Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Gel, Transdermal:
Gelnique: 3% (92 g [DSC]) [contains propylene glycol]
Gel, Transdermal, as chloride:
Gelnique: 10% (1 g) [contains alcohol, usp]
Gelnique Pump: 10% (30 g [DSC])
Patch Twice Weekly, Transdermal:
Oxytrol: 3.9 mg/24 hr (1 ea, 8 ea)
Oxytrol For Women: 3.9 mg/24 hr (1 ea, 4 ea [DSC], 8 ea)
Syrup, Oral, as chloride:
Generic: 5 mg/5 mL (473 mL)
Tablet, Oral, as chloride:
Generic: 5 mg
Tablet Extended Release 24 Hour, Oral, as chloride:
Ditropan XL: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg [DSC] [contains polysorbate 80]
Generic: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Direct antispasmodic effect on smooth muscle, also inhibits the action of acetylcholine on smooth muscle (exhibits 1/5 the anticholinergic activity of atropine, but has 4-10 times the antispasmodic activity); does not block effects at skeletal muscle or at autonomic ganglia; increases bladder capacity, decreases uninhibited contractions, and delays desire to void, therefore, decreases urgency and frequency
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Oral: Rapid and well absorbed; Transdermal: High
Distribution
IV: Vd: 193 L
Metabolism
Hepatic via CYP3A4; Oral: High first-pass metabolism; forms active and inactive metabolites
Excretion
Urine (<0.1% as metabolites and unchanged drug)
Onset of Action
Oral: Immediate release: 30 to 60 minutes; Peak effect: 3 to 6 hours; Extended release: Peak effect: 3 days
Time to Peak
Serum: Oral: Immediate release: ~60 minutes; Extended release: 4 to 6 hours; Transdermal: 24 to 48 hours
Duration of Action
Oral: Immediate release: 6 to 10 hours; Extended release: Up to 24 hours; Transdermal 96 hours
Half-Life Elimination
IV: ~2 hours (parent drug), 7 to 8 hours (metabolites); Oral: Immediate release: ~2 to 3 hours; Extended release: ~13 hours; Transdermal: 64 hours
Protein Binding
>99% primarily to alpha-1 acid glycoprotein
Use: Labeled Indications
Overactive bladder: Treatment of symptoms associated with overactive bladder (eg, urge urinary incontinence, urgency, frequency, urinary leakage, dysuria); treatment of symptoms associated with overactive bladder due to a neurological condition (eg, spina bifida) in patients ≥6 years of age (extended-release tablet only).
Use: Off Label
Primary focal hyperhidrosisc
Data from randomized, placebo-controlled trials with limited numbers of patients and of short duration suggest that oxybutynin may be beneficial for treatment of primary hyperhidrosis Schollhammer 2015, Wolosker 2012.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to oxybutynin or any component of the formulation; patients with or at risk for uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma, urinary retention, gastric retention or conditions with severely decreased GI motility.
OTC labeling: When used for self-medication, do not use if you have pain or burning when urinating, blood in urine, unexplained lower back or side pain, cloudy or foul-smelling urine; in males; age <18 years; only experience accidental urine loss when cough, sneeze, or laugh; diagnosis of urinary or gastric retention; glaucoma; hypersensitivity to oxybutynin.
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling): Severe GI conditions; myasthenia gravis.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Overactive bladder (urinary urgency with or without incontinence): Note: Consider use after inadequate response to or in conjunction with nonpharmacologic measures (AUA/SUFU [Gormley 2015]). Full benefit may not be observed until after several weeks of treatment; a trial of ≥4 to 12 weeks, including the titration period if needed to optimize dose, is suggested before considering other options (Lukacz 2019); antimuscarinic agents are not recommended in patients with stress type incontinence (ACP [Qaseem 2014]).
Oral:
Extended release: Note: Extended-release formulations are (or may be) preferred due to improved tolerability (AUA/SUFU [Gormley 2015]; D’Souza 2008).
