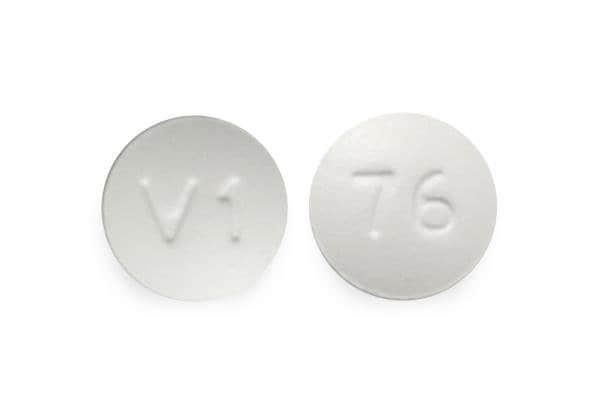
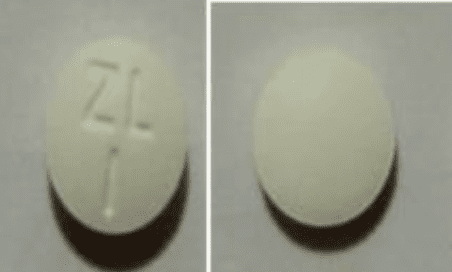
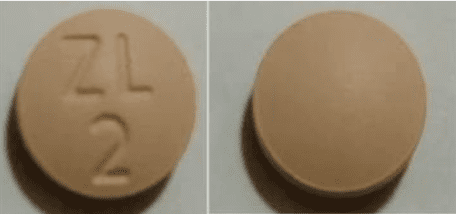
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral, as succinate:
Motegrity: 1 mg
Motegrity: 2 mg [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Prucalopride is a selective, high affinity 5-HT4 receptor agonist whose action at the receptor site promotes cholinergic and nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission by enteric neurons leading to stimulation of the peristaltic reflex, intestinal secretions, and gastrointestinal motility.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Rapid
Distribution
Vd: 567 L (IV administration)
Metabolism
Minor route of elimination; 8 metabolites produced (in vitro data suggest that 4 of 8 metabolites have lower or similar affinity to prucalopride for 5-HT4 receptor) (Resotran Canadian product labeling)
Excretion
Primarily as unchanged drug: Urine (84.2%); feces (13.3%)
Time to Peak
2 to 3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
~24 hours; terminal half-life increases to 34, 43, and 47 hours in mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, respectively (Resotran Canadian product labeling)
Protein Binding
~30%
Use: Labeled Indications
Chronic idiopathic constipation: Treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation in adults
Use: Off Label
Opioid-induced constipation in patients with chronic pain (noncancer)a
Data from a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study support the use of prucalopride in the treatment of opioid-induced constipation in noncancer, chronic pain patients. Prucalopride improved patient-rated severity of constipation and effectiveness of treatment Sloots 2010. Additional trials may be necessary to further define the role of prucalopride in this condition.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to prucalopride or any component of the formulation; intestinal perforation or obstruction due to structural or functional disorder of the gut wall, obstructive ileus, severe inflammatory conditions of the GI tract (eg, Crohn disease, ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon/megarectum).
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications not in US labeling: Renal impairment requiring dialysis
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Chronic idiopathic constipation: Oral: 2 mg once daily; consider adjunctive laxative therapy if no bowel movement within ≥3 consecutive days (Camilleri 2008; Yiannakou 2015)
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing; use with caution due to increased likelihood of decreased renal function. In some clinical trials, patients >65 years of age were initiated on 1 mg/day with the option to increase to 2 mg/day if needed after 2 or 4 weeks of treatment (Yiannakou 2015).
Administration
Oral: Administer without regard to meals.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store in original container to protect from moisture.
Prucalopride Images
Drug Interactions
Anticholinergic Agents: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
Fosfomycin: Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic) may decrease the serum concentration of Fosfomycin. Monitor therapy
Levosulpiride: Benzamide Derivatives may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Levosulpiride. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
P-glycoprotein/ABCB1 Inhibitors: May increase the serum concentration of Prucalopride. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
>10%:
Central nervous system: Headache (19%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain (16%), nausea (14%), diarrhea (13%)
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Dizziness (4%), fatigue (2%), migraine (<2%)
Genitourinary: Pollakiuria (<2%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal distension (5%), flatulence (3%), vomiting (3%), severe diarrhea (2%), abnormal bowel sounds (<2%), decreased appetite (<2%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Amnesia (Anton 2017), dyspnea, facial edema, loss of balance (Anton 2017), palpitations (Anton 2017), pruritus, skin rash, suicidal ideation, suicidal tendencies, urticaria, vaginal hemorrhage, visual hallucination (Anton 2017)
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- CNS effects: May cause dizziness and fatigue; caution patients about performing tasks that require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
- Diarrhea: May cause diarrhea, sometimes severe; most often reported during first week of treatment and typically resolved within a few days. If severe or persistent diarrhea occurs, discontinue therapy and advise patient to consult health care provider.
- Suicidal ideation/behavior: Suicide, suicide attempts, and suicide ideation have been reported. Closely monitor patients for persistent worsening of depression or the emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors and discontinue therapy immediately for any symptoms.
Disease-related concerns:
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; prucalopride mainly undergoes renal elimination. Dose reduction is required in severe impairment; avoid use in patients requiring dialysis.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Elderly: Use with caution in the elderly (limited data); dose reductions may be necessary.
Monitoring Parameters
Frequency of bowel movements; worsening of depression or emergence of suicidal thoughts and behavior
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Information related to use in pregnancy is limited; spontaneous abortions were observed in clinical trials; however, available data is insufficient to evaluate the risk of adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Consider use of appropriate contraception in females of reproductive potential.
Patient Education
- Discuss specific use of drug and side effects with patient as it relates to treatment. (HCAHPS: During this hospital stay, were you given any medicine that you had not taken before? Before giving you any new medicine, how often did hospital staff tell you what the medicine was for? How often did hospital staff describe possible side effects in a way you could understand?)
- Patient may experience headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, passing gas, dizziness, or loss of strength and energy. Have patient report immediately to prescriber behavioral changes, mood changes, depression, or thoughts of suicide (HCAHPS).
- Educate patient about signs of a significant reaction (eg, wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat). Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Patient should consult prescriber for additional questions.
Intended Use and Disclaimer: Should not be printed and given to patients. This information is intended to serve as a concise initial reference for health care professionals to use when discussing medications with a patient. You must ultimately rely on your own discretion, experience, and judgment in diagnosing, treating, and advising patients.