Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral:
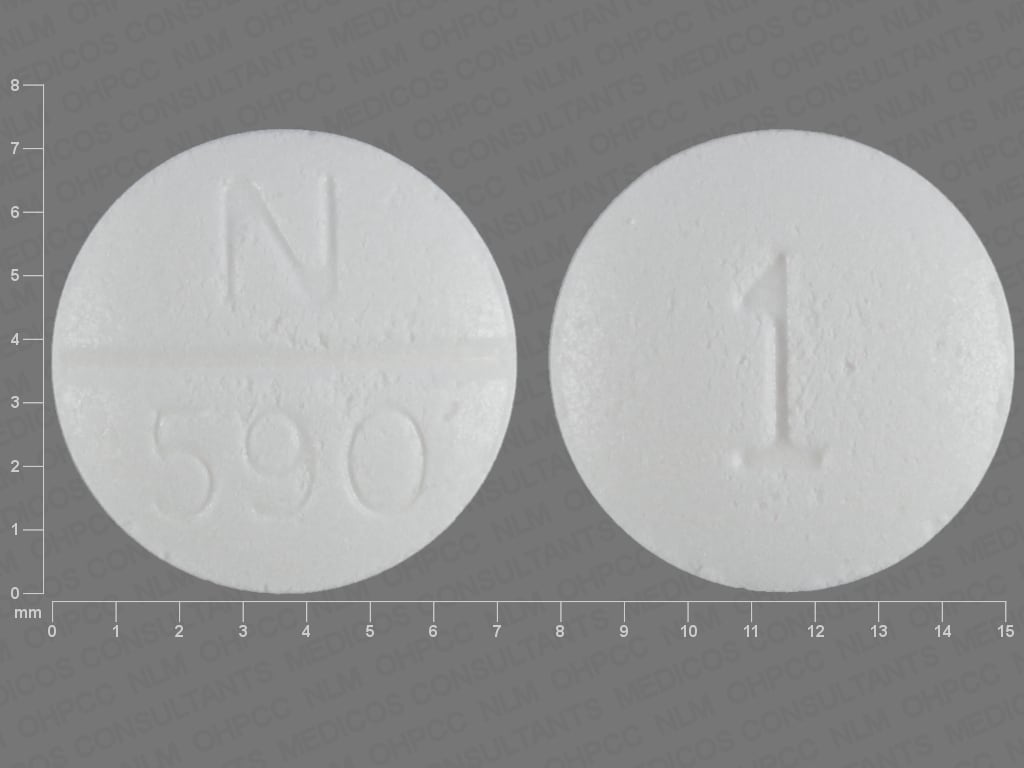
Cardura: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg [scored]
Generic: 1 mg, 2 mg, 4 mg
Tablet, Oral, as mesylate:
Cardura: 8 mg [scored]
Generic: 8 mg
Tablet Extended Release 24 Hour, Oral:
Cardura XL: 4 mg, 8 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Hypertension: Competitively inhibits postsynaptic alpha1-adrenergic receptors which results in vasodilation of veins and arterioles and a decrease in total peripheral resistance and blood pressure; ~50% as potent on a weight by weight basis as prazosin.
BPH: Competitively inhibits postsynaptic alpha1-adrenergic receptors in prostatic stromal and bladder neck tissues. This reduces the sympathetic tone-induced urethral stricture causing BPH symptoms.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Extensively hepatic to active metabolites; primarily via CYP3A4; secondary pathways involve CYP2D6 and 2C9
Excretion
Feces (~63%, primarily as metabolites [4.8% as unchanged]); urine (9%, primarily as metabolites)
Time to Peak
Serum: Immediate release: 2 to 3 hours; Extended release: 8 ± 3.7 to 9 ± 4.7 hours
Duration of Action
>24 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Immediate release: ~22 hours; Extended release: 15 to 19 hours
Protein Binding
~98%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
Immediate release: 40% increase in exposure in mild impairment (Child-Pugh class A).
Special Populations: Elderly
Extended release: Cmax and AUC increased 27% and 34% respectively in elderly patients.
Use: Labeled Indications
Benign prostatic hyperplasia: Treatment of signs and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Hypertension (immediate release only): Management of hypertension. Note: Alpha blockers are not recommended as first line therapy (ACC/AHA [Whelton 2017]).
