Boxed Warning
Hematologic toxicity:
Severe leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and bone marrow failure including aplastic anemia have been reported in patients treated with valganciclovir.
Impairment of fertility:
Based on animal data and limited human data, valganciclovir may cause temporary or permanent inhibition of spermatogenesis in males and suppression of fertility in females.
Fetal toxicity:
Based on animal data, valganciclovir has the potential to cause birth defects in humans.
Mutagenesis and carcinogenesis:
Based on animal data, valganciclovir has the potential to cause cancers in humans.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Solution Reconstituted, Oral:
Valcyte: 50 mg/mL (88 mL) [contains saccharin sodium, sodium benzoate; tutti-frutti flavor]
Generic: 50 mg/mL (88 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Valcyte: 450 mg
Generic: 450 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Valganciclovir is rapidly converted to ganciclovir in the body. Ganciclovir is phosphorylated to a substrate which competitively inhibits the binding of deoxyguanosine triphosphate to DNA polymerase resulting in inhibition of viral DNA synthesis.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Well absorbed; high-fat meal increases AUC by 30%
Distribution
Vdss: Ganciclovir: 0.7 L/kg; widely to all tissue including CSF and ocular tissue
Metabolism
Converted to ganciclovir by intestinal mucosal cells and hepatocytes
Excretion
Urine (80% to 90%; primarily as ganciclovir)
Time to Peak
Ganciclovir: 1.7 to 3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Pediatric patients (heart, kidney, or liver transplant): Mean range:
4 months to 2 years: 2.8 to 4.5 hours
2 to 12 years: 2.8 to 3.8 hours
12 to 16 years: 4.9 to 6 hours
Adults:
Ganciclovir: 4.08 hours, prolonged with renal impairment; Severe renal impairment: Up to 68 hours
Heart, kidney, kidney-pancreas, or liver transplant patients: Mean range: 6.18 to 6.77 hours
Protein Binding
Ganciclovir: 1% to 2%
Use: Labeled Indications
Cytomegalovirus, prophylaxis (solid organ transplant recipients):
Prevention of cytomegalovirus (CMV) in high-risk adult patients (donor CMV seropositive/recipient CMV seronegative) undergoing kidney, heart, or kidney/pancreas transplantation
Prevention of CMV in high risk pediatric patients undergoing kidney transplant (age 4 months to 16 years) or heart transplant (age 1 month to 16 years)
CMV retinitis, treatment (AIDS-related): Treatment of cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
Use: Off Label
Cytomegalovirus disease (mild to moderate), treatment (solid organ transplant recipients):yes
Based on the Transplantation Society International Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Consensus Group guidelines, valganciclovir is an effective and recommended agent in the treatment of mild to moderate CMV disease in solid organ transplant recipients TTS [Kotton 2018].
CMV esophagitis or colitis treatment in HIV-infected patientsyes
Based on the US Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Opportunistic Infections in HIV-Infected Adults and Adolescents, valganciclovir is an effective and recommended agent for the treatment of esophagitis or colitis due to CMV disease in HIV-infected patients.
CMV, preemptive therapy (hematopoietic cell transplant recipients)yes
Based on the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT) Guidelines for Preventing Infectious Complications among Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients, valganciclovir is an effective and recommended agent in the preemptive management of CMV in bone marrow transplant recipients.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (eg, anaphylaxis) to valganciclovir, ganciclovir, or any component of the formulation
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling): Hypersensitivity to acyclovir or valacyclovir
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis, treatment (AIDS-related): Oral:
Induction: 900 mg twice daily for 14 to 21 days (HHS [OI adult 2016])
Maintenance: 900 mg once daily; may consider discontinuation of chronic maintenance therapy in patients that have received 3 to 6 months of treatment, have inactive lesions, and CD4 count >100 cells/mm3 for 3 to 6 months in response to antiretroviral therapy (HHS [OI adult 2016])
CMV, prophylaxis (solid organ transplant recipients): Oral:
900 mg once daily; duration of prophylaxis is dependent on type of transplant, as well as donor and recipient CMV serostatus (TTS [Kotton 2018]). Note: Based on limited data (Heldenbrand 2016), some centers utilize a lower dose of 450 mg once daily in intermediate-risk (CMV-seropositive [CMV R+] transplant recipients) (TTS [Kotton 2018]; Le Page 2013). This dosing strategy has not been studied prospectively and has only been primarily described in renal transplant recipients.
