Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Solution Prefilled Syringe, Subcutaneous:
Copaxone: 20 mg/mL (1 mL); 40 mg/mL (1 mL)
Glatopa: 20 mg/mL (1 mL) [contains mannitol]
Glatopa: 40 mg/mL (1 mL)
Solution Prefilled Syringe, Subcutaneous [preservative free]:
Generic: 20 mg/mL (1 mL); 40 mg/mL (1 mL)
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
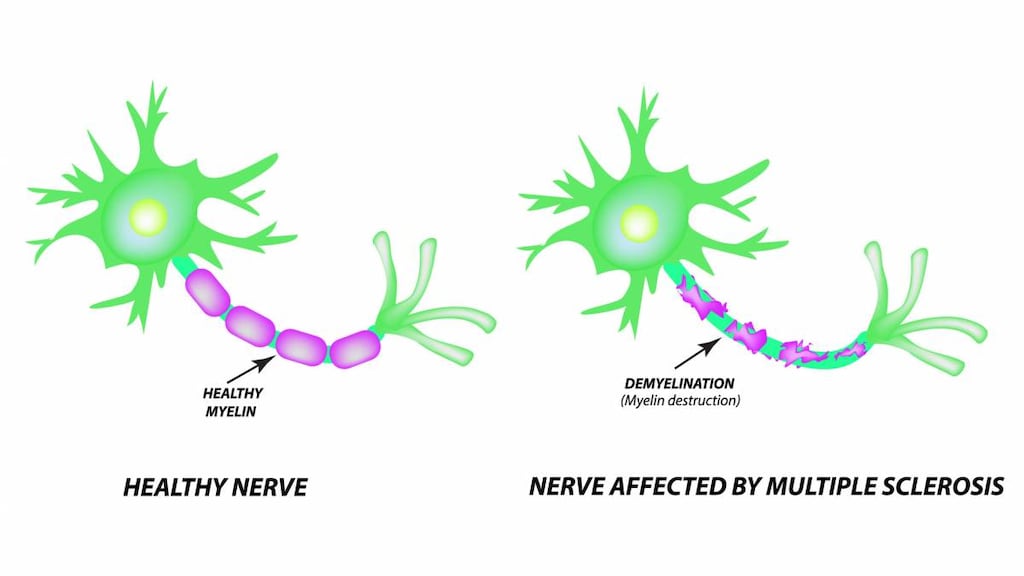
Glatiramer is a mixture of random polymers of four amino acids; L-alanine, L-glutamic acid, L-lysine, and L-tyrosine, the resulting mixture is antigenically similar to myelin basic protein, which is an important component of the myelin sheath of nerves; glatiramer is thought to induce and activate T-lymphocyte suppressor cells specific for a myelin antigen, it is also proposed that glatiramer interferes with the antigen-presenting function of certain immune cells opposing pathogenic T-cell function
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Distribution
A small percentage of intact and partial hydrolyzed drug is presumed to enter lymphatic circulation.
Metabolism
SubQ: Large percentage hydrolyzed locally
Use: Labeled Indications
Multiple sclerosis, relapsing: Treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis, including clinically isolated syndrome, relapsing-remitting disease, and active secondary progressive disease.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to glatiramer acetate, mannitol, or any component of the formulation
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Note:Glatiramer 20 mg/mL and 40 mg/mL formulations are not interchangeable.
Multiple sclerosis, relapsing: SubQ: 20 mg once daily or 40 mg 3 times per week administered at least 48 hours apart.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
SubQ: For SubQ administration in the arms, abdomen, hips, or thighs; rotate injection sites to possibly minimize the occurrence of lipoatrophy. Do not administer IV. Administer the 40 mg dose on the same 3 days each week (eg, Monday, Wednesday, Friday) at least 48 hours apart. Allow syringe to stand at room temperature for 20 minutes prior to injection. Discard unused portions.
Storage
Store at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). If needed, may store at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) for up to 1 month (refrigeration is preferred). Avoid exposure to high temperatures; protect from intense light. Do not freeze. Discard if syringe freezes.