Use: Off Label
Ureteral calculi expulsionbyes
Use of alpha-1 adrenergic blockers, including doxazosin, for treating ureteral calculi is supported by data from a meta-analysis as well as numerous controlled trials. Tamsulosin has the most data, but doxazosin has also demonstrated efficacy in facilitating expulsion of ureteral stones (<10 mm) as medical therapy alone or as an adjunct to shock wave lithotripsy and ureteroscopy. Some trials indicate a class effect of alpha-1 adrenergic blockers, with doxazosin reported to be equally effective as terazosin, tamsulosin, and alfuzosin Ates 2012, Campshroer 2018, Gurbuz 2011, Hollingsworth 2016, Zehri 2010
American Urological Association/Endourological Society guidelines and European Association of Urology guidelines recommend use of alpha-1 blockers, including doxazosin, for treating ureteral calculi
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to doxazosin, other quinazolines (eg, prazosin, terazosin), or any component of the formulation.
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling): Galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
BPH: Oral:
Immediate release: Initial: 1 mg once daily; may titrate (by doubling the daily dose [eg, to 2 mg, then 4 mg, then 8 mg]) at 1- to 2-week intervals up to 8 mg once daily based on patient response and tolerability (maximum: 8 mg/day).
Reinitiation of therapy: If therapy is discontinued for several days, restart at 1 mg dose and titrate using initial dosing regimen.
Extended release: 4 mg once daily; may titrate based on response and tolerability every 3 to 4 weeks to 8 mg once daily (maximum: 8 mg/day).
Reinitiation of therapy: If therapy is discontinued for several days, restart at 4 mg dose and titrate using initial dosing regimen.
Note: Conversion to extended release from immediate release: Omit final evening dose of immediate release prior to starting morning dosing with extended release product; initiate extended release product using 4 mg once daily.
Hypertension (alternative agent): Oral: Immediate release: Initial: 1 mg once daily; titrate as needed based on patient response up to a dose of 16 mg once daily (ACC/AHA [Whelton 2017]); maximum: 16 mg/day.
Reinitiation of therapy: If therapy is discontinued for several days, restart at 1 mg dose and titrate using initial dosing regimen.
Ureteral calculi expulsion (off-label use): Oral: Immediate release: 4 mg once daily in evening (Gurbuz 2011; Resorlu 2011). Note: Patients with stones >10 mm were excluded from studies.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Avoid use for hypertension treatment (alternative agents have superior risk-benefit profiles) (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
Dosing: Pediatric
Note: If drug is discontinued for greater than several days, consider beginning with initial dose and retitrate as needed.
Dysfunctional voiding: Limited data available, efficacy results variable: Children ≥3 years and Adolescents: Oral: Immediate release: Initial: 0.5 mg once daily at bedtime; some trials maintained a fixed dose; others titrated at weekly or biweekly intervals to effect as tolerated (maximum daily dose: 2 mg/day) (Austin 1999; Cain 2003; El-Hefnawy 2012; Yucel 2005). In some trials, a larger initial dose (1 mg/day) was used in patients weighing >40 to 50 kg (Austin 1999; Yucel 2005).
Hypertension: Limited data available: Children and Adolescents: Oral: Immediate release: Initial: 1 mg/day; maximum daily dose: 4 mg/day (NHBPEP 2004; NHLBI 2011)
Administration
Oral:
Extended release: Swallow tablets whole; do not crush, cut, chew, or divide. Administer with morning meal.
Immediate release: Administer daily dose either in the morning or evening.
Dietary Considerations
Administer extended-release tablet with morning meal.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Doxazosin Images
Drug Interactions
Alpha-/Beta-Agonists: Alpha1-Blockers may diminish the vasoconstricting effect of Alpha-/Beta-Agonists. Similarly, Alpha-/Beta-Agonists may antagonize Alpha1-Blocker vasodilation. Monitor therapy
Alpha1-Agonists: Alpha1-Blockers may diminish the vasoconstricting effect of Alpha1-Agonists. Similarly, Alpha1-Agonists may antagonize Alpha1-Blocker vasodilation. Monitor therapy
Alpha1-Blockers: May enhance the antihypertensive effect of other Alpha1-Blockers. Avoid combination
Amifostine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Amifostine. Management: When amifostine is used at chemotherapy doses, blood pressure lowering medications should be withheld for 24 hours prior to amifostine administration. If blood pressure lowering therapy cannot be withheld, amifostine should not be administered. Consider therapy modification
Amphetamines: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]): Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]). Monitor therapy
Aprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Benperidol: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Beta-Blockers: May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Alpha1-Blockers. The risk associated with ophthalmic products is probably less than systemic products. Exceptions: Levobunolol; Metipranolol. Monitor therapy
Bosentan: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Brigatinib: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Brigatinib may enhance the bradycardic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Bromperidol. Bromperidol may diminish the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Avoid combination
Calcium Channel Blockers: Alpha1-Blockers may enhance the hypotensive effect of Calcium Channel Blockers. Monitor therapy
Clofazimine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Conivaptan: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inducers (Moderate): May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May increase the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Consider an alternative for one of the interacting drugs. Some combinations may be specifically contraindicated. Consult appropriate manufacturer labeling. Consider therapy modification
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Consider therapy modification
Dabrafenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Seek alternatives to the CYP3A4 substrate when possible. If concomitant therapy cannot be avoided, monitor clinical effects of the substrate closely (particularly therapeutic effects). Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Alpha1-Blockers. Monitor therapy
Deferasirox: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Dexmethylphenidate: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Diazoxide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
DULoxetine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of DULoxetine. Monitor therapy
Duvelisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Enzalutamide: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Concurrent use of enzalutamide with CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided. Use of enzalutamide and any other CYP3A4 substrate should be performed with caution and close monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Erdafitinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosaprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosnetupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Herbs (Hypertensive Properties): May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Herbs (Hypotensive Properties): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Hypotension-Associated Agents: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Hypotension-Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Idelalisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Ivosidenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Larotrectinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Levodopa-Containing Products: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Levodopa-Containing Products. Monitor therapy
Lorlatinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Avoid concurrent use of lorlatinib with any CYP3A4 substrates for which a minimal decrease in serum concentrations of the CYP3A4 substrate could lead to therapeutic failure and serious clinical consequences. Consider therapy modification
Lormetazepam: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Methylphenidate: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
MiFEPRIStone: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Minimize doses of CYP3A4 substrates, and monitor for increased concentrations/toxicity, during and 2 weeks following treatment with mifepristone. Avoid cyclosporine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, fentanyl, pimozide, quinidine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus. Consider therapy modification
Mitotane: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Doses of CYP3A4 substrates may need to be adjusted substantially when used in patients being treated with mitotane. Consider therapy modification
Molsidomine: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Netupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Nicorandil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nitroprusside: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Nitroprusside. Monitor therapy
Obinutuzumab: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Management: Consider temporarily withholding blood pressure lowering medications beginning 12 hours prior to obinutuzumab infusion and continuing until 1 hour after the end of the infusion. Consider therapy modification
Palbociclib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Pentoxifylline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Pholcodine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Pholcodine. Monitor therapy
Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Alpha1-Blockers (Nonselective). Management: Ensure patient is stable on one agent prior to initiating the other, and always initiate combination using the lowest possible dose of the drug being added. When tadalafil is used for treatment of BPH, concurrent alpha 1-blockers are not recommended. Consider therapy modification
Prostacyclin Analogues: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Quinagolide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Rilmenidine: Alpha1-Blockers may enhance the hypotensive effect of Rilmenidine. Monitor therapy
Sarilumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Siltuximab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Simeprevir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Stiripentol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Use of stiripentol with CYP3A4 substrates that are considered to have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided due to the increased risk for adverse effects and toxicity. Any CYP3A4 substrate used with stiripentol requires closer monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Tocilizumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Yohimbine: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
>10%: Central nervous system: Dizziness (5% to 19%), malaise (≤12%), fatigue (8% to ≤12%), headache (6% to 10%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Edema (3% to 4%), hypotension (1% to 2%), orthostatic hypotension (<1% to 2%), cardiac arrhythmia (1%), facial edema (1%), flushing (1%), palpitations (1%)
Central nervous system: Drowsiness (1% to 5%), vertigo (2% to 4%), pain (2%), anxiety (1%), ataxia (1%), hypertonia (1%), insomnia (1%), movement disorder (1%), myasthenia (1%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Sexual disorder (2%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain (2%), nausea (1% to 2%), dyspepsia (1%), xerostomia (1%)
Genitourinary: Urinary incontinence (1%), urinary tract infection (1%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness (4% to 7%), muscle cramps (1%), myalgia (1%), arthralgia (≤1%), arthritis (≤1%)
Ophthalmic: Visual disturbance (2%)
Otic: Tinnitus (1%)
Renal: Polyuria (2%)
Respiratory: Respiratory tract infection (5%), rhinitis (3%), dyspnea (1% to 3%), epistaxis (1%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormal hepatic function tests, abnormal lacrimation, abnormality in thinking, agitation, alopecia, altered sense of smell, amnesia, angina pectoris, anorexia, back pain, blurred vision, bradycardia, bronchospasm (aggravated), cerebrovascular accident, chest pain, cholestasis, cholestatic hepatitis, confusion, cough, decreased libido, depersonalization, diaphoresis, diarrhea, dysgeusia, dysuria, eczema, emotional lability, fecal incontinence, fever, flu-like symptoms, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal obstruction, gout, gynecomastia, hematuria, hepatitis, hot flash, hypersensitivity reaction, hypoesthesia, hypokalemia, impotence, increased appetite, increased thirst, infection, intraoperative floppy iris syndrome (cataract surgery), jaundice, lack of concentration, leukopenia, lymphadenopathy, mastalgia, migraine, myocardial infarction, nephrolithiasis, nervousness, neutropenia, nocturia, orthostatic dizziness, otalgia, pallor, paranoia, paresis, paresthesia, peripheral ischemia, pharyngitis, photophobia, priapism, pruritus, purpura, rigors, sinusitis, skin rash, syncope, tachycardia, thrombocytopenia, tremor, twitching, urinary frequency, urination disorder, urticaria, vomiting, weight gain, weight loss, xeroderma
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Allergic reactions: May occur, including skin rash, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, and respiratory symptoms.
