Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Solution, Injection:
Robaxin: 1000 mg/10 mL (10 mL) [pyrogen free; contains polyethylene glycol 300]
Generic: 1000 mg/10 mL (10 mL)
Solution, Injection [preservative free]:
Robaxin: 1000 mg/10 mL (10 mL) [contains polyethylene glycol 300]
Generic: 1000 mg/10 mL (10 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Robaxin: 500 mg [scored; contains fd&c yellow #6 (sunset yellow), saccharin sodium]
Robaxin-750: 750 mg [contains fd&c yellow #10 (quinoline yellow), fd&c yellow #6 (sunset yellow), saccharin sodium]
Generic: 500 mg, 750 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Causes skeletal muscle relaxation by general CNS depression
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Hepatic via dealkylation and hydroxylation
Excretion
Urine (primarily as metabolites); Clearance: Adults: 0.2 to 0.8 L/hour/kg
Onset of Action
Muscle relaxation: Oral: ~30 minutes
Time to Peak
Serum: Oral: 1 to 2 hours
Half-Life Elimination
1 to 2 hours
Protein Binding
46% to 50%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Cl is decreased approximately 40% in patients with severe renal impairment.
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
Cl is decreased approximately 70%; t1/2 is prolonged ~3-fold in cirrhosis patients.
Use: Labeled Indications
Adjunctive treatment of muscle spasm associated with acute painful musculoskeletal conditions
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to methocarbamol or any component of the formulation; renal impairment (injection formulation)
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Muscle spasm:
Oral: 1.5 g 4 times/day for 2-3 days (up to 8 g/day may be given in severe conditions), then decrease to 4-4.5 g/day in 3-6 divided doses
IM, IV: Initial: 1 g; may repeat every 8 hours if oral administration not possible; maximum dose: 3 g/day for no more than 3 consecutive days. If condition persists, may repeat course of therapy after a drug-free interval of 48 hours.
Tetanus: IV: Initial dose: 1-2 g by direct IV injection, which may be followed by an additional 1-2 g by infusion (maximum initial dose: 3 g total); may repeat initial dose every 6 hours until NG tube or oral therapy possible; total oral daily dose of up to 24 g may be needed; injection should not be used for more than 3 consecutive days
Dosing: Geriatric
Avoid use (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
Dosing: Pediatric
Muscle spasm: Adolescents ≥16 years: Oral: 1,500 mg 4 times daily for 2 to 3 days; maximum daily dose: 8 g/day (reserved for severe conditions); then decrease dose to 4,000 to 4,500 mg/day in 3 to 6 divided doses (ie, 1,000 mg 4 times daily or 750 mg every 4 hours or 1,500 mg 3 times/day)
Tetanus: Note: Use has generally been replaced by other agents (eg, benzodiazepines) (Hsu 2001): Infants, Children, and Adolescents: IV: 15 mg/kg/dose or 500 mg/m2/dose, may repeat every 6 hours as needed; usual adult dose: 1,000 to 2,000 mg/dose; maximum total dose: 1.8 g/m2 for 3 days; in adults, injection is not recommended for use longer than 3 days
Reconstitution
Solution for injection: May administer undiluted or diluted in D5W or NS (1 vial/≤250 mL diluent).
Administration
Solution for injection:
IM: A maximum of 5 mL can be administered into each gluteal region.
IV: Maximum rate: 3 mL/minute; may be administered undiluted or diluted. Monitor closely for extravasation. Administer IV while in recumbent position. Maintain position for at least 10-15 minutes following infusion.
Tablet: May be crushed and mixed with food or liquid if needed.
Storage
Solution for injection: Prior to dilution, store at controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Tablet: Store at controlled room temperature of 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
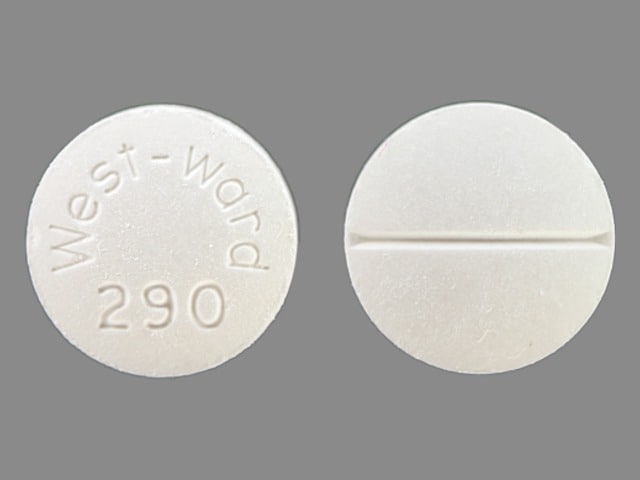
Methocarbamol Images
Drug Interactions
Alcohol (Ethyl): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Alcohol (Ethyl). Monitor therapy
Alizapride: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Azelastine (Nasal): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Azelastine (Nasal). Avoid combination
Blonanserin: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Blonanserin. Consider therapy modification
Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products: Muscle Relaxants (Centrally Acting) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products. Specifically, the risk for increased muscle weakness may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Brexanolone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Brexanolone. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Bromopride: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
Buprenorphine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Buprenorphine. Management: Consider reduced doses of other CNS depressants, and avoiding such drugs in patients at high risk of buprenorphine overuse/self-injection. Initiate buprenorphine at lower doses in patients already receiving CNS depressants. Consider therapy modification
Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cannabis: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Chlormethiazole: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Monitor closely for evidence of excessive CNS depression. The chlormethiazole labeling states that an appropriately reduced dose should be used if such a combination must be used. Consider therapy modification
Chlorphenesin Carbamate: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
CNS Depressants: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Dimethindene (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Doxylamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: The manufacturer of Diclegis (doxylamine/pyridoxine), intended for use in pregnancy, specifically states that use with other CNS depressants is not recommended. Monitor therapy
Dronabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Droperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider dose reductions of droperidol or of other CNS agents (eg, opioids, barbiturates) with concomitant use. Exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Consider therapy modification
Eperisone: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Methocarbamol. Monitor therapy
Esketamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Flunitrazepam: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Flunitrazepam. Consider therapy modification
HYDROcodone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of HYDROcodone. Management: Avoid concomitant use of hydrocodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
HydrOXYzine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Kava Kava: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Lemborexant: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Dosage adjustments of lemborexant and of concomitant CNS depressants may be necessary when administered together because of potentially additive CNS depressant effects. Close monitoring for CNS depressant effects is necessary. Consider therapy modification
