10 mg when it must be used with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Parecoxib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Parecoxib. Monitor therapy
Paricalcitol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Paricalcitol. Monitor therapy
PAZOPanib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of PAZOPanib. Avoid combination
PAZOPanib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of PAZOPanib. Avoid combination
Pexidartinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pexidartinib. Management: Avoid use of pexidartinib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors if possible. If combined use cannot be avoided, the pexidartinib dose should be reduced. Decrease 800 mg or 600 mg daily doses to 200 mg twice daily. Decrease doses of 400 mg/day to 200 mg/day. Consider therapy modification
P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors: May increase the serum concentration of P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Substrates. P-glycoprotein inhibitors may also enhance the distribution of p-glycoprotein substrates to specific cells/tissues/organs where p-glycoprotein is present in large amounts (e.g., brain, T-lymphocytes, testes, etc.). Monitor therapy
P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Substrates: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Substrates. P-glycoprotein inhibitors may also enhance the distribution of p-glycoprotein substrates to specific cells/tissues/organs where p-glycoprotein is present in large amounts (e.g., brain, T-lymphocytes, testes, etc.). Exceptions: Loperamide. Monitor therapy
PHENobarbital: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Management: Increased doses of lopinavir may be necessary when using these agents in combination. Do not use a once daily lopinavir/ritonavir regimen together with phenobarbital. Increase monitoring of therapeutic response in all patients using this combination. Consider therapy modification
Phenytoin: May decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Phenytoin. Management: The manufacturer of lopinavir/ritonavir recommends avoiding once-daily administration if used together with phenytoin. Consider therapy modification
Phenytoin: May decrease the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Phenytoin. Consider therapy modification
Pimavanserin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pimavanserin. Management: Decrease the pimavanserin dose to 10 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Pimecrolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease the metabolism of Pimecrolimus. Monitor therapy
Pimozide: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Pimozide. Avoid combination
Pimozide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pimozide. Avoid combination
Piperaquine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Piperaquine. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Piperaquine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of piperaquine and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. If the combination cannot be avoided, frequent ECG monitoring is recommended due to the risk for QTc prolongation. Exceptions are discussed separately. Consider therapy modification
Polatuzumab Vedotin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Polatuzumab Vedotin. Exposure to unconjugated MMAE, the cytotoxic small molecule component of polatuzumab vedotin, may be increased. Monitor therapy
PONATinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of PONATinib. Management: Per ponatinib U.S. prescribing information, the adult starting dose of ponatinib should be reduced to 30 mg daily during treatment with any strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Posaconazole: May increase the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Monitor therapy
Pranlukast: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Pranlukast. Monitor therapy
Praziquantel: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Praziquantel. Monitor therapy
PrednisoLONE (Systemic): Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of PrednisoLONE (Systemic). Management: Consider prednisolone dose reductions in patients receiving ritonavir and monitor for increased adverse effects with concomitant use. Consider therapy modification
PredniSONE: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of PredniSONE. Monitor therapy
Progestins (Contraceptive): Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Progestins (Contraceptive). Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Progestins (Contraceptive). Management: Consider using an alternative or additional means of contraception. Injected depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and etonogestrel implants may be used without a need for additional contraception. Consider therapy modification
Proguanil: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Proguanil. Monitor therapy
Propafenone: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Propafenone. Avoid combination
Protease Inhibitors: May increase the serum concentration of other Protease Inhibitors. Management: Atazanavir--indinavir combination contraindicated. Tipranavir/ritonavir or atazanavir/ritonavir not recommended with other protease inhibitors (PI). Darunavir/cobicistat not recommended with PI that require boosting.Other combos may require dose changes. Consider therapy modification
