Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Solution, Injection, as maleate:
Generic: 0.2 mg/mL (1 mL)
Solution, Injection, as maleate [preservative free]:
Generic: 0.2 mg/mL (1 mL)
Tablet, Oral, as maleate:
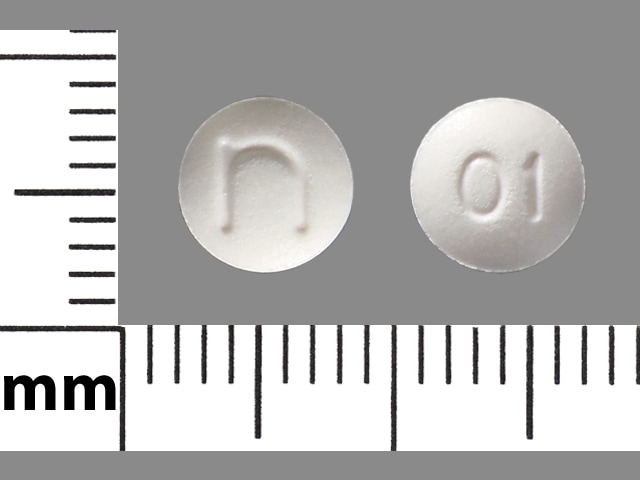
Methergine: 0.2 mg [contains methylparaben, propylparaben]
Generic: 0.2 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Increases the tone, rate and amplitude of contractions on the smooth muscles of the uterus, producing sustained contractions which shortens the third stage of labor and reduces blood loss.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Rapid
Distribution
Vd: 39-73 L
Metabolism
Hepatic
Excretion
Urine and feces
Onset of Action
Oxytocic: Oral: 5-10 minutes; IM: 2-5 minutes; IV: Immediately
Time to Peak
Serum: Oral: 0.3-2 hours; IM: 0.2-0.6 hours
Duration of Action
Oral: ~3 hours; IM: ~3 hours; IV: 45 minutes
Half-Life Elimination
~3 hours (range: 1.5-12.7 hours)
Use: Labeled Indications
Management of uterine atony, hemorrhage and subinvolution of the uterus following delivery of the placenta; control of uterine hemorrhage following delivery of the anterior shoulder in the second stage of labor
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to methylergonovine or any component of the formulation; hypertension; preeclampsia; pregnancy
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Prevention of hemorrhage:
Oral: 0.2 mg 3 to 4 times daily in the puerperium for up to 7 days (maximum duration: 1 week)
IM, IV: 0.2 mg after delivery of anterior shoulder, after delivery of placenta, or during puerperium; may be repeated every 2 to 4 hours as needed. Note: IV administration should only be considered during life-threatening situations.
Administration
IV: Administer slowly over a period of no less than 60 seconds with careful monitoring of blood pressure. Should not be routinely administered IV because of possibility of inducing sudden hypertension and cerebrovascular accident. IV administration should only be considered during life-threatening situations.
IM: May be administered intramuscularly.
Oral: Available in tablets for oral administration.
Storage
Injection: Store under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect from light. The following stability information has also been reported: May be stored at room temperature for up to 14 days (Cohen, 2007).
Tablet: Store below 25°C (77°F).
