Boxed Warning
Women of childbearing potential:
Misoprostol administration to women who are pregnant can cause birth defects, abortion, premature birth, or uterine rupture. Uterine rupture has been reported when misoprostol was administered in pregnant women to induce labor or to induce abortion. The risk of uterine rupture increases with advancing gestational ages and with prior uterine surgery, including cesarean delivery. Misoprostol should not be taken by pregnant women to reduce the risk of ulcers induced by NSAIDs.
Patients must be advised of the abortifacient property and warned not to give the drug to others.
Misoprostol should not be used for reducing the risk of NSAID-induced ulcers in women of childbearing potential unless the patient is at high risk of complications from gastric ulcers associated with use of the NSAID, or is at high risk of developing gastric ulceration. In such patients, misoprostol may be prescribed if the patient has had a negative serum pregnancy test within 2 weeks prior to beginning therapy; is capable of complying with effective contraceptive measures; has received both oral and written warnings of the hazards of misoprostol, the risk of possible contraception failure, and the danger to other women of childbearing potential if the drug is taken by mistake; and will begin misoprostol only on the second or third day of the next normal menstrual period.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral:
Cytotec: 100 mcg
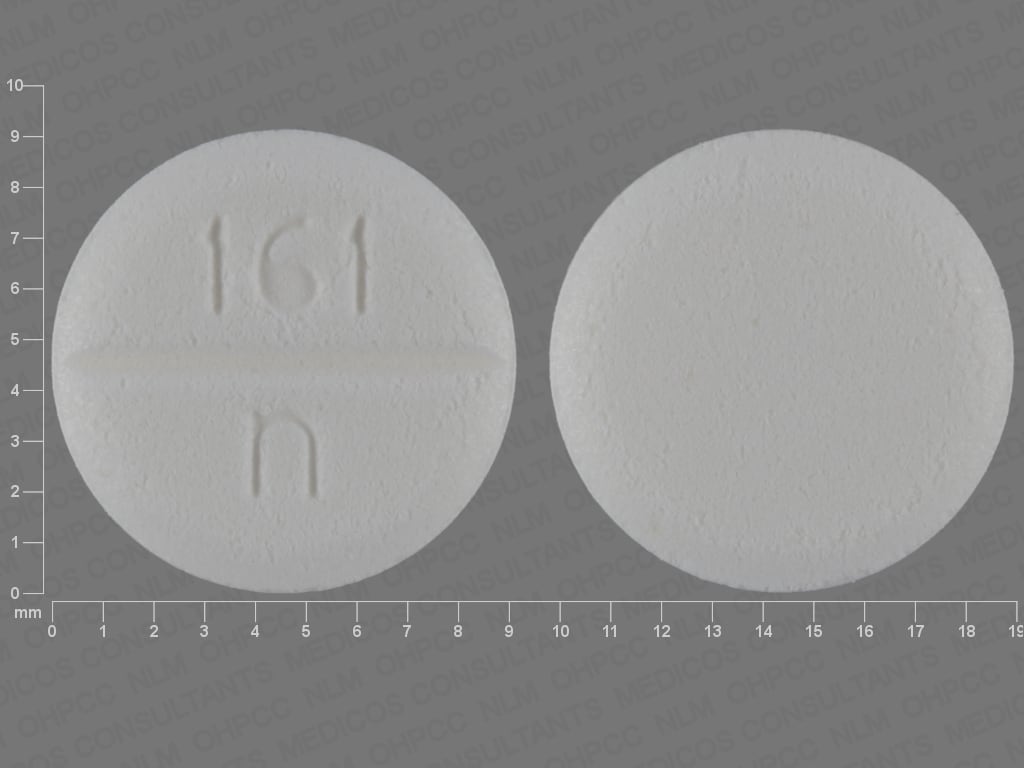
Cytotec: 200 mcg [scored]
Generic: 100 mcg, 200 mcg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Misoprostol is a synthetic prostaglandin E1 analog that replaces the protective prostaglandins consumed with prostaglandin-inhibiting therapies (eg, NSAIDs); has been shown to induce uterine contractions
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Rapid and extensive; food decreases absorption of misoprostol acid
Metabolism
Hepatic; rapid de-esterification to misoprostol acid (active)
Excretion
Urine (80%)
Onset of Action
Inhibition of gastric acid secretion: 30 minutes
Time to Peak
Serum: Misoprostol acid: Fasting: 12 ± 3 minutes
Duration of Action
Inhibition of gastric acid secretion: 3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Misoprostol acid: 20 to 40 minutes
Protein Binding
Misoprostol acid: <90%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Cmax, AUC, and t½ are almost doubled, but no clear correlation between degree of impairment and AUC is shown.
Special Populations: Elderly
AUC is increased in patients >64 years of age.