Prucalopride: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Prucalopride. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk): QT-prolonging Agents (Indeterminate Risk - Avoid) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QUEtiapine: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of QUEtiapine. Management: The ritonavir Canadian labeling states this combination should not be used. U.S. labeling recommends using an alternative when possible; if the combination must be used, quetiapine dose reductions are needed. Consider therapy modification
QuiNIDine: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of QuiNIDine. Avoid combination
QuiNIDine: Lopinavir may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QuiNIDine. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of QuiNIDine. Specifically, lopinavir/ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of quinidine. Avoid combination
QuiNINE: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of QuiNINE. This effect has been seen with lopinavir/ritonavir. The individual contributions of lopinavir and ritonavir to this effect are unclear. QuiNINE may increase the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of QuiNINE. Avoid combination
QuiNINE: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of QuiNINE. This effect has been seen with lopinavir/ritonavir. The individual contributions of lopinavir and ritonavir to this effect are unclear. Avoid combination
Radotinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Radotinib. Avoid combination
Ramelteon: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ramelteon. Monitor therapy
Ranolazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ranolazine. Avoid combination
Reboxetine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Reboxetine. Consider therapy modification
Red Yeast Rice: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Red Yeast Rice. Specifically, concentrations of lovastatin and related compounds found in Red Yeast Rice may be increased. Avoid combination
Regorafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Regorafenib. Avoid combination
Repaglinide: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Repaglinide. Management: The addition of a CYP2C8 inhibitor to this drug combination may substantially increase the magnitude of increase in repaglinide exposure. Monitor therapy
Retapamulin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Retapamulin. Management: Avoid this combination in patients less than 2 years old. No action is required in other populations. Monitor therapy
Revefenacin: OATP1B1/1B3 (SLCO1B1/1B3) Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
Ribociclib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ribociclib. Management: Avoid use of ribociclib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible; if combined use cannot be avoided, reduce ribociclib dose to 400 mg once daily. Exceptions are discussed in separate monographs. Consider therapy modification
Rifabutin: Lopinavir may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Rifabutin. Rifabutin may increase the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Rifabutin. Management: Reduce rifabutin doses. Lopinavir/ritonavir US labeling recommends a decrease of at least 75%, to 150 mg every other day or 3 times per week for adults, while clinical guidelines recommend 150 mg/day or 300 mg 3 times per week. Consider therapy modification
Rifabutin: Ritonavir may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Rifabutin. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Rifabutin. Management: Ritonavir US prescribing information recommends reducing rifabutin doses by at least 75%. Refer to drug interaction monographs addressing concomitantly administered protease inhibitors for dosing recommendations specific to ritonavir-boosted regimens. Consider therapy modification
RifAMPin: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Lopinavir. Specifically, the risk of hepatocellular toxicity may be increased. RifAMPin may decrease the serum concentration of Lopinavir. Avoid combination
RifAMPin: May decrease the serum concentration of Ritonavir. Avoid combination
RifAXIMin: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of RifAXIMin. Monitor therapy
Rilpivirine: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Rilpivirine. Monitor therapy
Riociguat: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Riociguat. Management: Consider starting with a reduced riociguat dose of 0.5 mg three times a day (for adults). Patients receiving such a combination should also be monitored extra closely for signs or symptoms of hypotension. Consider therapy modification
Rivaroxaban: Inhibitors of CYP3A4 (Strong) and P-glycoprotein may increase the serum concentration of Rivaroxaban. Avoid combination
RomiDEPsin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of RomiDEPsin. Monitor therapy
Rosuvastatin: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Rosuvastatin. Management: Start at the lowest rosuvastatin dose and monitor for toxicity. See full drug interaction monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Rupatadine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Rupatadine. Avoid combination
Ruxolitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ruxolitinib. Management: This combination should be avoided under some circumstances. See monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Salmeterol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Salmeterol. Avoid combination
Sarilumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
