Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Implant, Subcutaneous:
Zoladex: 3.6 mg (1 ea); 10.8 mg (1 ea)
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Goserelin (a gonadotropin-releasing hormone [GnRH] analog) causes an initial increase in luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), chronic administration of goserelin results in a sustained suppression of pituitary gonadotropins. Serum testosterone falls to levels comparable to surgical castration. The exact mechanism of this effect is unknown, but may be related to changes in the control of LH or down-regulation of LH receptors.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
SubQ: Rapid and can be detected in serum in 30 to 60 minutes; 3.6 mg: released slowly in first 8 days, then rapid and continuous release for 28 days
Distribution
Vd: Males: 44.1 L; Females: 20.3 L
Metabolism
Hepatic hydrolysis of the C-terminal amino acids
Excretion
Urine (>90%; 20% as unchanged drug)
Onset of Action
Females: Estradiol suppression reaches postmenopausal levels within 3 weeks and FSH and LH are suppressed to follicular phase levels within 4 weeks of initiation.
Males: Testosterone suppression reaches castrate levels within 2 to 4 weeks after initiation.
Time to Peak
SubQ: Male: 12 to 15 days, Female: 8 to 22 days
Duration of Action
Females: Estradiol, LH and FSH generally return to baseline levels within 12 weeks following the last monthly implant.
Males: Testosterone levels maintained at castrate levels throughout the duration of therapy.
Protein Binding
~27%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Gender
The total body Cl of goserelin was significantly (P <0.05) greater (163.9 vs 110.5 L/min) in women compared with men.
Special Populations Note
Body weight: A decline in AUC of approximately 1% to 2.5% was observed with a kg increase in body weight.
Use: Labeled Indications
Breast cancer, advanced (3.6 mg only): Palliative treatment of advanced breast cancer in pre- and perimenopausal women (estrogen and progesterone receptor values may help to predict if goserelin is likely to be beneficial).
Endometrial thinning (3.6 mg only): Endometrial-thinning agent prior to endometrial ablation for dysfunctional uterine bleeding.
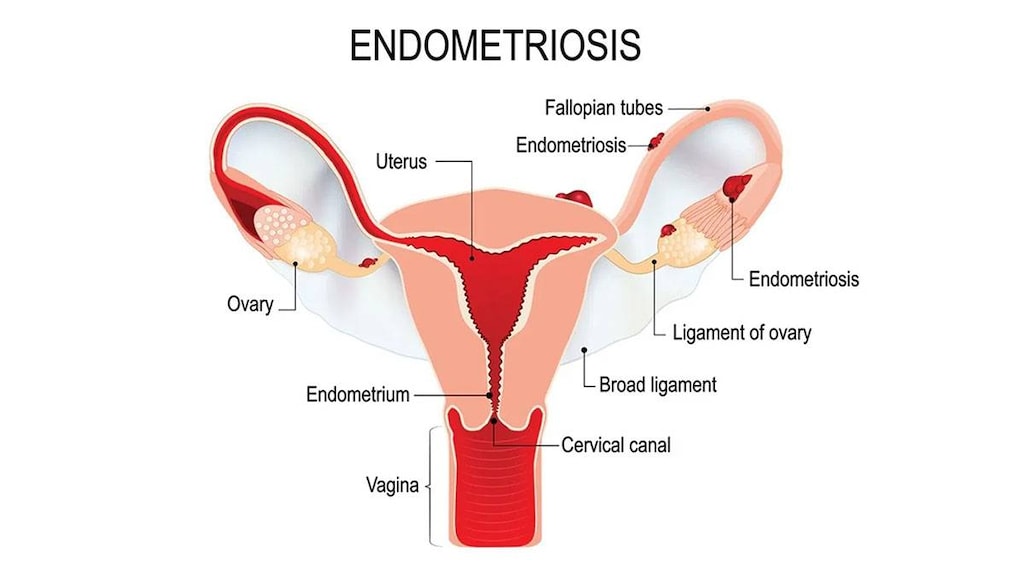
Endometriosis (3.6 mg only): Management of endometriosis, including pain relief and reduction of endometriotic lesions for the duration of therapy (goserelin experience for endometriosis has been limited to women 18 years and older treated for 6 months).
