Boxed Warning
Inadvertent intravenous administration:
Do not administer nimodipine intravenously (IV) or by other parenteral routes. Deaths and serious, life-threatening adverse reactions have occurred when the contents of nimodipine capsules have been injected parenterally.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Capsule, Oral:
Generic: 30 mg
Solution, Oral:
Nymalize: 30 mg/10 mL (10 mL); 60 mg/20 mL (20 mL, 473 mL) [contains alcohol, usp, methylparaben, polyethylene glycol]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Nimodipine shares the pharmacology of other calcium channel blockers; animal studies indicate that nimodipine has a greater effect on cerebral arterials than other arterials; this increased specificity may be due to the drug's increased lipophilicity and cerebral distribution as compared to nifedipine; inhibits calcium ion from entering the “slow channels” or select voltage sensitive areas of vascular smooth muscle and myocardium during depolarization
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Extensively hepatic via CYP3A4; undergoes first-pass metabolism
Excretion
Urine (<1% as unchanged drug); feces
Time to Peak
Serum: ~1 hour
Half-Life Elimination
1 to 2 hours; prolonged with renal impairment
Protein Binding
>95%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
In patients with cirrhosis, bioavailability is increased and Cmax almost doubles; dosage adjustment is recommended.
Special Populations: Elderly
AUC and Cmax were ~2-fold higher in elderly patients compared with younger patients; this response is not considered clinically significant.
Use: Labeled Indications
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: For the improvement of neurological outcome by reducing the incidence and severity of ischemic deficits in adult patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) from ruptured intracranial berry aneurysms regardless of their postictus neurological condition (ie, Hunt and Hess grades I to V)
Contraindications
US labeling:
Concomitant use with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (eg, clarithromycin, telithromycin, delavirdine, indinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, ketoconazole, itraconazole, voriconazole, and nefazodone).
Nymalize: There are no contraindications listed in the manufacturer’s labeling.
Canadian labeling: Hypersensitivity to nimodipine or any component of the formulation; concomitant use with phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, or rifampin
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Note: For oral administration ONLY.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Oral: 60 mg every 4 hours for 21 consecutive days. Note: Start therapy within 96 hours of the onset of subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
For enteral administration ONLY. Life-threatening adverse events have occurred when administered parenterally. Administer on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
Oral:
US labeling: Administer on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals.
Canadian labeling: Administer without regards to meals; but administer consistently with or without meals. Tablet should be swallowed whole with an adequate amount of fluid (eg, glass of water). Do not crush tablet. Avoid alkaline mixtures for 2 hours before or after administration. Patient should not be lying down during administration.
Nasogastric (NG) or gastric tube administration:
Oral solution (Nymalize): Administer using the supplied oral syringe labeled "ORAL USE ONLY". Following administration, refill the oral syringe with 20 mL of NS and flush any remaining contents from NG or gastric tube into the stomach.
Capsules: If the capsules cannot be swallowed, the liquid may be removed by making a hole in each end of the capsule with an 18-gauge needle and extracting the contents into a syringe; transfer these contents into an oral syringe (amber-colored oral syringe preferred). It is strongly recommended that preparation be done in the pharmacy. Label oral syringe with "WARNING: For ORAL use only” or “Not for IV use.” Follow with a flush of 30 mL NS.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Protect capsules from light and freezing. Protect solution from light and do not refrigerate.