SAXagliptin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SAXagliptin. Management: Limit the saxagliptin dose to 2.5 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. When using the saxagliptin combination products saxagliptin/dapagliflozin or saxagliptin/dapagliflozin/metformin, avoid use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Sibutramine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Sibutramine. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sibutramine. Monitor therapy
Sildenafil: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Sildenafil. Management: Erectile dysfunction: sildenafil max = 25 mg/48 hrs with ritonavir, atazanavir, or darunavir; starting dose = 25 mg with other protease inhibitors (adult doses). Contraindicated if sildenafil being used for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Consider therapy modification
Sildenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sildenafil. Management: Use of sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension should be avoided with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. When used for erectile dysfunction, starting adult dose should be reduced to 25 mg. Maximum adult dose with ritonavir or cobicistat is 25 mg per 48 hours. Consider therapy modification
Silodosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Silodosin. Avoid combination
Siltuximab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Simeprevir: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Simeprevir. Avoid combination
Simeprevir: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Simeprevir. Simeprevir may increase the serum concentration of Protease Inhibitors. Avoid combination
Simvastatin: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Simvastatin. Avoid combination
Simvastatin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Simvastatin. Avoid combination
Sirolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sirolimus. Management: Consider avoiding concurrent use of sirolimus with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors in order to minimize the risk for sirolimus toxicity. Concomitant use of sirolimus and voriconazole or posaconazole is contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Solifenacin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Solifenacin. Management: Limit solifenacin doses to 5 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Sonidegib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Sonidegib. Avoid combination
SORAfenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Monitor therapy
St John's Wort: May increase the metabolism of Protease Inhibitors. Avoid combination
SUFentanil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SUFentanil. Management: If a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor is initiated in a patient on sufentanil, consider a sufentanil dose reduction and monitor for increased sufentanil effects and toxicities (eg, respiratory depression). Consider therapy modification
SUNItinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of SUNItinib. Management: Avoid when possible. If such a combination cannot be avoided, sunitinib dose decreases are recommended, and vary by indication. See full monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Suvorexant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Suvorexant. Avoid combination
Tacrolimus (Systemic): Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Tacrolimus (Systemic). Management: Tacrolimus dose reductions may be needed with concurrent ritonavir. Monitor tacrolimus concentrations closely to determine dose; doses of tacrolimus 0.5 mg to 1 mg every week may be adequate. Consider therapy modification
Tacrolimus (Topical): Protease Inhibitors may decrease the metabolism of Tacrolimus (Topical). Monitor therapy
Tadalafil: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Tadalafil. Management: Recommendations regarding use of tadalafil in patients also receiving ritonavir may vary based on indication and/or international labeling. Consult appropriate product labeling. Consider therapy modification
Talazoparib: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Talazoparib. Management: These listed exceptions are discussed in detail in separate interaction monographs. Monitor therapy
Talazoparib: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Talazoparib. Monitor therapy
Tamsulosin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tamsulosin. Avoid combination
Tasimelteon: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tasimelteon. Monitor therapy
Tazemetostat: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tazemetostat. Avoid combination
Tegaserod: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Tegaserod. Monitor therapy
Telithromycin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Telithromycin. Monitor therapy
Temsirolimus: Protease Inhibitors may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Temsirolimus. Levels of sirolimus, the active metabolite, may be increased, likely due to inhibition of CYP-mediated metabolism. Consider therapy modification
Temsirolimus: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Temsirolimus. Management: Avoid concomitant use of temsirolimus and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors whenever possible. If combined, decrease temsirolimus dose to 12.5 mg per week and monitor patients for increased temsirolimus effects and toxicities. Consider therapy modification
Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate: Lopinavir may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate. Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate. Monitor therapy