CMV disease (mild to moderate), treatment (solid organ transplant recipients) (off-label use): Oral: 900 mg twice daily until 1 or 2 consecutive weekly undetectable CMV viral load samples are obtained and clinical resolution of disease (minimum treatment course: 2 weeks) (TTS [Kotton 2018])
CMV esophagitis or colitis in HIV-infected patients (off-label use): Oral: Treat initially with ganciclovir IV; once patient is able to absorb and tolerate oral therapy, may switch to oral valganciclovir 900 mg twice daily for a total duration of 21 to 42 days, or until signs and symptoms have resolved (HHS [OI adult 2016])
CMV, preemptive therapy (hematopoietic cell transplant recipients) (off-label use) (Tomblyn 2009): Oral:
<100 days post-transplant: 900 mg twice daily for 7 days (autologous transplant) or 7 to 14 days (allogenic transplant), then 900 mg once daily for 1 to 2 weeks or until the indicator test is negative (minimum total induction and maintenance treatment is 2 weeks when 14 days of twice daily is used and 3 weeks when a 7-day induction course is used)
>100 days post-transplant: 900 mg twice daily for 7 to 14 days, then 900 mg once daily for 1 to 2 weeks or until the indicator test is negative
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Note: Valganciclovir tablets and ganciclovir capsules cannot be substituted on a mg-per-mg basis since they are NOT BIOEQUIVALENT. In pediatric patients, valganciclovir oral solution is the preferred oral dosage form in pediatric patients for accuracy in dosing; valganciclovir tablets can be considered if the calculated dose is within 10% of the available tablet strength (450 mg). In pediatric patients, dosing may be based on either BSA (mg/m2) or weight (mg/kg); use extra precaution to verify dosing parameters during calculations.
Congenital CMV infection; treatment (continuation from neonatal period): Limited data available: Infants 1 to 6 months: Oral: 16 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours for 6 months; dosing based on a pharmacokinetic study of 24 neonates demonstrated that 16 mg/kg/dose twice daily produced similar serum concentrations to ganciclovir 6 mg/kg intravenously twice daily with a 6-week recommended duration of therapy based on ganciclovir experience (Acosta 2007; DHHS [pediatric] 2013; Kimberlin 2008; Red Book [AAP 2012]). A longer duration of therapy (6 months) was evaluated in a randomized trial of 96 neonates (GA >32 weeks weighing ≥1.8 kg; PNA at time of therapy initiation <30 days) which compared treatment with 6 weeks of therapy (n=47) to 6 months of therapy (n=49); results demonstrated a modest improvement in long-term hearing and developmental outcomes (evaluated at 12 and 24 months of age) with the longer duration of therapy (6 month course); however, short-term improvement (evaluated at 6 months of age) in hearing was not demonstrated (Kimberlin 2015).
Prevention of CMV disease: Oral:
Following solid organ transplantation:
Heart transplantation: Begin therapy within 10 days of transplantation; continue therapy until 100 days post transplantation. Doses should be rounded to the nearest 10 mg increment; maximum daily dose: 900 mg/day
Infants, Children, and Adolescents 1 month to 16 years:
Once daily dose (mg) = 7 x body surface area x creatinine clearance*
Adolescents ≥17 years: 900 mg once daily
Kidney transplantation: Begin therapy within 10 days of transplantation; continue therapy until 200 days post transplantation or 100 days post transplantation if kidney-pancreas transplant in adolescents ≥17 years. Doses should be rounded to the nearest 10 mg increment; maximum daily dose: 900 mg/day
Infants, Children, and Adolescents 4 months to 16 years:
Once daily dose (mg) = 7 x body surface area x creatinine clearance*
Adolescents ≥17 years: 900 mg once daily
Liver transplantation: Limited data available: Infants, Children, and Adolescents 4 months to 16 years (Kotton 2013; Lapidus-Krol 2010; Vaudry 2009): Note: In adults, studies in liver transplant patients reported a higher incidence of tissue-invasive CMV with valganciclovir relative to oral ganciclovir. In pediatric trials, therapy was initiated within 10 days of transplantation and continued therapy until 100 days post transplantation (Vaundry 2009); maximum daily dose: 900 mg/day
Once daily dose (mg) = 7 x body surface area x creatinine clearance*
HIV-exposed/-positive: Infants, Children, and Adolescents 4 months to 16 years (DHHS [pediatric] 2013):
Once daily dose (mg) = 7 x body surface area x creatinine clearance*
Consider therapy initiation for children <6 years of age who are CMV-seropositive and have a CD4 percentage <5% of and for children ≥6 years of age who are CMV-seropositive and have CD4 cell counts <50 cells/mm3. Consider cessation of therapy when CD4 cell count is >10% in children <6 years of age and >100 cells/mm3 for children ≥6 years of age; maximum daily dose: 900 mg/day
* Creatinine clearance calculation (based on the modified Schwartz formula):
CrCl (mL/minute/1.73 m2) = [k x height (cm)] ÷ serum creatinine (mg/dL)
Note: If the calculated CrCl is >150 mL/minute/1.73 m2, then a maximum value of 150 mL/minute/1.73 m2 should be used to calculate the dose.