Drug Interactions
Baricitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Baricitinib. Management: Use of baricitinib in combination with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine or cyclosporine is not recommended. Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted. Consider therapy modification
BCG (Intravesical): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
Cladribine: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Coccidioides immitis Skin Test: Immunosuppressants may diminish the diagnostic effect of Coccidioides immitis Skin Test. Monitor therapy
Denosumab: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Specifically, the risk for serious infections may be increased. Monitor therapy
Echinacea: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Fingolimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Fingolimod. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of fingolimod and other immunosuppressants when possible. If combined, monitor patients closely for additive immunosuppressant effects (eg, infections). Consider therapy modification
Leflunomide: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Leflunomide. Specifically, the risk for hematologic toxicity such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and/or thrombocytopenia may be increased. Management: Consider not using a leflunomide loading dose in patients receiving other immunosuppressants. Patients receiving both leflunomide and another immunosuppressant should be monitored for bone marrow suppression at least monthly. Consider therapy modification
Natalizumab: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Natalizumab. Specifically, the risk of concurrent infection may be increased. Avoid combination
Nivolumab: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Nivolumab. Consider therapy modification
Ocrelizumab: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
Pidotimod: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pidotimod. Monitor therapy
Pimecrolimus: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Roflumilast: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Siponimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Siponimod. Monitor therapy
Sipuleucel-T: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sipuleucel-T. Management: Evaluate patients to see if it is medically appropriate to reduce or discontinue therapy with immunosuppressants prior to initiating sipuleucel-T therapy. Consider therapy modification
Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live). Monitor therapy
Tacrolimus (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Tertomotide: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Tertomotide. Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Tofacitinib. Management: Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted, and this warning seems particularly focused on more potent immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Trastuzumab: May enhance the neutropenic effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
Upadacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Upadacitinib. Avoid combination
Vaccines (Inactivated): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Inactivated). Management: Vaccine efficacy may be reduced. Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations at least 2 weeks prior to starting an immunosuppressant. If vaccinated during immunosuppressant therapy, revaccinate at least 3 months after immunosuppressant discontinuation. Consider therapy modification
Vaccines (Live): Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vaccines (Live). Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Live). Management: Avoid use of live organism vaccines with immunosuppressants; live-attenuated vaccines should not be given for at least 3 months after immunosuppressants. Exceptions: Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live). Avoid combination
Adverse Reactions
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Vasodilation (3% to 20%), chest pain (2% to 13%)
Central nervous system: Pain (20%), anxiety (13%)
Dermatologic: Skin rash (2% to 19%), diaphoresis (15%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (2% to 15%)
Hypersensitivity: Immediate hypersensitivity (2% to 16%; postinjection, including flushing, chest pain, palpitations, anxiety, dyspnea, throat constriction, and/or urticaria)
Immunologic: Development of IgG antibodies (3 months: ≥3 x baseline: 80%; 12 months: 90%; ≥3 x baseline: 30%)
Infection: Infection (30%)
Local: Inflammation at injection site (2% to 49%), erythema at injection site (22% to 43%), pain at injection site (10% to 40%), itching at injection site (6% to 27%), residual mass at injection site (6% to 27%), swelling (1% to 19%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness (22%), back pain (12%)
Respiratory: Dyspnea (3% to 14%), flu-like symptoms (3% to 14%), nasopharyngitis (11%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Palpitations (7% to 9%), edema (8%), tachycardia (5%), facial edema (3%), peripheral edema (3%), syncope (3%), hypertension (1%)
Central nervous system: Migraine (4%), chills (2% to 3%), nervousness (2%), speech disturbance (2%), abnormal dreams (1%), emotional lability (1%), stupor (1%)
Dermatologic: Hyperhidrosis (7%), pruritus (5%), erythema (2% to 4%), urticaria (3%), skin atrophy (≥1%), warts (≥1%), eczema (1%), pustular rash (1%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Weight gain (3%), amenorrhea (1%), hypermenorrhea (1%)
Gastrointestinal: Vomiting (7%), gastroenteritis (6%), dysphagia (2%), aphthous stomatitis (≥1%), bowel urgency (≥1%), dental caries (≥1%), enlargement of salivary glands (≥1%), oral candidiasis (≥1%)
Genitourinary: Urinary urgency (5%), vulvovaginal candidiasis (4%), abnormal Pap smear (≥1%), hematuria (≥1%), vaginal hemorrhage (≥1%), impotence (1%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Bruise (8%), lymphadenopathy (7%), benign skin neoplasm (2%)
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity (3%)