Terfenadine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Terfenadine. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Avoid combination
Tetrahydrocannabinol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tetrahydrocannabinol. Monitor therapy
Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tezacaftor and Ivacaftor. Management: When combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors, tezacaftor/ivacaftor should be administered in the morning, twice a week, approximately 3 to 4 days apart. No evening doses of ivacaftor alone should be administered. Consider therapy modification
Theophylline Derivatives: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Theophylline Derivatives. Exceptions: Dyphylline. Monitor therapy
Thiotepa: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Thiotepa. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Thiotepa. Management: Thiotepa prescribing information recommends avoiding concomitant use of thiotepa and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If concomitant use is unavoidable, monitor for adverse effects and decreased efficacy. Consider therapy modification
Thyroid Products: Ritonavir may diminish the therapeutic effect of Thyroid Products. Monitor therapy
Ticagrelor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Ticagrelor. CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ticagrelor. Avoid combination
Tipranavir: May decrease the serum concentration of Protease Inhibitors. Avoid combination
Tocilizumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tofacitinib. Management: Tofacitinib dose reductions are recommended when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Recommended dose adjustments vary by tofacitinib formulation and therapeutic indication. See full monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Tolterodine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tolterodine. Management: The maximum recommended adult dose of tolterodine is 2 mg/day when used together with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
Tolvaptan: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Tolvaptan. Avoid combination
Topotecan: BCRP/ABCG2 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Topotecan. Avoid combination
Topotecan: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Topotecan. Avoid combination
Toremifene: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Toremifene. Management: Use of toremifene with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors should be avoided if possible. If coadministration is necessary, monitor for increased toremifene toxicities, including QTc interval prolongation. Exceptions are discussed in separate monograph. Consider therapy modification
Trabectedin: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Trabectedin. Avoid combination
TraMADol: Ritonavir may decrease serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of TraMADol. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of TraMADol. Monitor therapy
TraZODone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of TraZODone. Management: Consider the use of a lower trazodone dose and monitor for increased trazodone effects (eg, sedation, QTc prolongation) if combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Triamcinolone (Systemic): Ritonavir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Triamcinolone (Systemic). Specifically, risks of developing iatrogenic Cushing syndrome and secondary adrenal insufficiency may be increased. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Triamcinolone (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Triazolam: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Triazolam. Avoid combination
Tricyclic Antidepressants: Protease Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Ubrogepant: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ubrogepant. Avoid combination
Udenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Udenafil. Avoid combination
Ulipristal: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Ulipristal. Management: This is specific for when ulipristal is being used for signs/symptoms of uterine fibroids (Canadian indication). When ulipristal is used as an emergency contraceptive, patients receiving this combo should be monitored for ulipristal toxicity. Avoid combination
Upadacitinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Upadacitinib. Monitor therapy
Valbenazine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Valbenazine. Management: Reduce the valbenazine dose to 40 mg daily when combined with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Valproate Products: Protease Inhibitors may decrease the serum concentration of Valproate Products. Monitor therapy
Vardenafil: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vardenafil. Management: Recommendations regarding concomitant use of vardenafil with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors may vary depending on brand name (e.g., Levitra, Staxyn) or by international labeling. See full drug interaction monograph for details. Consider therapy modification
Velpatasvir: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Velpatasvir. Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Velpatasvir. Consider therapy modification
Vemurafenib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vemurafenib. Management: Avoid concurrent use of vemurafenib with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors when possible. Consider use of an alternative that is not a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4 as clinically appropriate. Consider therapy modification