Note: Calculated using a modified Schwartz formula where k =
- 0.33 in infants <1 year of age with low birthweight for gestational age
- 0.45 in infants <1 year of age with birthweight appropriate for gestational age
- 0.45 in children 1 year to <2 years
- 0.55 in boys age 2 to <13 years
- 0.55 in girls age 2 to <16 years
- 0.7 in boys age 13 to 16 years
CMV retinitis; treatment: Adolescents (DHHS [adult] 2013): Oral:
Induction (active retinitis): 900 mg twice daily for 14 to 21 days
Maintenance: Following induction treatment or for patients with inactive CMV retinitis who require maintenance therapy: 900 mg once daily for at least 3 to 6 months
Reconstitution
Oral solution: Reconstitute powder for oral solution with appropriate amount of water (in 2 equal portions) as specified in the manufacturer's labeling. Shake well for 1 minute after each addition. Discard any unused medication after 49 days. A reconstituted 100 mL bottle will only provide 88 mL of solution for administration.
Extemporaneously Prepared
Note: Commercial preparation is available (50 mg/mL)
A 60 mg/mL oral suspension may be with tablets and a 1:1 mixture of Ora-Sweet® and Ora-Plus®. Crush sixteen 450 mg tablets and reduce to a fine powder. Add 1 mL portions of chosen vehicle (10 mL total) and mix to a uniform paste; mix while adding the vehicle in incremental proportions to almost 120 mL; transfer to a calibrated amber glass bottle, rinse mortar with vehicle, and add quantity of vehicle sufficient to make 120 mL. Label "shake well" and "refrigerate". Stable for 35 days refrigerated.
Henkin CC, Griener JC, and Ten Eick AP, "Stability of Valganciclovir in Extemporaneously Compounded Liquid Formulations," Am J Health Syst Pharm, 2003, 60(7):687-90.12701551
Administration
Oral: Valganciclovir should be administered with meals. Do not break or crush tablets.
Dietary Considerations
Should be taken with meals.
Storage
Oral solution: Store dry powder at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store reconstituted oral solution at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F); do not freeze. Discard any unused medication after 49 days.
Tablet: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
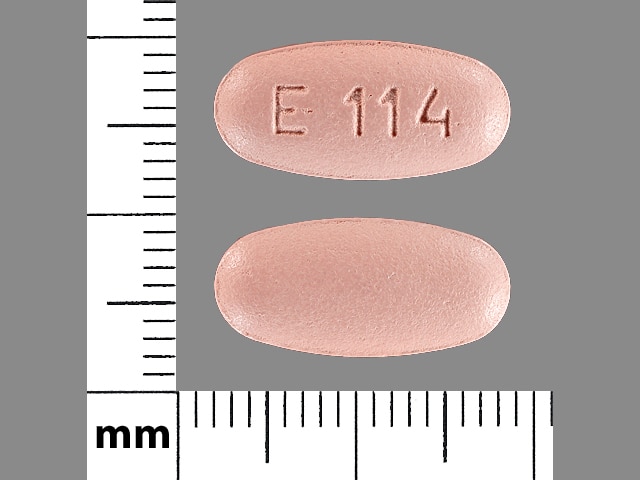
ValGANciclovir Images
Drug Interactions
Amphotericin B: Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Amphotericin B. Monitor therapy
Cladribine: Agents that Undergo Intracellular Phosphorylation may diminish the therapeutic effect of Cladribine. Avoid combination
CycloSPORINE (Systemic): Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of CycloSPORINE (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Didanosine: Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may increase the serum concentration of Didanosine. Monitor therapy
Imipenem: Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Imipenem. Specifically, the risk of seizures may be increased. Management: Avoid concomitant use of these agents unless the prospective benefits of therapy outweigh the risks. Consider therapy modification
Mycophenolate: May increase the serum concentration of Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir. Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may increase the serum concentration of Mycophenolate. Monitor therapy
Probenecid: May increase the serum concentration of Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir. Monitor therapy
Tenofovir Products: May increase the serum concentration of Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir. Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may increase the serum concentration of Tenofovir Products. Monitor therapy
Zidovudine: Ganciclovir-Valganciclovir may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Zidovudine. Specifically, hematologic toxicity may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Hypertension (12% to 18%)