Lofexidine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Monitor therapy
Magnesium Sulfate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Methotrimeprazine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Methotrimeprazine. Methotrimeprazine may enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Reduce adult dose of CNS depressant agents by 50% with initiation of concomitant methotrimeprazine therapy. Further CNS depressant dosage adjustments should be initiated only after clinically effective methotrimeprazine dose is established. Consider therapy modification
MetyroSINE: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of MetyroSINE. Monitor therapy
Minocycline (Systemic): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Nabilone: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Opioid Agonists. Management: Avoid concomitant use of opioid agonists and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Orphenadrine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Orphenadrine. Avoid combination
Oxomemazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
OxyCODONE: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of OxyCODONE. Management: Avoid concomitant use of oxycodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Paraldehyde: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Paraldehyde. Avoid combination
Perampanel: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Patients taking perampanel with any other drug that has CNS depressant activities should avoid complex and high-risk activities, particularly those such as driving that require alertness and coordination, until they have experience using the combination. Consider therapy modification
Piribedil: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Piribedil. Monitor therapy
Pramipexole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Pramipexole. Monitor therapy
Pyridostigmine: Methocarbamol may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pyridostigmine. Monitor therapy
ROPINIRole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of ROPINIRole. Monitor therapy
Rotigotine: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Rotigotine. Monitor therapy
Rufinamide: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Specifically, sleepiness and dizziness may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors: CNS Depressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Specifically, the risk of psychomotor impairment may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Sodium Oxybate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider alternatives to combined use. When combined use is needed, consider minimizing doses of one or more drugs. Use of sodium oxybate with alcohol or sedative hypnotics is contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Suvorexant: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Suvorexant. Management: Dose reduction of suvorexant and/or any other CNS depressant may be necessary. Use of suvorexant with alcohol is not recommended, and the use of suvorexant with any other drug to treat insomnia is not recommended. Consider therapy modification
Tapentadol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Avoid concomitant use of tapentadol and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Tetrahydrocannabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Thalidomide: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Thalidomide. Avoid combination
Tolperisone: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Muscle Relaxants (Centrally Acting). Management: Monitor for increased sedation or CNS effects if tolperisone is combined with other centrally acting muscle relaxants. Consider decreasing the tolperisone dose if these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Trimeprazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Zolpidem: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Zolpidem. Management: Reduce the Intermezzo brand sublingual zolpidem adult dose to 1.75 mg for men who are also receiving other CNS depressants. No such dose change is recommended for women. Avoid use with other CNS depressants at bedtime; avoid use with alcohol. Consider therapy modification
Test Interactions
May cause color interference in certain screening tests for 5-HIAA using nitrosonaphthol reagent and in screening tests for urinary VMA using the Gitlow method.
Adverse Reactions
Frequency not defined:
Cardiovascular: Bradycardia, flushing, hypotension, syncope, thrombophlebitis
Central nervous system: Amnesia, ataxia, confusion, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, insomnia, metallic taste, sedation, seizure, vertigo
Dermatologic: Pruritus, skin rash, urticaria
Gastrointestinal: Dyspepsia, nausea, vomiting
Hematologic & oncologic: Leukopenia
Hepatic: Cholestatic jaundice, jaundice
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypersensitivity reaction
Local: Local skin exfoliation (injection), pain at injection site
Ophthalmic: Blurred vision, conjunctivitis, diplopia, nystagmus
Respiratory: Nasal congestion
Miscellaneous: Fever
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- CNS depression: May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks which require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
Disease-related concerns:
- Hepatic impairment: Plasma protein binding and clearance are decreased and the half-life is increased in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Renal impairment: Use of IV formulation is contraindicated.
- Seizure disorder: Use the oral formulation with caution in patients with a history of seizure disorder. Intravenous administration to patients with a seizure disorder is not recommended.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Sedatives: Effects may be potentiated when used with other sedative drugs or ethanol.
Special populations:
- Pediatric: IV formulation: Recommended only for the treatment of tetanus in pediatric patients.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Injection: Contraindicated in renal impairment. Contains polyethylene glycol. Rate of injection should not exceed 3 mL/minute; solution is hypertonic; avoid extravasation.
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor closely for extravasation, bradycardia, hypotension (IV administration).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted. The manufacturer notes that fetal and congenital abnormalities have been reported following in utero exposure (Hall 1982).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to relax muscles.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Flushing
- Trouble sleeping
- Stuffy nose
- Metallic taste
- Injection site pain
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe injection site irritation
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Yellow skin
- Seizures
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Slow heartbeat
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Trouble with memory
- Confusion
- Vision changes
- Involuntary eye movements
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.