Use: Labeled Indications
NSAID-induced gastric ulcers, prevention: To reduce the risk of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers in patients at high risk of complications
Termination of intrauterine pregnancy: Medical termination of intrauterine pregnancy through 70 days' gestation in combination with mifepristone (Mifeprex prescribing information March 2016)
Use: Off Label
Cervical ripening and labor inductionyes
Based on the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Practice Bulletin: Induction of Labor, misoprostol tablets administered intravaginally for cervical ripening and labor induction is effective and recommended in the management of this condition ACOG 107 2009.
Early pregnancy lossbyes
Data from a large randomized multicenter study support the use of intravaginal misoprostol in the management of early pregnancy loss (<13 weeks gestation) Zhang 2005.
Based on the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Practice Bulletin for Early Pregnancy Loss, misoprostol given within the first 12 6/7 weeks of gestation is effective and recommended for the medical management of early pregnancy loss. Use may be considered in patients who do not want to undergo surgical evacuation and who do not show signs of an infection, hemorrhage, severe anemia, or bleeding disorders. The addition of mifepristone prior to misoprostol administration may significantly increase efficacy, and this combination should be considered when mifepristone is available ACOG 200 2018.
Incomplete or missed abortion (treatment)yes
Based on the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) Practice Bulletin: Misoprostol for Postabortion Care, misoprostol given for treatment of incomplete or missed abortion in women <12 weeks gestation is effective and recommended in the management of this condition ACOG 427 2009.
Postpartum hemorrhage (prevention/treatment)yes
Based on the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage With Misoprostol guidelines and the FIGO Treatment of Postpartum Hemorrhage With Misoprostol guidelines, misoprostol given for the prevention and treatment of postpartum hemorrhage is effective and recommended in the management of this condition FIGO, 2012a, FIGO, 2012b.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to misoprostol, other prostaglandins, or any component of the formulation; pregnancy
When used for termination of intrauterine pregnancy (additional contraindications): Refer to Mifepristone monograph.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
NSAID-induced gastric ulcers, prevention: Oral: 200 mcg 4 times daily; if not tolerated, may decrease dose to 100 mcg 4 times daily
Termination of intrauterine pregnancy: Oral: Refer to Mifepristone monograph.
Early pregnancy loss (off-label use): Intravaginal (off-label route): Initial dose: 800 mcg. May repeat with one dose if needed, ≥3 hours after the first dose and typically within 7 days if no response to the initial dose is observed. Consider using in combination with oral mifepristone when mifepristone is available (ACOG 200 2018; Schreiber 2018).
Incomplete abortion (treatment) (off-label use): Oral: 600 mcg as a single dose (ACOG 427 2009)
Labor induction or cervical ripening (off-label uses):
Intravaginal (off-label route): 25 mcg (one-fourth of 100 mcg tablet); may repeat at intervals no more frequent than every 3 to 6 hours; 50 mcg every 6 hours may be used in some cases (ACOG 107 2009).
Oral: 25 mcg (one-fourth of 100 mcg tablet) every 2 hours (Tang 2013); 20 mcg doses every 2 hours have also been evaluated (Alfirevic 2014; Kundodyiwa 2009).
Note: The vaginal route may be more efficient; however, some adverse events may occur less frequently when misoprostol is administered orally for this indication (ACOG 107 2009; Alfirevic 2014; Chen 2016; Kundodyiwa 2009). Sublingual and buccal routes should not be used for cervical ripening or induction of labor (ACOG 107 209). Additional data may be necessary to further define the optimal dose and route of administration.
Missed abortion (treatment) (off-label use):
Intravaginal (off-label route): 800 mcg; may repeat every 3 hours for 2 additional doses if needed (ACOG 427 2009)
Sublingual (off-label route): 600 mcg; may repeat every 3 hours for 2 additional doses if needed (ACOG 427 2009)
Postpartum hemorrhage (prevention) (off-label use): Note: Side effects are associated with use and may be dose and route related (Leduc 2009; Ugwu 2016). Additional data may be necessary to further define the optimal dose and route of administration (Bolhmann 2014).
Oral: 600 mcg as a single dose administered immediately after delivery (FIGO 2012a).
Postpartum hemorrhage (treatment) (off-label use): Note: Side effects are associated with use and may be dose and route related (FIGO 2012b; Leduc 2009). Additional data may be necessary to further define the optimal dose and route of administration (Bolhmann 2014).
Oral: 600 to 1,000 mcg as a single dose (ACOG 183 2017).
Rectal (off-label route): 600 to 1,000 mcg as a single dose (ACOG 183 2017).
Sublingual (off-label route): 800 mcg as a single dose. Use caution if a prophylactic dose was already given, especially if adverse events were observed (FIGO 2012b). Dosage ranges of 600 to 1,000 mcg as a single dose have been noted (ACOG 183 2017), however a lower 400 mcg dose has also been recommended (Leduc 2009).