Initial: 5 to 10 mg once daily; adjust dose as needed and tolerated in 5 mg increments every 1 to ≥2 weeks (Lukacz 2019). Maximum: 30 mg once daily.
Immediate release: 5 mg 2 to 3 times daily; adjust dose as needed and tolerated in 5 mg increments every 1 to ≥2 weeks (Lukacz 2019). In patients with overactive bladder associated with neurodegenerative diseases, may consider initiation at 2.5 mg 2 to 3 times daily (Factor 2019; Olek 2019). Maximum: 5 mg 4 times daily.
Note: In patients with nocturia, some experts suggest a single daily dose of 2.5 to 5 mg at bedtime may be sufficient (Johnson 2019).
Topical gel: Apply contents of 1 sachet (100 mg/g) or 1 actuation of the pump (100 mg/g) once daily.
Transdermal: Apply one 3.9 mg/day patch twice weekly (every 3 to 4 days); change the patch on the same 2 days each week.
OTC labeling (patient-guided therapy): Females: Apply one 3.9 mg/day patch every 4 days.
Primary focal hyperhidrosis (alternative agent) (off-label use): Oral:
Extended release: 5 to 10 mg once daily (Smith 2019).
Immediate release: Initial: 2.5 mg once daily; gradually titrate as needed and tolerated; usual effective dose range: 5 to 10 mg/day in 2 divided doses (Schollhammer 2015; Smith 2019; Wolosker 2012).
Dosing: Geriatric
Oral: Immediate release: Initial: 2.5 mg 2 to 3 times daily; increase cautiously.
Extended-release tablets, topical gel, transdermal patch: Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Neurogenic/Overactive bladder:
Oral:
Immediate release:
Infants and Children ≤5 years: Limited data available: 0.1 to 0.2 mg/kg/dose 2 to 3 times daily; maximum dose: 5 mg/dose (Buyse 1998a; Buyse 1998b; Ferrara 2001; Kleigman 2016); one retrospective study reported doses as high 0.2 mg/kg/dose every 6 hours (Kaefer 1999)
Children >5 years and Adolescents: Initial: 5 mg twice daily, increase as necessary up to 5 mg 3 times daily; adult maximum dose: 5 mg 4 times daily
Extended release: Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: Initial: 5 mg once daily; adjust dose as needed in 5 mg increments at weekly intervals; maximum daily dose: 20 mg/day
Intravesical: Limited data available: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: 0.2 mg/kg/dose twice daily at 8 to 12 hour intervals; maximum dose: 5 mg/dose (Amark 1998; Buyse 1998a; Buyse 1998b; Ferrara 2001)
Overactive bladder, idiopathic: Limited data available: Transdermal: Children ≥4 years and Adolescents: Apply one 3.9 mg/day patch twice weekly (every 3 to 4 days); dosing based on a retrospective study of 35 children (mean age: 8 years; range: 4 to 16 years) with idiopathic overactive bladder; most patients (97%) reported good symptom control; skin irritation at the application site was reported in 35% of patients with 20% resulting in discontinuation of therapy; no other significant side effects were reported (Gleason 2014)
Administration
Oral: Extended release tablets: Administer without regard to meals. Must be swallowed whole with liquid; do not crush, divide, or chew; take at approximately the same time each day.
Topical gel: For topical use only. Apply to clean, dry, intact skin on abdomen, thighs, or upper arms/shoulders. Rotate application sites; do not apply to the same site on consecutive days. Wash hands after use. Cover treated area with clothing after gel has dried to prevent transfer of medication to others. Do not bathe, shower, or swim until 1 hour after gel applied. Do not apply to recently shaved skin.
Pump: Prior to initial use, prime pump several times (≥ 4 times) until gel begins to come out; after gel is observed, fully depress the pump one more time and discard gel dispensed from pump during priming. One full depression of the pump provides one dose; discard after 30 doses.