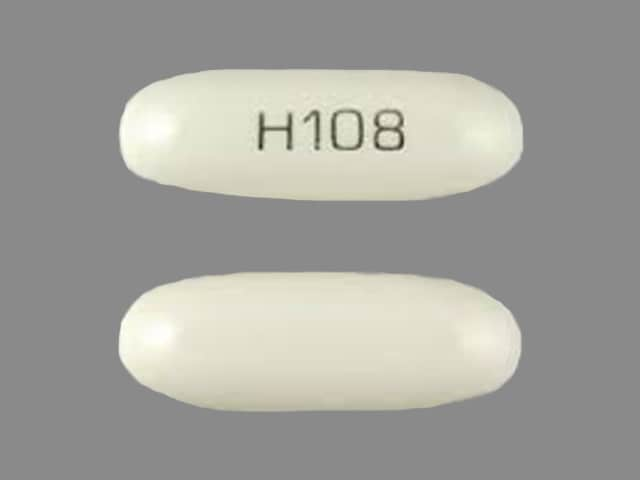
NiMODipine Images
Drug Interactions
Alfuzosin: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Alpha1-Blockers: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Amifostine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Amifostine. Management: When amifostine is used at chemotherapy doses, blood pressure lowering medications should be withheld for 24 hours prior to amifostine administration. If blood pressure lowering therapy cannot be withheld, amifostine should not be administered. Consider therapy modification
Amphetamines: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]): Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]). Monitor therapy
Aprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Atosiban: Calcium Channel Blockers may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Atosiban. Specifically, there may be an increased risk for pulmonary edema and/or dyspnea. Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May increase the metabolism of Calcium Channel Blockers. Management: Monitor for decreased therapeutic effects of calcium channel blockers with concomitant barbiturate therapy. Calcium channel blocker dose adjustments may be necessary. Nimodipine Canadian labeling contraindicates concomitant use with phenobarbital. Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Benperidol: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Bosentan: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Brigatinib: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Brigatinib may enhance the bradycardic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Bromperidol. Bromperidol may diminish the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Avoid combination
Calcium Channel Blockers (Nondihydropyridine): Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine) may enhance the hypotensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers (Nondihydropyridine). Calcium Channel Blockers (Nondihydropyridine) may increase the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine). Monitor therapy
Calcium Salts: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Cimetidine: May increase the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers. Management: Consider alternatives to cimetidine. If no suitable alternative exists, monitor for increased effects of calcium channel blockers following cimetidine initiation/dose increase, and decreased effects following cimetidine discontinuation/dose decrease. Consider therapy modification
Cladribine: Inhibitors of Equilibrative Nucleoside (ENT1) and Concentrative Nucleoside (CNT3) Transport Proteins may increase the serum concentration of Cladribine. Management: Avoid concomitant use of ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitors during the 4 to 5 day oral cladribine treatment cycles whenever possible. If combined, consider an ENT1 or CNT3 inhibitor dose reduction and separation in the timing of administration. Consider therapy modification
Clofazimine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Clopidogrel: Calcium Channel Blockers may diminish the therapeutic effect of Clopidogrel. Monitor therapy
Conivaptan: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
CycloSPORINE (Systemic): Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine) may increase the serum concentration of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). CycloSPORINE (Systemic) may increase the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Moderate): May decrease the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May decrease the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inducers (Weak): May decrease the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate): May increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Weak): May increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Monitor therapy
Dabrafenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Seek alternatives to the CYP3A4 substrate when possible. If concomitant therapy cannot be avoided, monitor clinical effects of the substrate closely (particularly therapeutic effects). Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Deferasirox: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Dexmethylphenidate: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Diazoxide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
DULoxetine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of DULoxetine. Monitor therapy
Duvelisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Efavirenz: May decrease the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fluconazole: May increase the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
FLUoxetine: May increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Monitor therapy
Fosaprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosnetupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Grapefruit Juice: May increase the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
Herbs (Hypertensive Properties): May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Herbs (Hypotensive Properties): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Hypotension-Associated Agents: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Hypotension-Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Idelalisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Ivosidenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Larotrectinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Levodopa-Containing Products: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Levodopa-Containing Products. Monitor therapy
Lorlatinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Avoid concurrent use of lorlatinib with any CYP3A4 substrates for which a minimal decrease in serum concentrations of the CYP3A4 substrate could lead to therapeutic failure and serious clinical consequences. Consider therapy modification
Lormetazepam: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Macrolide Antibiotics: May decrease the metabolism of Calcium Channel Blockers. Management: Consider using a noninteracting macrolide. Felodipine Canadian labeling specifically recommends avoiding its use in combination with clarithromycin. Exceptions: Azithromycin (Systemic); Fidaxomicin; Roxithromycin; Spiramycin. Consider therapy modification
Magnesium Salts: Calcium Channel Blockers may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Magnesium Salts. Magnesium Salts may enhance the hypotensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Melatonin: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine). Monitor therapy