Dosing: Geriatric
NSAID-induced gastric ulcers, prevention: Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
Administer with food and avoid magnesium containing antacids (minimizes diarrhea); last dose of the day should be taken at bedtime. Therapy should continue through the duration of NSAID therapy.
Termination of intrauterine pregnancy: Refer to Mifepristone monograph.
Labor induction or cervical ripening (off-label uses): Because the recommended doses require breaking of the commercially available tablets, some reports recommend weighing the tablet fragments (for oral or vaginal use) or preparing a solution (for oral use) to ensure accurate dosing (Alfirevic 2014; Williams 2002)
Dietary Considerations
When used for the prevention of NSAID-induced ulcers, take with food.
Storage
Store at or below 25°C (77°F).
Misoprostol Images
Drug Interactions
Antacids: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of MiSOPROStol. More specifically, concomitant use with magnesium-containing antacids may increase the risk of diarrhea. Management: Avoid concomitant use of misoprostol and magnesium-containing antacids. In patients requiring antacid therapy, employ magnesium-free preparations. Monitor for increased adverse effects (e.g., diarrhea, dehydration). Exceptions: Aluminum Hydroxide; Calcium Carbonate; Potassium Bicarbonate; Sodium Bicarbonate. Avoid combination
Carbetocin: MiSOPROStol may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Carbetocin. Specifically, Carbetocin oxytocic effects may be enhanced. Avoid combination
Oxytocin: MiSOPROStol may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Oxytocin. Specifically, oxytocic effects may be enhanced. Management: The manufacturer of misoprostol recommends avoiding concomitant use with oxytocin. Misoprostol may augment effects of oxytocin, particularly when given within 4 hours of oxytocin initiation. Consider therapy modification
Phenylbutazone: May enhance the neurotoxic effect of MiSOPROStol. Specifically, the combination may result in headache, dizziness, and transient diplopia. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
>10%: Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, abdominal pain
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Headache
Gastrointestinal: Constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, nausea, vomiting
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormal hepatobiliary function, alopecia, anaphylaxis, anemia, anxiety, arterial thrombosis, arthralgia, back pain, bronchitis, bronchospasm, cardiac arrhythmia, cerebrovascular accident, change in appetite, chest pain, chills, confusion, conjunctivitis, deafness, depression, dermatitis, diaphoresis, dizziness, drowsiness, dysgeusia, dysphagia, dyspnea, dysuria, edema, epistaxis, fatigue, fever, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, GI inflammation, gingivitis, glycosuria, gout, gynecological disease (cramps, dysmenorrhea, hypermenorrhea, spotting, postmenopausal vaginal bleeding, and other menstrual disorders), hematuria, hypertension, hypotension, impotence, increased amylase, increased blood urea nitrogen, increased cardiac enzymes, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, increased serum alkaline phosphatase, increased thirst, loss of libido, mastalgia, muscle cramps, myalgia, myocardial infarction, neuropathy, otalgia, pallor, phlebitis, pneumonia, polyuria, psychoneurosis, pulmonary embolism, purpura, rigors, skin rash, stiffness, syncope, thrombocytopenia, tinnitus, upper respiratory tract infection, urinary tract infection, uterine rupture, visual disturbance, weakness, weight changes
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Abortifacient: [US Boxed Warning]: Due to the abortifacient property of this medication, patients must be warned not to give this drug to others.
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular disease.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; dosage adjustment may be needed.
Special populations:
- Pregnancy: Adverse events have been reported when used outside of current product labeling (cervical ripening, induction of labor, treatment of serious postpartum hemorrhage). Uterine tachysystole may occur and progress to uterine tetany; uteroplacental blood flow may be impaired and uterine rupture or amniotic fluid embolism leading to adverse fetal heart changes may occur. The risk of uterine rupture may be increased with advanced gestational age, grand multiparity, or prior uterine surgery (including cesarean delivery). Uterine activity and fetal status should be monitored in a hospital setting. Misoprostol should not be used in situations where uterotonic drugs are otherwise contraindicated or inappropriate.
- Women of childbearing potential: [US Boxed Warning]: Use of misoprostol during pregnancy may cause birth defects, abortion, premature birth, or uterine rupture. Uterine rupture has been reported when misoprostol was administered in pregnant women to induce labor or to induce abortion. The risk of uterine rupture increases with advancing gestational ages and with prior uterine surgery, including cesarean delivery. Misoprostol is not to be used to reduce the risk of NSAID-induced ulcers in woman of childbearing potential unless she is at risk of complications from gastric ulcers associated with NSAID use, or is at high risk of developing gastric ulceration. In such patients, misoprostol may be prescribed if the patient has had a negative serum pregnancy test within 2 weeks prior to beginning therapy; is capable of complying with effective contraceptive measures; has received both oral and written warnings of the hazards of misoprostol, the risk of possible contraception failure, and the danger to other women of childbearing potential if the drug is taken by mistake; and will begin misoprostol only on the second or third day of the next normal menstrual period. Due to the abortifacient property of this medication, patients must be warned not to give this drug to others.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Termination of pregnancy: Misoprostol is approved for use with mifepristone for termination of pregnancy. Refer to mifepristone warnings, precautions, and contraindications for appropriate use of misoprostol for this indication.