Transdermal: Apply to clean, dry, smooth (fold-free) skin on abdomen, hip, or buttock; do not apply to areas treated with oils, lotions, or powders. Do not apply to areas with cuts, scrapes, or other irritation (ie, rashes). Do not cut the patch. Apply each system at a new site (avoid reapplication to same site within 7 days). Contact with water while bathing, swimming, showering, or exercising will not change the effect; however, rubbing of the patch area should be avoided during these activities. Patch should be worn under clothing; do not expose to sunlight.
Dietary Considerations
Food causes a slight delay in the absorption of the oral solution and bioavailability is increased by ~25%. Absorption of the extended release tablet is not affected by food. May be taken without regard to meals.
Storage
Immediate release tablet and syrup: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from light.
Extended release tablet: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Protect from moisture and humidity.
Topical gel: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°C to 77°F). Protect from moisture and humidity. Keep away from open flame. Do not store outside the sealed pouch or pump dispenser; apply immediately after removal from the protective pouch or once contents expelled from pump dispenser. Discard used sachets such that accidental application or ingestion by children, pets, or others are avoided.
Transdermal patch: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from moisture and humidity. Do not store outside the sealed pouch; apply immediately after removal from the protective pouch. Discard used patches such that accidental application or ingestion by children, pets, or others is avoided.
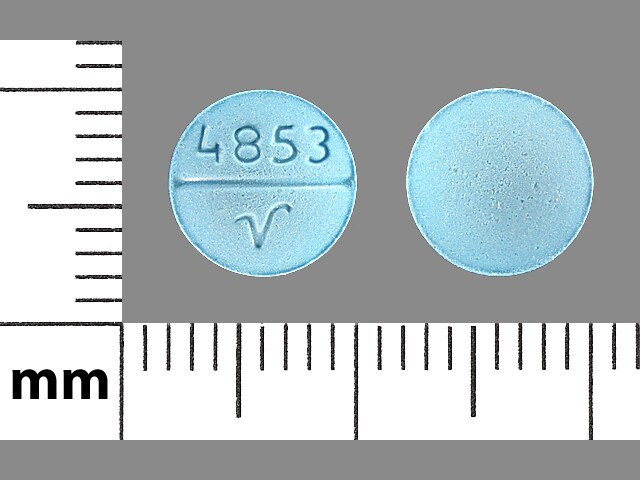
Oxybutynin Images
Drug Interactions
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Aclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Alcohol (Ethyl): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of Oxybutynin. Monitor therapy
Amantadine: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Anticholinergic Agents: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Cannabinoid-Containing Products: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the tachycardic effect of Cannabinoid-Containing Products. Exceptions: Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Chloral Betaine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Cimetropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Cimetropium. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May increase the serum concentration of Oxybutynin. Monitor therapy
Eluxadoline: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Eluxadoline. Avoid combination
Erythromycin (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of Oxybutynin. Monitor therapy
Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic): Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
Glucagon: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Glucagon. Specifically, the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects may be increased. Monitor therapy
Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation): Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation). Avoid combination
Glycopyrronium (Topical): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Ipratropium (Oral Inhalation): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Itopride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Itopride. Monitor therapy
Levosulpiride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Levosulpiride. Avoid combination
Mianserin: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Mirabegron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Mirabegron. Monitor therapy
Nitroglycerin: Anticholinergic Agents may decrease the absorption of Nitroglycerin. Specifically, anticholinergic agents may decrease the dissolution of sublingual nitroglycerin tablets, possibly impairing or slowing nitroglycerin absorption. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Opioid Agonists. Specifically, the risk for constipation and urinary retention may be increased with this combination. Monitor therapy
Oxatomide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Potassium Chloride: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Chloride. Management: Patients on drugs with substantial anticholinergic effects should avoid using any solid oral dosage form of potassium chloride. Avoid combination
Potassium Citrate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Citrate. Avoid combination
Pramlintide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. These effects are specific to the GI tract. Consider therapy modification
Ramosetron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Ramosetron. Monitor therapy
Revefenacin: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
Secretin: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Secretin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of anticholinergic agents and secretin. Discontinue anticholinergic agents at least 5 half-lives prior to administration of secretin. Consider therapy modification
Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics: Anticholinergic Agents may increase the serum concentration of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Tiotropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Tiotropium. Avoid combination
Topiramate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Topiramate. Monitor therapy
Umeclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Test Interactions
May suppress the wheal and flare reactions to skin test antigens.