Venetoclax: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Venetoclax. Management: This combination is contraindicated during venetoclax initiation and ramp-up in patients with CLL/SLL. Reduced venetoclax doses are required during ramp-up for patients with AML, and reduced doses are required for all patients during maintenance therapy. Consider therapy modification
Venetoclax: P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Venetoclax. Management: Consider a venetoclax dose reduction by at least 50% in patients requiring concomitant treatment with P-glycoprotein (P-gp) inhibitors. Consider therapy modification
Vilanterol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong). Monitor therapy
Vilazodone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vilazodone. Management: Limit maximum adult vilazodone dose to 20 mg daily in patients receiving strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. The original vilazodone dose can be resumed following discontinuation of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Consider therapy modification
VinBLAStine: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of VinBLAStine. Management: Monitor closely for signs and symptoms of vinblastine toxicity; consider temporary interruption of lopinavir/ritonavir antiviral therapy if patients develop significant toxicity with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
VinBLAStine: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of VinBLAStine. Management: Monitor closely for signs and symptoms of vinblastine toxicity; consider temporary interruption of ritonavir antiviral therapy if patients develop significant toxicity with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
VinCRIStine: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine. Management: Monitor closely for signs and symptoms of vincristine toxicity; consider temporary interruption of lopinavir/ritonavir antiviral therapy if patients develop significant toxicity with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
VinCRIStine: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine. Management: Monitor closely for signs and symptoms of vincristine toxicity; consider temporary interruption of ritonavir antiviral therapy if patients develop significant toxicity with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
VinCRIStine (Liposomal): CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine (Liposomal). Avoid combination
VinCRIStine (Liposomal): P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of VinCRIStine (Liposomal). Avoid combination
Vindesine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vindesine. Monitor therapy
Vinflunine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vinflunine. Avoid combination
Vinorelbine: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vinorelbine. Monitor therapy
Vorapaxar: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Vorapaxar. Avoid combination
Voriconazole: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Voriconazole. Management: Concurrent voriconazole and high-dose ritonavir (adult doses of 400 mg every 12 hrs or greater) is contraindicated. Voriconazole with lower-dose ritonavir should be avoided unless benefits outweigh risk of inadequate voriconazole concentrations. Avoid combination
Voriconazole: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Voriconazole. Avoid combination
Voxelotor: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Voxelotor. Management: Avoid concomitant use of voxelotor and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. If concomitant use is unavoidable, reduce the voxelotor dose to 1,000 mg once daily. Consider therapy modification
Voxilaprevir: Lopinavir may increase the serum concentration of Voxilaprevir. Avoid combination
Warfarin: Lopinavir may decrease the serum concentration of Warfarin. Monitor therapy
Warfarin: Ritonavir may decrease the serum concentration of Warfarin. Monitor therapy
Zanubrutinib: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Zanubrutinib. Management: Decrease the zanubrutinib dose to 80 mg once daily during coadministration with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Further dose adjustments may be required for zanubrutinib toxicities, refer to prescribing information for details. Consider therapy modification
Zidovudine: Protease Inhibitors may decrease the serum concentration of Zidovudine. Monitor therapy
Zolpidem: Ritonavir may increase the serum concentration of Zolpidem. Monitor therapy
Zopiclone: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Zopiclone. Management: The initial starting adult dose of zopiclone should not exceed 3.75 mg if combined with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of zopiclone toxicity if these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Zuclopenthixol: CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong) may increase the serum concentration of Zuclopenthixol. Management: Consider zuclopenthixol dosage reduction with concomitant use of a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (eg, ketoconazole) in poor CYP2D6 metabolizers or with strong CYP2D6 inhibitors (eg, paroxetine). Monitor for increased zuclopenthixol levels/toxicity. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
Data presented for short- and long-term combination antiretroviral therapy in both protease inhibitor experienced and naïve patients.