Prostate cancer, advanced (3.6 mg or 10.8 mg): Palliative treatment of advanced carcinoma of the prostate.
Prostate cancer, stage B2 to C (3.6 mg or 10.8 mg): Management of locally confined stage T2b to T4 (stage B2 to C) prostate cancer (in combination with an antiandrogen [eg, flutamide]); begin goserelin and antiandrogen therapy 8 weeks prior to initiating radiation therapy and continue during radiation therapy.
Use: Off Label
Breast cancer, advanced (second-line endocrine-based combination therapy)a
Data from a large, randomized phase III study supports the use of goserelin in pre- or perimenopausal women (in combination with palbociclib and fulvestrant) as second-line endocrine-based combination therapy in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-negative advanced breast cancer with progression on prior endocrine therapy Turner 2015.
Hormone therapy for transgender females (male-to-female)yes
Based on the Endocrine Society guidelines for the endocrine treatment of gender dysphoric/gender incongruent persons, gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists like goserelin are effective when used in combination with estrogen supplementation for suppressing gonadotropin secretion, thereby decreasing serum testosterone levels into the normal range for females. The result is decreased hair growth, muscle mass, sexual desire, sperm production, spontaneous erections, and testicular volume, as well as breast growth, male sexual dysfunction, redistribution of body fat, and skin and voice changes Dittrich 2005, ES [Hembree 2017].
Prevention of early menopause during chemotherapy for early stage hormone receptor negative breast cancerb
Data from a randomized phase III study supports the use of goserelin (starting 1 week prior to chemotherapy initiation) to prevent premature ovarian failure in women with early stage hormone receptor negative breast cancer Moore, 2015.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to goserelin, GnRH, GnRH agonist analogues, or any component of the formulation; pregnancy (except if using for palliative treatment of advanced breast cancer)
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in the US labeling): Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding, pregnancy, breastfeeding
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Prostate cancer, advanced: Males: SubQ:
28-day implant: 3.6 mg every 28 days
12-week implant: 10.8 mg every 12 weeks
Prostate cancer, stage B2 to C (in combination with an antiandrogen and radiotherapy; begin 8 weeks prior to radiotherapy): Males: SubQ:
Combination 28-day/12-week implant: 3.6 mg implant, followed in 28 days by 10.8 mg implant
28-day implant (alternate dosing): 3.6 mg; repeated every 28 days for a total of 4 doses
Breast cancer, advanced: Females: SubQ: 3.6 mg every 28 days
Endometriosis: Females: SubQ: 3.6 mg every 28 days for 6 months
Endometrial thinning: Females: SubQ: 3.6 mg every 28 days for 1 or 2 doses
Hormone therapy for transgender females (male-to-female) (adjunct) (off-label use): SubQ: 3.6 mg every 4 weeks in combination with other appropriate agents (Mueller 2011).
Prevention of early menopause during chemotherapy for early stage hormone receptor negative breast cancer (off-label use): Adult females: SubQ: 3.6 mg every 28 days starting 1 week prior to the first chemotherapy dose; continue until within 2 weeks before or after the final chemotherapy dose (Moore 2015).
Dosing: Geriatric
Males: Refer to adult dosing.