Adverse Reactions
As reported with oral administration, unless otherwise noted.
>10%:
Central nervous system: Dizziness (oral: 5% to 17%; topical gel: 3%), drowsiness (6% to 14%)
Gastrointestinal: Xerostomia (oral: 35% to 72%; topical gel, transdermal: 4% to 10%), constipation (oral: 9% to 15%; transdermal: 3%; topical gel: 1%), nausea (5% to 12%)
Local: Application site pruritus (transdermal: 14% to 17%; topical gel: 2%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Decreased blood pressure (1% to <5%), edema (1% to <5%), flushing (1% to <5%), increased blood pressure (1% to <5%), palpitations (1% to <5%), peripheral edema (1% to <5%), sinus arrhythmia (1% to <5%)
Central nervous system: Headache (oral: 8%; topical gel: 2%), nervousness (7%), insomnia (3% to 6%), confusion (1% to <5%), falling (1% to <5%), flank pain (1% to <5%), pain (1% to <5%), fatigue (oral, topical gel: 2% to 3%)
Dermatologic: Macular eruption (transdermal: 3%; application site), xeroderma (2% to 3%), pruritus (oral, topical gel: 1% to 2%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Fluid retention (<5%), increased thirst (<5%), increased serum glucose (1% to <5%)
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (3% to 8%), dyspepsia (5% to 6%), coated tongue (1% to <5%), eructation (1% to <5%), upper abdominal pain (1% to <5%), flatulence (1% to 3%), abdominal pain (2%), dysgeusia (2%), viral gastroenteritis (topical gel: 2%), vomiting (1% to 2%), gastroesophageal reflux disease (≤1%)
Genitourinary: Urinary hesitancy (2% to 9%), urinary tract infection (oral, topical gel: 7%), urinary retention (1% to 6%), cystitis (1% to <5%), pollakiuria (1% to <5%), increased post-void residual urine volume (2% to 4%), dysuria (oral, transdermal: 2%)
Infection: Fungal infection (1% to <5%)
Local: Application site erythema (transdermal: 6% to 8%), application site reaction (topical gel: 5%), application site rash (transdermal: 3%), application site vesicles (transdermal: 3%), application site dermatitis (topical gel: 2%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia (1% to <5%), back pain (1% to <5%), limb pain (1% to <5%), asthenia (1% to <5%)
Ophthalmic: Blurred vision (4% to 10%), eye irritation (1% to <5%), keratoconjunctivitis sicca (1% to <5%), visual disturbance (transdermal: 3%), xerophthalmia (3%)
Respiratory: Dry nose (2% to 5%), upper respiratory tract infection (oral, topical gel: 1% to 5%), asthma (1% to <5%), bronchitis (1% to <5%), hoarseness (1% to <5%), nasal congestion (1% to <5%), nasopharyngitis (oral, topical gel: 1% to <5%), paranasal sinus congestion (1% to <5%), pharyngolaryngeal pain (1% to <5%), sinus headache (1% to <5%), cough (2% to 3%), dry throat (2% to 3%), oropharyngeal pain (2%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormal behavior, agitation, anaphylaxis, angioedema, anorexia, cardiac arrhythmia, chest discomfort, confusion, cycloplegia, decreased gastrointestinal motility, delirium, dizziness, drowsiness, dysphagia, facial edema, frequent bowel movements, glaucoma, hallucination, headache, hot flash, hypersensitivity reaction, hypertension, hypohidrosis, impotence, lactation insufficiency, memory impairment, mydriasis, prolonged Q-T interval on ECG, psychotic reaction, seizure, skin rash, tachycardia, urticaria, voice disorder
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Angioedema/hypersensitivity reactions: May cause hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis and angioedema. Cases of angioedema involving the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx have been reported with oral oxybutynin; some cases have occurred after a single dose. Discontinue immediately if tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx is involved; promptly initiate appropriate management.