>10%:
Dermatologic: Skin rash (children 12%; adults ≤5%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypercholesterolemia (3% to 39%), increased serum triglycerides (3% to 36%), increased gamma-glutamyl transferase (10% to 29%)
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (7% to 28%; greater with once-daily dosing), dysgeusia (children 22%; adults <2%), vomiting (children 21%; adults 2% to 7%), nausea (5% to 16%), abdominal pain (1% to 11%)
Hepatic: Increased serum ALT (grade 3/4: 1% to 11%)
Respiratory: Upper respiratory tract infection (14%)
>2% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Vasodilation (≤3%)
Central nervous system: Fatigue (8%, including weakness), headache (2% to 6%), anxiety (4%), insomnia (≤4%)
Dermatologic: Skin infection (3%, including cellulitis, folliculitis, furuncle)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypertriglyceridemia (6%), hyperglycemia (≤5%), hyperuricemia (≤5%), alteration in sodium (children 3%), weight loss (≤3%)
Gastrointestinal: Increased serum amylase (3% to 8%), dyspepsia (≤6%), increased serum lipase (3% to 5%), flatulence (1% to 4%), gastroenteritis (3%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Thrombocytopenia (grade 3/4: 4% children), neutropenia (grade 3/4: 1% to 5%)
Hepatic: Increased serum AST (grade 3/4: 2% to 10%), hepatitis (4%, including increased AST, ALT, and gamma-glutamyl transferase), increased serum bilirubin (children 3%; adults 1%)
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity (3%, including urticaria and angioedema)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness (≤9%), musculoskeletal pain (6%)
Respiratory: Lower respiratory tract infection (8%)
≤2%: Abdominal distension, abnormal dreams, abnormality in thinking, acne vulgaris, ageusia, agitation, alopecia, amenorrhea, amnesia, anemia, anorexia, apathy, arthralgia, asthma, ataxia, atherosclerotic disease, atrial fibrillation, atrioventricular block (second and third degree), atrophic striae, back pain, bacterial infection, benign neoplasm, bradycardia, brain disease, breast hypertrophy, bronchitis, cerebral infarction, cerebrovascular accident, change in appetite, chest pain, chills, cholangitis, cholecystitis, confusion, constipation, cough, Cushing's syndrome, cyst, decreased creatinine clearance, decreased glucose tolerance, decreased libido, deep vein thrombosis, dehydration, depression, dermal ulcer, diabetes mellitus, dizziness, drowsiness, duodenitis, dyskinesia, dysphagia, dyspnea, eczema, edema, ejaculatory disorder, emotional lability, enteritis, enterocolitis, erectile dysfunction, eructation, erythema multiforme, esophagitis, exfoliative dermatitis, extrapyramidal reaction, facial edema, facial paralysis, fecal incontinence, fever, first degree atrioventricular block, flu-like symptoms, gastritis, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal ulcer, gynecomastia, hematuria, hemorrhagic colitis, hemorrhoids, hepatic insufficiency, hepatomegaly, hyperacusis, hyperhidrosis, hypermenorrhea, hypersensitivity reaction, hypertension, hypertonia, hypogonadism (males), hypophosphatemia, hypothyroidism, immune reconstitution syndrome, impotence, jaundice, lactic acidosis, leukopenia, lipoma, liver steatosis, liver tenderness, lymphadenopathy, maculopapular rash, malaise, migraine, myalgia, myocardial infarction, neoplasm, nephritis, nervousness, neuropathy, night sweats, obesity, oral mucosa ulcer, orthostatic hypotension, osteonecrosis, otitis media, palpitations, pancreatitis, paresthesia, periodontitis, peripheral edema, peripheral neuropathy, pharyngitis, prolonged Q-T interval on ECG, propylene glycol toxicity (preterm neonates [includes cardiomyopathy, lactic acidosis, acute renal failure, respiratory complications]), pruritus, pulmonary edema, rectal hemorrhage, redistribution of body fat (including facial wasting), renal failure, rhabdomyolysis, rhinitis, seborrhea, seizure, sialadenitis, sinusitis, skin discoloration, splenomegaly, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, stomatitis, thrombophlebitis, tinnitus, torsades de pointes, tremor, tricuspid regurgitation, vasculitis, vertigo, viral infection, visual disturbance, vitamin deficiency, weight gain, xeroderma, xerostomia
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Altered cardiac conduction: May alter cardiac conduction and prolong the QTc and/or PR interval; second and third degree AV block and torsade de pointes have been observed. Use with caution in patients with underlying structural heart disease, preexisting conduction system abnormalities, ischemic heart disease or cardiomyopathies. Avoid use in combination with QTc- or PR-interval prolonging drugs or in patients with hypokalemia or congenital long QT syndrome.