Methylergonovine Images
Drug Interactions
Alpha-/Beta-Agonists: Ergot Derivatives may enhance the hypertensive effect of Alpha-/Beta-Agonists. Ergot Derivatives may enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Alpha-/Beta-Agonists. Avoid combination
Alpha1-Agonists: Ergot Derivatives may enhance the hypertensive effect of Alpha1-Agonists. Ergot Derivatives may enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Alpha1-Agonists. Avoid combination
Antihepaciviral Combination Products: May increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Aprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Beta-Blockers: May enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Ergot Derivatives. Consider therapy modification
Chloroprocaine: May enhance the hypertensive effect of Ergot Derivatives. Monitor therapy
Clofazimine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Cobicistat: May increase the serum concentration of Methylergonovine. Avoid combination
Conivaptan: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Consider therapy modification
Duvelisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosaprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosnetupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Idelalisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Itraconazole: May increase the serum concentration of Methylergonovine. Avoid combination
Ketoconazole (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of Methylergonovine. Avoid combination
Larotrectinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Letermovir: May increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Lorcaserin: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ergot Derivatives. Specifically, use of these drugs together may increase the risk of developing valvular heart disease. Lorcaserin may enhance the serotonergic effect of Ergot Derivatives. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Macrolide Antibiotics: May increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Cabergoline and Clarithromycin may interact, see specific monograph for full details. Exceptions: Azithromycin (Systemic); Fidaxomicin; Spiramycin. Consider therapy modification
MiFEPRIStone: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Minimize doses of CYP3A4 substrates, and monitor for increased concentrations/toxicity, during and 2 weeks following treatment with mifepristone. Avoid cyclosporine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, fentanyl, pimozide, quinidine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus. Consider therapy modification
Nefazodone: Ergot Derivatives may enhance the serotonergic effect of Nefazodone. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Nefazodone may increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Netupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Nitroglycerin: Ergot Derivatives may diminish the vasodilatory effect of Nitroglycerin. This is of particular concern in patients being treated for angina. Nitroglycerin may increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Palbociclib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Posaconazole: May increase the serum concentration of Methylergonovine. Avoid combination
Protease Inhibitors: May increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Reboxetine: May enhance the hypertensive effect of Ergot Derivatives. Monitor therapy
Roxithromycin: May increase the serum concentration of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Serotonergic Agents (High Risk): Ergot Derivatives may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Nefazodone. Monitor therapy
Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans): Ergot Derivatives may enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans). Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans) may enhance the vasoconstricting effect of Ergot Derivatives. Avoid combination
Simeprevir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Stiripentol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Use of stiripentol with CYP3A4 substrates that are considered to have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided due to the increased risk for adverse effects and toxicity. Any CYP3A4 substrate used with stiripentol requires closer monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Voriconazole: May increase the serum concentration of Methylergonovine. Avoid combination
Adverse Reactions
Frequency not defined.
Cardiovascular: Angina pectoris, atrioventricular block, bradycardia, cerebrovascular accident, chest pain, coronary artery vasospasm, hypertension, hypotension, local thrombophlebitis, myocardial infarction, palpitations, paresthesia, tachycardia, vasospasm, ventricular fibrillation
Central nervous system: Dizziness, hallucination, headache, seizure
Dermatologic: Diaphoresis, skin rash
Endocrine & metabolic: Water intoxication
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, unpleasant taste, vomiting
Genitourinary: Hematuria
Hypersensitivity: Anaphylaxis
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Leg cramps
Otic: Tinnitus
Respiratory: Dyspnea, nasal congestion
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Coronary artery disease: Patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) or risk factors for CAD may be more likely to develop myocardial ischemia and infarction following methylergonovine-induced vasospasm.
- Ergotism: Ergot alkaloid use may result in ergotism (intense vasoconstriction) resulting in peripheral vascular ischemia and possible gangrene. Ergotism is usually associated with overdosage or prolonged chronic use; do not exceed dosing guidelines and avoid prolonged administration.
- Pleural/retroperitoneal fibrosis: Rare cases of pleural and/or retroperitoneal fibrosis have been reported with prolonged daily use of other ergot alkaloids.
Disease-related concerns:
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Labor: Use with caution in the second stage of labor.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment.
- Sepsis: Use with caution in patients with sepsis.
- Vascular disease: Use with caution in patients with obliterative vascular disease.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- CYP3A4 inhibitors: Concomitant use with potent inhibitors of CYP3A4 (includes protease inhibitors, azole antifungals, and some macrolide antibiotics) and ergot alkaloids has been associated with acute ergot toxicity (ergotism); concurrent use of certain ergot alkaloids (eg, ergotamine and dihydroergotamine) are not recommended by the manufacturer.
Other warnings/precautions:
- IV administration: Not for routine IV administration due to risk of inducing sudden hypertensive and cerebrovascular accidents. IV administration should only be considered during life-threatening situations.
- Medication errors: Inadvertent administration to newborns has been reported.
Monitoring Parameters
Blood pressure
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
C
Pregnancy Considerations
Methylergonovine is intended for use after delivery of the anterior shoulder, after delivery of the placenta, or during the puerperium; use is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Methylergonovine is recommended when a supplemental uterotonic agent is needed; due to maternal side effects it is not preferred for initial use (ACOG 183 2017).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to stop or treat bleeding that happens after a birth.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Vomiting
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe cerebrovascular disease like change in strength on one side is greater than the other, trouble speaking or thinking, change in balance, or change in eyesight.
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Severe headache
- Vision changes
- Seizures
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.