- CNS effects: Anticholinergics may cause agitation, confusion, drowsiness, dizziness, hallucinations, headache, somnolence, and/or blurred vision, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks which require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving). Dose reduction or discontinuation should be considered if CNS effects occur.
- Heat prostration: May increase the risk of heat prostration.
Disease-related concerns:
- Bladder flow obstruction: Use with caution in patients with bladder flow obstruction; may increase the risk of urinary retention.
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with CAD, heart failure, hypertension, and/or cardiac arrhythmias; may exacerbate condition.
- Dementia: Use with caution in patients with dementia treated with cholinesterase inhibitors; may aggravate symptoms of disease.
- GI disorders: Use with caution in patients with decreased GI motility or GI obstructive disorders; may increase the risk of gastric retention. Use with caution in patients with ulcerative colitis, intestinal atony, pyloric stenosis, gastroesophageal reflux, or with medications that may cause or exacerbate esophagitis (eg, bisphosphonates). In patients with ulcerative colitis, use may decrease gastric motility to the point of increasing the risk of paralytic ileus or toxic megacolon.
- Glaucoma: Use with caution in patients with treated angle-closure glaucoma; may exacerbate condition; use is contraindicated with uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma.
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment (limited experience).
- Hiatal hernia: Use with caution in patients with hiatal hernia.
- Hyperthyroidism: Use with caution in patients with hyperthyroidism; may exacerbate condition.
- Myasthenia gravis: Avoid use in patients with myasthenia gravis; may exacerbate condition. Discontinue therapy if signs/symptoms occur.
- Neuropathy: Use with caution in patients with autonomic neuropathy; may aggravate symptoms of decreased GI motility.
- Parkinson disease: Use with caution in patients with Parkinson disease; may aggravate symptoms of disease.
- Prostatic hyperplasia/urinary stricture: Use with caution in patients with prostatic hyperplasia and/or urinary stricture; may cause urinary retention.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment (limited experience).
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Extended release formulation: The extended release formulation consists of drug within a nondeformable matrix; following drug release/absorption, the matrix/shell is expelled in the stool. The use of nondeformable products in patients with known stricture/narrowing of the GI tract has been associated with symptoms of obstruction (rare).
- Topical gel: To minimize transferring medication to others, cover treatment area with clothing after gel has dried. Discontinue use if skin irritation occurs. Contains ethanol; do not expose to open flame or smoking until gel has dried.
- Transdermal patch: May contain conducting metal (eg, aluminum); remove patch prior to MRI.
Other warnings/precautions:
- OTC labeling: Other causes of frequent urination (UTI, diabetes, early pregnancy, other serious conditions) may need to be considered prior to use. Patients should contact a health care provider if symptoms do not improve within 2 weeks of initial use or for new or worsening symptoms.
Monitoring Parameters
Incontinence episodes, postvoid residual (PVR), anticholinergic reactions (eg, dry mouth, constipation, dizziness).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
B
Pregnancy Considerations
Adverse events were not observed in animal reproduction studies.
Information related to the use of oxybutynin in patients treated for neurogenic bladder during pregnancy is limited (Andretta 2018).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat an overactive bladder.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Blurred vision
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Loss of strength and energy
- Anxiety
- Trouble sleeping
- Application site redness, irritation, or itching
- Dry mouth
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Urinary tract infection like blood in the urine, burning or painful urination, passing a lot of urine, fever, lower abdominal pain, or pelvic pain.
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Confusion
- Sensing things that seem real but are not
- Agitation
- Mood changes
- Lack of sweat
- Unable to pass urine
- Severe abdominal pain
- Muscle weakness
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.