Administration
SubQ: Administer implant by inserting needle at a 30- to 45-degree angle into the anterior abdominal wall below the navel line. Use caution while injecting goserelin into the anterior abdominal wall (due to the proximity of underlying inferior epigastric artery and its branches). Goserelin is an implant; therefore, do not attempt to eliminate air bubbles prior to injection (may displace implant). Do not attempt to aspirate prior to injection; if a large vessel is penetrated, blood will be visualized in the syringe chamber (if vessel is penetrated, withdraw needle and inject elsewhere with a new syringe). Do not penetrate into muscle or peritoneum. Implant may be detected by ultrasound if removal is required. Monitor for signs/symptoms of abdominal hemorrhage. Use extra care when administering goserelin to patients with a low BMI and/or to patients receiving full dose anticoagulation.
Storage
Store at room temperature not to exceed 25°C (77°F). Keep in foil pouch until ready to use to protect from light and moisture.
Drug Interactions
Antidiabetic Agents: Hyperglycemia-Associated Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Antidiabetic Agents. Monitor therapy
Choline C 11: Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Analogs may diminish the therapeutic effect of Choline C 11. Monitor therapy
Corifollitropin Alfa: Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Analogs may enhance the therapeutic effect of Corifollitropin Alfa. Avoid combination
Haloperidol: QT-prolonging Agents (Indeterminate Risk - Caution) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Haloperidol. Monitor therapy
Indium 111 Capromab Pendetide: Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Analogs may diminish the diagnostic effect of Indium 111 Capromab Pendetide. Avoid combination
QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk): QT-prolonging Agents (Indeterminate Risk - Caution) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
Interferes with pituitary gonadotropic and gonadal function tests during and for up to 12 weeks after discontinued
Adverse Reactions
Some frequencies not defined. Percentages reported with the 1-month implant:
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Vasodilation (females 57%), peripheral edema (females 21%)
Central nervous system: Headache (females 32% to 75%; males 1% to 5%), emotional lability (females 60%), depression (females 54%; males 1% to 5%), pain (8% to 17%), dyspareunia (females 14%), insomnia (5% to 11%)
Dermatologic: Diaphoresis (females 16% to 45%; males 6%), acne vulgaris (females 42%; usually within 1 month after starting treatment), seborrhea (females 26%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hot flash (females 57% to 96%; males 64%), decreased libido (females 48% to 61%), increased libido (females 12%)
Gastrointestinal: Abdominal pain (females 7% to 11%), nausea (5% to 11%)
Genitourinary: Vaginitis (75%), breast atrophy (females 33%), sexual disorder (males 21%), breast hypertrophy (females 18%), decrease in erectile frequency (18%), pelvic symptoms (females 18%), genitourinary signs and symptoms (lower; males 13%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Tumor flare (females 23%; males: Incidence not reported)
Infection: Infection (females 13%; males: Incidence not reported)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Decreased bone mineral density (females 23%; ~4% decrease from baseline in 6 months; male: Incidence not reported), weakness (females 11%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Edema (females 5%; male 7%), hypertension (1% to 6%), cardiac failure (males 5%), cardiac arrhythmia (males >1% to <5%), cerebrovascular accident (males >1% to <5%), peripheral vascular disease (males >1% to <5%), varicose veins (males >1% to <5%), chest pain (1% to <5%), myocardial infarction (males <1% to <5%), palpitations, tachycardia (females)
Central nervous system: Lethargy (females ≤8%), migraine (females 1% to 7%), dizziness (females 6%; male 5%), malaise (females ≤5%), chills (males >1% to <5%), anxiety (1% to <5%), nervousness (females 3% to 5%), voice disorder (females 3%), abnormality in thinking, drowsiness, paresthesia
Dermatologic: Skin rash (males 6% to 8%; female frequency not reported), hair disease (females 4%), pruritus (females 2%), alopecia, skin discoloration, xeroderma
Endocrine & metabolic: Gynecomastia (males 8%), hirsutism (7%), gout (males >1% to <5%), hyperglycemia (males >1% to <5%), weight gain (>1% to <5%)