Methylphenidate: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Molsidomine: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Naftopidil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Netupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Neuromuscular-Blocking Agents (Nondepolarizing): Calcium Channel Blockers may enhance the neuromuscular-blocking effect of Neuromuscular-Blocking Agents (Nondepolarizing). Monitor therapy
Nicergoline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nicorandil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nitroprusside: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Nitroprusside. Monitor therapy
Obinutuzumab: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Management: Consider temporarily withholding blood pressure lowering medications beginning 12 hours prior to obinutuzumab infusion and continuing until 1 hour after the end of the infusion. Consider therapy modification
Palbociclib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Pentoxifylline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Pholcodine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Pholcodine. Monitor therapy
Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Prostacyclin Analogues: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Quinagolide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
QuiNIDine: Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine) may decrease the serum concentration of QuiNIDine. Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine) may increase the serum concentration of QuiNIDine. QuiNIDine may increase the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine). Monitor therapy
Rifamycin Derivatives: May decrease the serum concentration of Calcium Channel Blockers. This primarily affects oral forms of calcium channel blockers. Management: The labeling for some US and Canadian calcium channel blockers contraindicate use with rifampin, however recommendations vary. Consult appropriate labeling. Consider therapy modification
Sarilumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Siltuximab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Simeprevir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Sincalide: Drugs that Affect Gallbladder Function may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sincalide. Management: Consider discontinuing drugs that may affect gallbladder motility prior to the use of sincalide to stimulate gallbladder contraction. Consider therapy modification
St John's Wort: May decrease the serum concentration of NiMODipine. Avoid combination
Stiripentol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Use of stiripentol with CYP3A4 substrates that are considered to have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided due to the increased risk for adverse effects and toxicity. Any CYP3A4 substrate used with stiripentol requires closer monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Tacrolimus (Systemic): Calcium Channel Blockers (Dihydropyridine) may increase the serum concentration of Tacrolimus (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Tocilizumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Yohimbine: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
May lead to false-negative aldosterone/renin ratio (ARR) (Funder 2016)
Adverse Reactions
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Decreased blood pressure (4% to 5%), bradycardia (1%)
Central nervous system: Headache (1%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (1%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Anemia, decreased platelet count, diaphoresis, disseminated intravascular coagulation, dizziness, edema, flushing, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal pseudo-obstruction, hematoma, hepatitis, hypertension, increased lactate dehydrogenase, increased serum alkaline phosphatase, increased serum ALT, increased serum glucose, intestinal obstruction, jaundice, muscle cramps, palpitations, pruritus, rebound vasospasm, thrombocytopenia, vomiting, wheezing
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Angina/MI: Increased angina and/or MI have occurred with initiation or dosage titration of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers. Reflex tachycardia may occur resulting in angina and/or MI in patients with obstructive coronary disease, especially in the absence of concurrent beta-blockade.
- Gastrointestinal events: Intestinal pseudo-obstruction and ileus have been reported (rarely) during therapy.
- Hypotension/syncope: Symptomatic hypotension with or without syncope can occur; blood pressure must be lowered at a rate appropriate for the patient's clinical condition. Monitor blood pressure closely during treatment.
- Peripheral edema: Peripheral edema is a common adverse event; occurs within 2-3 weeks of starting therapy.
Disease-related concerns:
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with cirrhosis due to the increased plasma concentrations of nimodipine and an increased risk of adverse reactions; a lower dose and close monitoring of blood pressure and heart rate are required.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction: Use with caution in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with outflow tract obstruction.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Inadvertent IV administration: [US Boxed Warning]: Nimodipine has inadvertently been administered IV when withdrawn from capsules into a syringe for subsequent nasogastric administration. Severe cardiovascular adverse events, including fatalities, have resulted; precautions (eg, adequate labeling, use of oral syringes) should be employed against such an event.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Nimodipine crosses the placenta (Belfort 1994).
Nimodipine has been evaluated for the management of preeclampsia (Belfort 1994; Belfort 2003), but it is not one of the agents currently recommended for severe intrapartum or postpartum hypertension associated with preeclampsia or eclampsia (ACOG 767 2019).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to help lower bad effects caused by bleeding in the brain.
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Slow heartbeat
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive weight gain
- Swelling of arms or legs
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.