- Cardiovascular concerns: Possible higher risk of myocardial infarction associated with the cumulative use of lopinavir/ritonavir; consider avoiding lopinavir/ritonavir-based regimens in patients with high cardiac risk (Bavinger 2013; HHS [adult] 2016).
- Fat redistribution: May cause redistribution/accumulation of fat (eg, central obesity, buffalo hump, peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, cushingoid appearance).
- Hepatotoxicity: May cause hepatitis and/or exacerbate pre-existing hepatic dysfunction; use with caution in patients with underlying hepatic disease, such as hepatitis B or C, cirrhosis, or unspecified hepatic impairment. Consider more frequent liver function test monitoring during therapy initiation in patients with preexisting hepatic dysfunction.
- Immune reconstitution syndrome: Patients may develop immune reconstitution syndrome resulting in the occurrence of an inflammatory response to an indolent or residual opportunistic infection during initial HIV treatment or activation of autoimmune disorders (eg, Graves’ disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome) later in therapy; further evaluation and treatment may be required.
- Increased cholesterol: Increases in total cholesterol and triglycerides have been reported; screening should be done prior to therapy and periodically throughout treatment.
Disease-related concerns:
- Diabetes: Changes in glucose tolerance, hyperglycemia, exacerbation of diabetes, DKA, and new-onset diabetes mellitus have been reported in patients receiving protease inhibitors. Consider monitoring for these conditions. In some patients who discontinued protease inhibitors, hyperglycemia persisted.
- Hemophilia A or B: Use with caution in patients with hemophilia A or B; increased bleeding during protease inhibitor therapy has been reported.
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution; lopinavir concentrations may be increased.
- Pancreatitis: Use with caution in patients with increased triglycerides; pancreatitis has been observed. Patients with history of pancreatitis or advanced HIV-1 disease may be at increased risk. Monitor for clinical symptoms (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain) and serum lipase and amylase.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Pediatric: Safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetic profiles of lopinavir and ritonavir have not been established for neonates <14 days of age. Neonates <14 days of age, particularly preterm neonates, are at risk for developing propylene glycol toxicity with use of the lopinavir/ritonavir oral solution. Oral solution contains ethanol and propylene glycol; ethanol competitively inhibits propylene glycol metabolism. Postmarketing reports in preterm neonates following use of the oral solution include cardiotoxicity (complete AV block, bradycardia, cardiomyopathy), lactic acidosis, CNS depression, respiratory complications, acute renal failure, and death. The oral solution should not be used in the immediate postnatal period, including full-term neonates age <14 days or preterm neonates until 14 days after their due date, unless the infant is closely monitored and benefits clearly outweigh risk. Once-daily dosing (oral solution or tablets) is not an approved regimen for children <18 years of age.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Oral solution: The oral solution is highly concentrated and contains large amounts of ethanol (42.4%) and propylene glycol (15.3%). Monitor patients with renal impairment or with decreased ability to metabolize propylene glycol (eg, patients of Asian origin) for propylene glycol toxicity (eg, seizures tachycardia, lactic acidosis, hyperosmolarity, stupor, hemolysis). Health care providers should pay special attention to accurate calculation, measurement, and administration of dose. Overdose (or cumulative ethanol or propylene glycol content in medications) in a child may lead to lethal ethanol or propylene glycol toxicity.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Once-daily dosing is not recommended in patients with ≥3 of the following lopinavir-resistance-associated amino acid substitutions in protease (L10F/I/R/V, K20M/N/R, L24I, L33F, M36I, I47V, G48V, I54L/T/V, V82A/C/F/S/T, and I84V); those receiving efavirenz, fosamprenavir, nevirapine, or nelfinavir, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, or in children <18 years of age.
Monitoring Parameters
Prior to therapy, consider genotypic or phenotypic testing for lopinavir resistance-associated substitutions.