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia (1% to 5%), gastric ulcer (males >1% to <5%), constipation (1% to <5%), diarrhea (1% to <5%), vomiting (1% to <5%), increased appetite (females 2%), dyspepsia, flatulence, xerostomia
Genitourinary: Pelvic pain (females 9%; males 6%), mastalgia (>1% to 7%), uterine hemorrhage (6%), vulvovaginitis (5%), breast swelling (males >1% to <5%), urinary tract obstruction (males: >1% to <5%), urinary tract infection (1% to <5%), urinary frequency, vaginal hemorrhage
Hematologic & oncologic: Anemia (males >1% to <5%), bruise, hemorrhage
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reaction
Infection: Sepsis (males >1% to <5%)
Local: Application site reaction (females 6%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Myalgia (females 3%, males frequency not reported), leg cramps (females 2%, males frequency not reported), hypertonia (females 1%; male frequency not reported), arthralgia, arthropathy
Ophthalmic: Amblyopia, dry eye syndrome
Renal: Renal insufficiency (<1% to >5%)
Respiratory: Upper respiratory tract infection (males 7%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (males 5%), flu-like symptoms (females 5%, male frequency not reported), pharyngitis (females 5%), sinusitis (females ≥1%; male frequency not reported), bronchitis, cough, epistaxis, rhinitis
Miscellaneous: Fever
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports (with monthly or 3-month implant): Anaphylaxis, bone fracture, convulsions, decreased glucose tolerance, decreased HDL cholesterol, deep vein thrombosis, diabetes mellitus, hypercalcemia, hypercholesterolemia, hyperlipidemia, hypotension, increased HDL cholesterol, increased LDL cholesterol, increased serum ALT, increased serum AST, increased serum triglycerides, injection site reaction (including vascular injury, pain, hematoma, hemorrhage, hemorrhagic shock), osteoporosis, ovarian cyst, ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, pituitary apoplexy, pituitary neoplasm (including adenoma), pulmonary embolism, psychotic reaction, transient ischemic attacks
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Cervical resistance: Cervical resistance may be increased; use caution when dilating the cervix for endometrial ablation.
- Decreased bone density: Has been reported in women and may be irreversible; use caution if other risk factors are present; evaluate and institute preventive treatment if necessary.
- Hypercalcemia: Hypercalcemia has been reported in prostate and breast cancer patients with bone metastases. Initiate appropriate management if hypercalcemia occurs.
- Hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia has been reported in males and may manifest as diabetes or worsening of preexisting diabetes (worsening glycemic control). Monitor blood glucose and HbA1c and manage diabetes appropriately.
- Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions (including acute anaphylactic reactions) and antibody formation may occur; monitor.
- Injection site injury: Injection site and vascular injury, including pain, hematoma, hemorrhage and hemorrhagic shock (requiring blood transfusions or surgical intervention) have been reported with goserelin. Use extra caution when administering to patients with a low BMI and/or to patients receiving full dose anticoagulation. Use caution while injecting goserelin into the anterior abdominal wall (due to the proximity of underlying inferior epigastric artery and its branches). Monitor for signs/symptoms of abdominal hemorrhage. Inform patient to immediately report abdominal pain, abdominal distention, dyspnea, dizziness, hypotension, and/or altered level of consciousness.
- Pituitary apoplexy: Rare cases of pituitary apoplexy (frequently secondary to pituitary adenoma) have been observed with GnRH agonist administration (onset from 1 hour to usually <2 weeks); may present as sudden headache, vomiting, visual or mental status changes, and infrequently cardiovascular collapse; immediate medical attention required.
- Tumor flare: Transient increases in serum testosterone (in men with prostate cancer) and estrogen (in women with breast cancer) may result in a worsening of disease signs and symptoms (tumor flare) during the first few weeks of treatment. Some patients experienced a temporary worsening of bone pain, which may be managed symptomatically. Spinal cord compression and urinary tract obstruction have been reported when used for prostate cancer; closely observe patients for symptoms (eg, ureteral obstruction, weakness, paresthesias) in first few weeks of therapy. Manage with standard treatment; consider orchiectomy for extreme cases.