Infection: Abscess (≥1%), herpes zoster (≥1%)
Local: Bleeding at injection site (5%), hypersensitivity reaction at injection site (4%), fibrosis at injection site (2%), lipoatrophy at injection site (≤2%), abscess at injection site (1%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Neck pain (8%), tremor (4%), laryngospasm (2%)
Ophthalmic: Diplopia (3%), visual field defect (1%)
Respiratory: Rhinitis (7%), bronchitis (6%), cough (6%), laryngismus (5%), viral respiratory tract infection (3%), hyperventilation (1%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (3% to 6%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports (Limited to important or life-threatening): Amyotrophy, anaphylactoid reaction, anemia, angina pectoris, angioedema, aphasia, arthritis, asthma, ataxia, atrial fibrillation, blepharoptosis, blindness, bradycardia, bursitis, carcinoma (breast, bladder, lung, ovarian), cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac failure, cardiomegaly, cardiomyopathy, cataract, cerebral edema, cerebrovascular accident, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, CNS neoplasm, colitis, coma, corneal ulcer, coronary occlusion, Cushing's syndrome, cyanosis, decreased libido, deep vein thrombophlebitis, depersonalization, dermatitis, dry eye syndrome, duodenal ulcer, eosinophilia, erythema nodosum, esophageal ulcer, esophagitis, facial paralysis, fibrocystic breast disease, fourth heart sound, fungal dermatitis, furunculosis, gastrointestinal carcinoma, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal ulcer, genitourinary neoplasm, glaucoma, gout, hallucination, hematemesis, hepatic cirrhosis, hepatitis, hepatomegaly, hernia, hydrocephalus, hypercholesterolemia, hyperthyroidism, hypokinesia, hypotension, hypothyroidism, hypoventilation, increased appetite, leukemia, leukopenia, lupus erythematosus, lymphedema, maculopapular rash, malignant neoplasm of cervix, malignant neoplasm of skin, mania, memory impairment, meningitis, mitral valve prolapse syndrome, moon face, muscle spasm, mydriasis, myelitis, myocardial infarction, myoclonus, nephrolithiasis, nephrosis, neuralgia, optic neuritis, oral mucosa ulcer, orthostatic hypotension, osteomyelitis, otitis externa, ovarian cyst, pancreatitis, pancytopenia, paraplegia, pericardial effusion, peripheral vascular disease, photophobia, pneumonia, priapism, pseudolymphoma, psoriasis, psychotic depression, pulmonary embolism, pyelonephritis, rectal hemorrhage, renal failure, seizures, sepsis, serum sickness, skin hypertrophy, skin photosensitivity, skin pigmentation, splenomegaly, stomatitis, suicidal tendencies, systemic lupus erythematosus, systolic heart murmur, tenosynovitis, thrombocytopenia, thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, tissue necrosis at injection site, urethritis, vesicobullous rash, weight loss, xeroderma
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Chest pain: May or may not occur with the immediate postinjection reaction; described as a transient pain usually resolving in a few minutes; often unassociated with other symptoms. Episodes usually begin ≥1 month after initiation of treatment.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Anaphylactoid reactions (rare) have been reported.
- Immune response: Although there has not been a systematic evaluation of glatiramer’s potential to affect other immune functions, it may interfere with recognition of foreign antigens undermining the body's tumor surveillance and defense system against infection.
- Lipoatrophy: May occur locally at injection site at various times after treatment (sometimes after several months) and may not resolve; to possibly minimize occurrence, advise patients to follow proper injection technique and rotate site with each injection. Skin necrosis has also been observed.
- Systemic reactions: Postinjection systemic reactions may occur immediately (within seconds to minutes of injection; majority of reactions observed within 1 hour) and in a substantial percentage of patients (~16% [20 mg/mL] and ~2% [40 mg/mL] in studies); symptoms (anxiety, chest pain, constriction of the throat, dyspnea, flushing, palpitations, tachycardia, urticaria) are usually self-limited and transient. These symptoms generally occur several months after initiation of treatment.
Concurrent drug therapy concerns:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Antigenic: Glatiramer acetate is antigenic and may possibly lead to the induction of untoward host responses. Glatiramer acetate-reactive antibodies (IgG subtype) form in most patients.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Information related to the use of glatiramer acetate in pregnancy is available (Fragoso 2014; Herbstritt 2016; MacDonald 2019; Nguyen 2019; Sandberg-Wollheim 2018).
In general, disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis (MS) are stopped prior to a planned pregnancy and not initiated during pregnancy, except in females at high risk of MS activity (AAN [Rae-Grant 2018]). When disease-modifying therapy is needed in females planning a pregnancy (eg, high risk of disease reactivation), glatiramer acetate may be considered until pregnancy is confirmed, and in select cases (eg, women with active disease), use may be continued during pregnancy. Delaying pregnancy is recommended for females with persistent high disease activity (ECTRIMS/EAN [Montalban 2018]).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to lower the number of setbacks with MS (multiple sclerosis).
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of strength and energy
- Back pain
- Injection site irritation
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Infection
- Chest pain
- Fast heartbeat
- Passing out
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Flushing
- Anxiety
- Sweating a lot
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath
- Swollen glands
- Injection site pain, skin discoloration, temperature change, or dent
- Swelling
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.