Central nervous system: Headache (6% to 22%), insomnia (6% to 20%)
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (16% to 41%), nausea (8% to 30%), vomiting (3% to 21%), abdominal pain (15%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia (≤31%), thrombocytopenia (≤22%), neutropenia (3% to 19%)
Immunologic: Graft rejection (24%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Tremor (12% to 28%)
Ophthalmic: Retinal detachment (15%)
Renal: Increased serum creatinine (Scr >1.5 to 2.5 mg/dL: 12% to 50%; Scr >2.5: 3% to 17%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (9% to 31%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Hypotension (≥5%), peripheral edema (≥5%), cardiac arrhythmia (<5%)
Central nervous system: Peripheral neuropathy (9%), paresthesia (≤8%), anxiety (≥5%), chills (≥5%), depression (≥5%), dizziness (≥5%), fatigue (≥5%), malaise (≥5%), pain (≥5%), agitation (<5%), confusion (<5%), hallucination (<5%), psychosis (<5%), seizure (<5%)
Dermatologic: Dermatitis (≥5%), increased wound secretion (≥5%), night sweats (≥5%), pruritus (≥5%), cellulitis (<5%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hyperkalemia (≥5%), hypophosphatemia (≥5%), weight loss (≥5%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal distention (≥5%), constipation (≥5%), decreased appetite (≥5%), dyspepsia (≥5%), oral mucosa ulcer (≥5%), dysgeusia (<5%), pancreatitis (<5%)
Genitourinary: Hematuria (≥5%), urinary tract infection (≥5%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Bone marrow depression (<5%; including aplastic anemia), febrile neutropenia (<5%), hemorrhage (<5%; associated with thrombocytopenia), pancytopenia (<5%)
Hepatic: Hepatic insufficiency (≥5%), increased serum ALT (<5%), increased serum AST (<5%)
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reaction (<5%)
Immunologic: Organ transplant rejection (6% to 9%)
Infection: Candidiasis (≥5%; including oral candidiasis), influenza (≥5%), wound infection (≥5%), sepsis (<5%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia (≥5%), back pain (≥5%), muscle spasm (≥5%), myalgia (≥5%), weakness (≥5%), limb pain (<5%)
Ophthalmic: Eye pain (≥5%), macular edema (<5%)
Otic: Deafness (<5%)
Renal: Decreased creatinine clearance (≥5%), renal impairment (≥5%), renal failure (<5%)
Respiratory: Cough (≥5%), dyspnea (≥5%), pharyngitis (≥5%; including nasopharyngitis), upper respiratory tract infection (≥5%)
Miscellaneous: Postoperative complication (≥5%), postoperative pain (<5%), wound dehiscence (<5%)
Frequency not defined: Genitourinary: Reduced fertility
<1%, postmarketing and/or case reports: Agranulocytosis, anaphylaxis, granulocytopenia
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Acute renal failure: Acute renal failure may occur; ensure adequate hydration and use with caution in patients receiving concomitant nephrotoxic agents.
- Blood dyscrasias: [US Boxed Warning]: Severe leukopenia, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, and bone marrow failure, including aplastic anemia have been reported. May occur at any time during treatment and worsen with continued use; cell counts usually begin to recover within 3 to 7 days of treatment discontinuation. Do not use in patients with an absolute neutrophil count <500 cells/mm3, platelet count <25,000/mm3, or hemoglobin <8 g/dL; use with caution in patients with preexisting bone marrow suppression, cytopenias, or in those receiving myelosuppressive drugs/irradiation. Monitor CBC and platelet count at baseline and frequently during therapy, especially in infants and in patients with renal impairment, those with previous drug-induced leukopenia, and those with neutrophil counts <1,000 cells/mm3 at treatment initiation.