- CNS depression: May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks that require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
- Floppy iris syndrome: Intraoperative floppy iris syndrome has been observed in cataract surgery patients who were on or were previously treated with alpha1-blockers; there appears to be no benefit in discontinuing alpha-blocker therapy prior to surgery. May require modifications to surgical technique.
- Hematologic effect: Decreases in white blood cells (WBC) and neutrophil count have been reported; WBC and neutrophils returned to normal after discontinuation.
- Orthostatic hypotension/syncope: May cause orthostatic hypotension and syncope within a few hours after dosing, but may occur later; anticipate a similar effect if therapy is interrupted for a few days, if dosage is increased, or if another antihypertensive drug, PDE-5 inhibitor, or nitrates are introduced. Use with caution in patients with symptomatic orthostatic hypotension.
- Priapism: Priapism has been associated with use (rarely); seek immediate medical assistance for erections lasting longer than 4 hours.
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with heart failure, angina pectoris, or recent acute myocardial infarction (within the last 6 months). If symptoms of angina pectoris appear or worsen, discontinue use. In a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, doxazosin has been determined to be an agent that may exacerbate underlying myocardial dysfunction (magnitude: moderate) (AHA [Page 2016]).
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with mild to moderate impairment (Child-Pugh class A and B); monitor blood pressure and for symptoms of hypotension. Not recommended in severe impairment (Child-Pugh class C) (extensively metabolized).
- Prostate cancer: Rule out prostatic carcinoma before beginning therapy (many symptoms of BPH and prostate cancer are similar).
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Extended release: Consists of drug within a nondeformable matrix; following drug release/absorption, the matrix/shell is expelled in the stool. The use of nondeformable products in patients with known stricture/narrowing of the GI tract has been associated with symptoms of obstruction. Use caution in patients with increased GI retention (eg, chronic constipation) as doxazosin exposure may be increased.
Other warning/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Extended release: Not indicated for use in women or for the treatment of hypertension.
Monitoring Parameters
Blood pressure routinely and for at least 6 hours after initial dose and with each dose increase (standing and sitting/supine); monitor patients with mild-to-moderate impairment for symptoms of hypotension.
Hypertension: The 2017 Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults (ACC/AHA [Whelton 2017]):
Confirmed hypertension and known CVD or 10-year ASCVD risk ≥10%: Target blood pressure <130/80 mm Hg is recommended
Confirmed hypertension without markers of increased ASCVD risk: Target blood pressure <130/80 mm Hg may be reasonable
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Doxazosin crosses the placenta (Versmissen 2016).
Chronic maternal hypertension may increase the risk of birth defects, low birth weight, preterm delivery, stillbirth, and neonatal death. Actual fetal/neonatal risks may be related to duration and severity of maternal hypertension. Untreated hypertension may also increase the risks of adverse maternal outcomes, including gestational diabetes, myocardial infarction, preeclampsia, stroke, and delivery complications (ACOG 203 2019).
Agents other than doxazosin are more commonly used to treat hypertension in pregnancy (ACOG 203 2019; ESC [Regitz-Zagrosek 2018]). Females with preexisting hypertension may continue their medication during pregnancy unless contraindications exist (ESC [Regitz-Zagrosek 2018]). Although rare, use of doxazosin for the treatment of hypertension due to a pheochromocytoma during pregnancy has been described; treatment was generally started after the first trimester (Lenders 2019; van der Weerd 2017).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat high blood pressure.
- In men, it is used to treat the signs of an enlarged prostate.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Fatigue
- Loss of strength and energy
- Headache
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling of arms or legs
- Erection that lasts more than 4 hours
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.