Triglycerides and cholesterol (prior to initiation then periodically thereafter), LFTs, electrolytes, basic HIV monitoring, viral load and CD4 count, glucose
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Lopinavir has a low level of transfer across the human placenta; fetal exposure is increased with ritonavir.
Based on information collected by the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry, an increased risk of teratogenic effects has not been observed in humans. Maternal antiretroviral therapy (ART) may be associated with adverse pregnancy outcomes including preterm delivery, stillbirth, low birth weight, and small for gestational age infants. Actual risks may be influenced by maternal factors, such as disease severity, gestational age at initiation of therapy, and specific ART regimen, therefore close fetal monitoring is recommended. However, regimens containing lopinavir/ritonavir may be more closely associated with preterm delivery compared to others. Because there is clear benefit to appropriate treatment, maternal ART should not be withheld due to concerns for adverse neonatal outcomes. Long-term follow-up is recommended for all infants exposed to antiretroviral medications; children without HIV but who were exposed to ART in utero and develop significant organ system abnormalities of unknown etiology (particularly of the CNS or heart) should be evaluated for potential mitochondrial dysfunction. Hyperglycemia, new onset of diabetes mellitus, or diabetic ketoacidosis have been reported with protease inhibitors; it is not clear if pregnancy increases this risk. Consider performing the standard glucose screening test earlier in pregnancy in women who initiated protease inhibitor therapy prior to conception.
The Health and Human Services (HHS) perinatal HIV guidelines consider lopinavir combined with ritonavir an alternative protease inhibitor for pregnant females living with HIV who are antiretroviral-naive (initial therapy), who have had ART therapy in the past but are restarting, who require a new ART regimen (due to poor tolerance or poor virologic response of current regimen), and who are not yet pregnant but are trying to conceive. Females who become pregnant while taking lopinavir combined with ritonavir may continue if viral suppression is effective and the regimen is well tolerated. Pharmacokinetic studies suggest that standard dosing during pregnancy may provide decreased plasma concentrations; dose adjustments are required in women during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Although there is an abundance of data related to the use of lopinavir/ritonavir during pregnancy, the HHS perinatal HIV guidelines consider lopinavir/ritonavir to be an alternative protease inhibitor for initial therapy in antiretroviral-naive pregnant women due to the need for twice daily dosing, the increased incidence of diarrhea and nausea, and an association with preterm delivery. Lopinavir/ritonavir is not recommended for use in pregnant women with lopinavir-associated resistance substitutions. In addition, once-daily dosing is not recommended during pregnancy and use of the oral solution should be avoided (due to alcohol and propylene glycol content).
In general, ART is recommended for all pregnant females living with HIV to keep the viral load below the limit of detection and reduce the risk of perinatal transmission. Therapy should be individualized following a discussion of the potential risks and benefits of treatment during pregnancy. Monitoring of pregnant females is more frequent than in nonpregnant adults. ART should be continued postpartum for all females living with HIV and can be modified after delivery.
Health care providers are encouraged to enroll pregnant females exposed to antiretroviral medications as early in pregnancy as possible in the Antiretroviral Pregnancy Registry (1-800-258-4263 or http://www.APRegistry.com). Health care providers caring for pregnant females living with HIV and their infants may contact the National Perinatal HIV Hotline (888-448-8765) for clinical consultation (HHS [perinatal] 2019).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat HIV infection.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Back pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Joint pain
- Muscle pain
- Headache
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Loss of strength and energy
- Common cold symptoms
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Infection
- Liver problems like dark urine, feeling tired, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin or eyes
- High blood sugar (confusion, feeling sleepy, more thirst, hunger, passing urine more often, flushing, fast breathing, or breath that smells like fruit
- Pancreatitis like severe abdominal pain, severe back pain, severe nausea, or vomiting
- Chest pain
- Fast heartbeat
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Dizziness
- Passing out
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Change in fat
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in mouth, throat, nose, or eyes
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.