- Appropriate use: Gastric ulcers: For use only in patients at high risk of complications from gastric ulcers (eg, elderly patients, patients with concomitant diseases) or patients at high risk for developing gastric ulcers (eg, those with a history of ulcers) taking NSAIDs. Misoprostol must be taken during the duration of NSAID therapy. It is not effective in preventing duodenal ulcers in patients taking NSAIDs.
Monitoring Parameters
Prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers: Pregnancy test in women of reproductive potential prior to therapy; adequate diagnostic measures in all cases of undiagnosed abnormal vaginal bleeding
Pregnancy-related uses: Uterine activity and fetal status. When used for incomplete or missed abortion, reevaluate 1 to 2 weeks after dosing (ACOG 427 2009). When used for termination of pregnancy: Prior to procedure, confirm pregnancy and Rh status; assess hemoglobin and hematocrit if anemia is suspected (ACOG 143 2014). Following procedure: Clinical exam, human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) testing, and/or ultrasound to confirm complete termination of pregnancy; hemoglobin, hematocrit, and red blood cell count in cases of heavy bleeding. Consider CBC in any patient who reports nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea and weakness with or without abdominal pain, and without fever or other signs of infection more than 24 hours after administration of misoprostol (Mifeprex prescribing information March 2016). When used for medical management of early pregnancy loss, evaluate Rh status; evaluate response to treatment within 7 days after the first dose (ACOG 200 2018).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Use for the prevention of NSAID-induced gastric ulcers is contraindicated in pregnant women.
[US Boxed Warning]: Use of misoprostol during pregnancy may cause birth defects, abortion, premature birth, or uterine rupture. Uterine rupture has been reported when misoprostol was administered in pregnant women to induce labor or to induce abortion. The risk of uterine rupture increases with advancing gestational ages and with prior uterine surgery, including cesarean delivery.
Congenital anomalies following first trimester exposure have been reported, including skull defects, cranial nerve palsies, facial malformations, and limb defects. Misoprostol may produce uterine contractions; fetal death, uterine perforation, and abortion may occur.
Misoprostol is FDA approved for the medical termination of pregnancy of ≤70 days in conjunction with mifepristone.
Because misoprostol may induce or augment uterine contractions, it has been used off-label as a cervical-ripening agent for induction of labor. Misoprostol should not be used for this purpose during the third trimester in conditions where a spontaneous labor and vaginal delivery would be contraindicated, including women who have had a prior cesarean delivery or major uterine surgery (because the risk of uterine rupture is increased) (ACOG 107 2009; ACOG 205 2019). It has also been used for the treatment of incomplete or missed abortion (ACOG 427 2009), early pregnancy loss (ACOG 200 2018), or severe postpartum hemorrhage (ACOG 183 2017; FIGO 2012a; FIGO 2012b). Some guidelines recommend misoprostol for postpartum hemorrhage only secondary to oxytocin in situations where oxytocin is not available (Leduc 2000; FIGO 2012a; FIGO 2012b). Various routes of administration have been used for postpartum hemorrhage. Sublingual administration has the most rapid onset, the oral route produces the most pronounced initial increase in tonus, and rectal and vaginal routes exhibit longer durations of action as compared to oral and sublingual routes (Leduc 2009). Adverse events associated with off-label obstetric uses include uterine tachysystole (may impair placental blood flow), uterine rupture, amniotic fluid embolism, or adverse fetal heart changes. Chills, fever, and/or shivering are commonly associated with use of sublingual misoprostol when used for postpartum hemorrhage; incidence of side effects may be dose related (FIGO 2012b).
[US Boxed Warning]: Misoprostol is not to be used to reduce the risk of NSAID-induced ulcers in woman of childbearing potential unless she is at risk of complications from gastric ulcers associated with NSAID use, or is at high risk of developing gastric ulceration. In such patients, misoprostol may be prescribed if the patient has had a negative serum pregnancy test within 2 weeks prior to beginning therapy; is capable of complying with effective contraceptive measures; has received both oral and written warnings of the hazards of misoprostol, the risk of possible contraception failure, and the danger to other women of childbearing potential if the drug is taken by mistake; and will begin misoprostol only on the second or third day of the next normal menstrual period. Due to the abortifacient property of this medication, patients must be warned not to give this drug to others.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to prevent NSAID-associated gastric ulcers in patients with a history of ulcers.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Severe diarrhea
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.