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Androgen deprivation therapy may increase the risk for cardiovascular disease (Levine, 2010). An increased risk for MI, sudden cardiac death, and stroke has been observed. Monitor for signs/symptoms of cardiovascular disease; manage according to current clinical practice. Androgen deprivation therapy may cause prolongation of the QT/QTc interval; evaluate risk versus benefit in patients with congenital long QT syndrome, heart failure, frequent electrolyte abnormalities, and in patients taking medication known to prolong the QT interval. Correct electrolytes prior to initiation and consider periodic electrolyte and ECG monitoring.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Obese patients: A decreased AUC may be observed when using the 3-month implant in obese patients. Monitor testosterone levels if desired clinical response is not observed.
- Underweight patients: Use extra care when administering to patients with a low BMI.
- Women: Women of childbearing potential should not receive therapy until pregnancy has been excluded. Nonhormonal contraception is recommended during therapy and for 12 weeks after therapy is discontinued. Chronic administration may result in effects on reproductive function due to antigonadotropic properties.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Implant removal: If removal is necessary, implant may be located by ultrasound.
Monitoring Parameters
Monitor blood glucose and HbA1c (periodically), bone mineral density, serum calcium, cholesterol/lipids; monitor for signs/symptoms of abdominal hemorrhage following injection.
Prostate cancer: Consider periodic ECG and electrolyte monitoring. Monitor for weakness, paresthesias, tumor flare, urinary tract obstruction, and spinal cord compression in first few weeks of therapy.
Transgender hormone therapy: Serum testosterone levels (goal <50 ng/dL) every 3 months during the first year and then annually or biannually; serum luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FHS), and prolactin levels at baseline and annually; routine cancer and laboratory screening as in non-transgender individuals for all tissues present (ES [Hembree 2017]; Mueller 2011).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Goserelin induces hormonal changes which increase the risk for fetal loss and use is contraindicated in pregnancy unless being used for palliative treatment of advanced breast cancer.
Breast cancer: If used for the palliative treatment of breast cancer during pregnancy, the potential for increased fetal loss should be discussed with the patient.
Endometriosis, endometrial thinning: Use is contraindicated during pregnancy. Women of childbearing potential should not receive therapy until pregnancy has been excluded. Nonhormonal contraception is recommended for premenopausal women during therapy and for 12 weeks after therapy is discontinued. Although ovulation is usually inhibited and menstruation may stop, pregnancy prevention is not ensured during goserelin therapy. Changes in reproductive function may occur following chronic administration.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat prostate cancer.
- It is used to treat endometriosis.
- It is used to treat breast cancer.
- It is used to treat uterine bleeding.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Acne
- Decreased sex drive
- Sexual dysfunction
- Diarrhea
- Hot flash
- Lack of appetite
- Nausea
- Common cold symptoms
- Change in breast size
- Sweating
- Breast soreness or pain
- Testicle changes
- Trouble sleeping
- Loss of strength and energy
- Vaginal irritation
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe cerebrovascular disease like change in strength on one side is greater than the other, trouble speaking or thinking, change in balance, or vision changes
- High blood sugar like confusion, fatigue, increased thirst, increased hunger, passing a lot of urine, flushing, fast breathing, or breath that smells like fruit
- High calcium like weakness, confusion, fatigue, headache, nausea and vomiting, constipation, or bone pain
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive weight gain
- Swelling of arms or legs
- Weakness
- Trouble moving
- Trouble urination
- Injection site irritation
- Back pain
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Dizziness
- Severe headache
- Vision changes
- Pelvic pain
- Blood in the urine
- Depression
- Mood changes
- Fast heartbeat
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Passing out
- Menstruation
- Bone pain
- Enlarged breasts (males)
- Pituitary apoplexy like sudden headache, vomiting, passing out, mood changes, eye weakness, unable to move eyes, or vision changes.
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.