- Carcinogenic/teratogenic: [US Boxed Warning]: May cause temporary or permanent inhibition of spermatogenesis and suppression of fertility; has the potential to cause birth defects and cancers in humans. Due to its teratogenic potential, females should undergo pregnancy testing prior to initiation and use effective contraception during treatment and for 30 days after; males should use barrier contraception during treatment and for 90 days after.
Disease-related concerns:
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with impaired renal function; dosage adjustment required.
Special populations:
- Elderly: Acute renal failure may occur in elderly patients with or without preexisting renal impairment; use with caution and adjust dose as needed based on renal function.
- Liver transplant recipients: Not indicated for use in liver transplant patients (higher incidence of tissue-invasive cytomegalovirus [CMV] relative to oral ganciclovir was observed in trials).
- Pediatric: The preferred dosage form for pediatric patients is the oral solution; however, valganciclovir tablets may be used so long as the calculated dose is within 10% of the available tablet strength (450 mg). Use of valganciclovir for the treatment of congenital CMV disease has not been evaluated.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Benzyl alcohol and derivatives: Some dosage forms may contain sodium benzoate/benzoic acid; benzoic acid (benzoate) is a metabolite of benzyl alcohol; large amounts of benzyl alcohol (≥99 mg/kg/day) have been associated with a potentially fatal toxicity (“gasping syndrome”) in neonates; the “gasping syndrome” consists of metabolic acidosis, respiratory distress, gasping respirations, CNS dysfunction (including convulsions, intracranial hemorrhage), hypotension, and cardiovascular collapse (AAP ["Inactive" 1997]; CDC 1982); some data suggests that benzoate displaces bilirubin from protein binding sites (Ahlfors 2001); avoid or use dosage forms containing benzyl alcohol derivative with caution in neonates. See manufacturer's labeling.
Monitoring Parameters
CBC, platelet count, serum creatinine at baseline and periodically during therapy; monitor CBC and platelet count more frequently during therapy in infants and in patients with renal impairment, those with previous drug-induced leukopenia, and those with neutrophil counts <1,000 cells/mm3 at treatment initiation; pregnancy test prior to initiation in females of reproductive potential.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
[US Boxed Warning]: Based on animal data, valganciclovir has the potential to cause birth defects in humans.
Valganciclovir is converted to ganciclovir and shares its reproductive toxicity. Ganciclovir crosses the placenta.
Adverse events following congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection may also occur. Hearing loss, mental retardation, microcephaly, seizures, and other medical problems have been observed. The indications for treating CMV retinitis during pregnancy are the same as in non-pregnant HIV infected woman; however systemic therapy should be avoided during the first trimester when possible. Use of valganciclovir is recommended to treat maternal infection, but not recommended for the treatment of asymptomatic maternal disease for the sole purpose of preventing infant infection. Monitoring of the fetus is recommended. Current recommendations for use of valganciclovir in HIV infected pregnant women are based on data from ganciclovir use in pregnant women following organ transplant or use late in pregnancy in non-HIV infected women (HHS [OI adult 2017]).
[US Boxed Warning]: Based on animal data and limited human data, valganciclovir may cause temporary or permanent inhibition of spermatogenesis in males and suppression of fertility in females. The manufacturer recommends females of reproductive potential undergo pregnancy testing prior to therapy. Females should use effective contraception during treatment and for 30 days after; males should use barrier contraception during treatment and for 90 days after therapy.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat a viral infection of the eyes in people with immune system problems.
- It is used to prevent cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease after organ transplant.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Constipation
- Lack of appetite
- Weight loss
- Back pain
- Muscle pain
- Joint pain
- Muscle spasm
- Trouble sleeping
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Infection
- Bleeding like vomiting blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds; coughing up blood; blood in the urine; black, red, or tarry stools; bleeding from the gums; abnormal vaginal bleeding; bruises without a reason or that get bigger; or any severe or persistent bleeding.
- Kidney problems like unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain.
- Urinary tract infection like blood in the urine, burning or painful urination, passing a lot of urine, fever, lower abdominal pain, or pelvic pain.
- Electrolyte problems like mood changes, confusion, muscle pain or weakness, abnormal heartbeat, seizures, lack of appetite, or severe nausea or vomiting.
- Abdominal edema
- Shortness of breath
- Night sweats
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Dark urine
- Yellow skin
- Tremors
- Depression
- Burning or numbness feeling
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Swelling of arms or legs
- Eye pain
- Severe eye irritation
- Vision changes
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.