Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Solution, Oral, as dihydrochloride:
Xyzal: 2.5 mg/5 mL (148 mL [DSC]) [contains methylparaben, propylparaben, saccharin]
Xyzal Allergy 24HR Childrens: 2.5 mg/5 mL (148 mL) [alcohol free, dye free; contains methylparaben, propylparaben, saccharin; tutti-frutti flavor]
Generic: 2.5 mg/5 mL (118 mL, 148 mL)
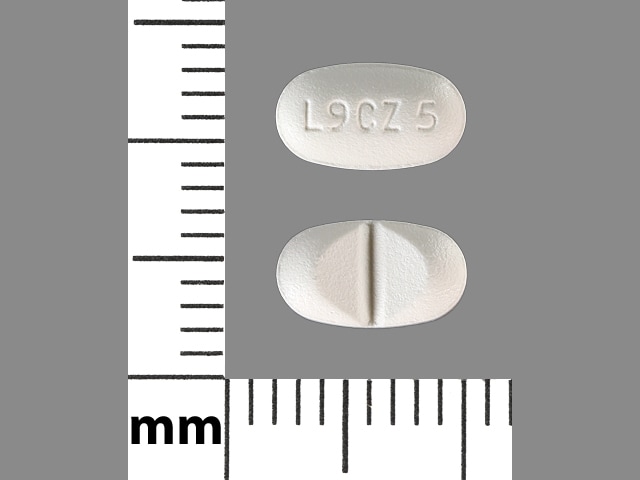
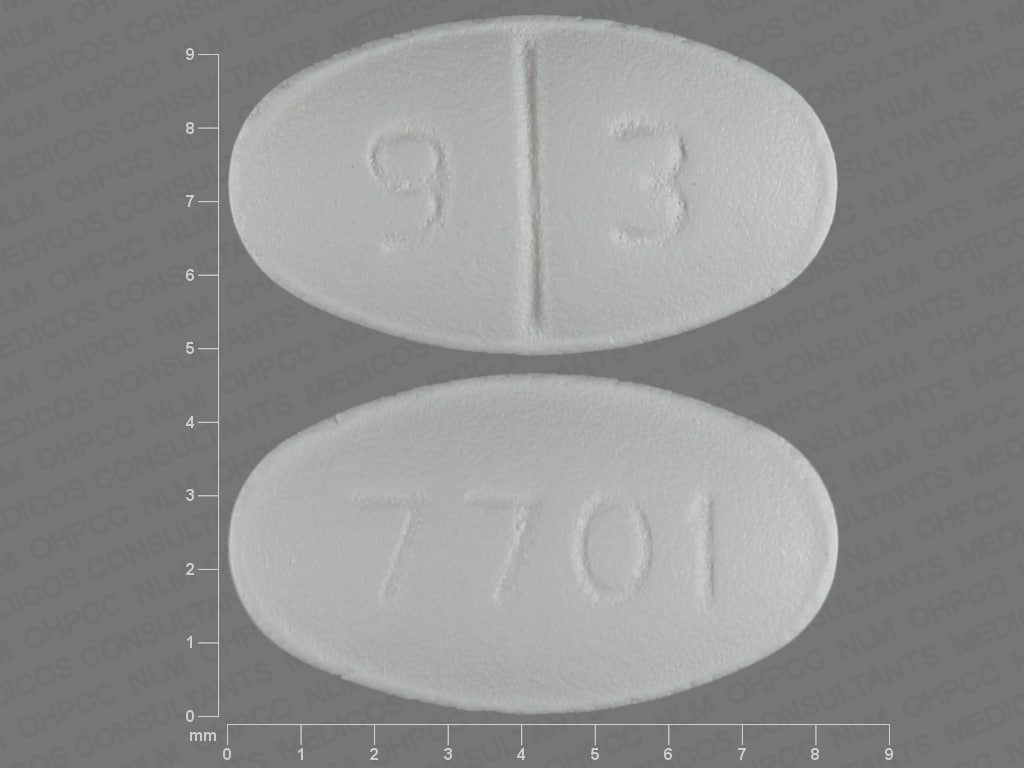
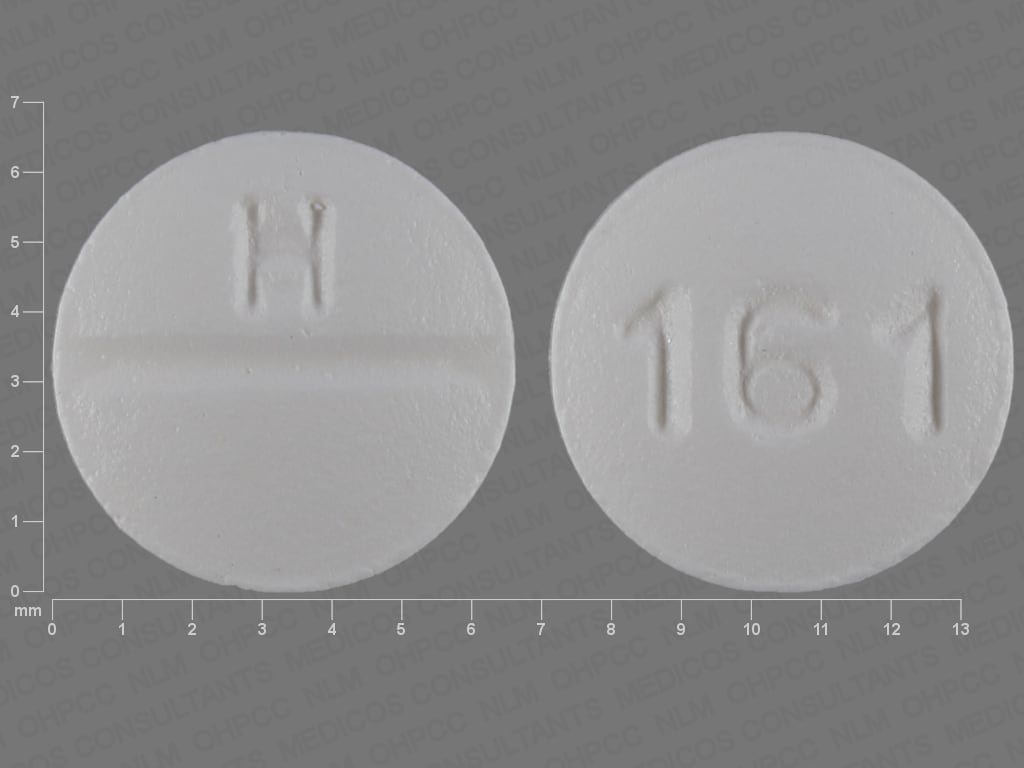
Tablet, Oral, as dihydrochloride:
Xyzal: 5 mg [DSC] [scored]
Xyzal Allergy 24HR: 5 mg [scored]
Generic: 5 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Levocetirizine is an antihistamine which selectively competes with histamine for H1-receptor sites on effector cells in the gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels, and respiratory tract. Levocetirizine, the active enantiomer of cetirizine, has twice the binding affinity at the H1-receptor compared to cetirizine.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Rapid and extensive
Distribution
Vd: Children 1 to 2 years: Oral solution: 0.37 ± 0.06 L/kg (Cranswick 2005); Children 6 to 11 years: Oral tablet: 0.4 ± 0.02 L/kg (Simons 2005); Adults: 0.4 L/kg
Metabolism
Minimal (<14%); via aromatic oxidation, N and O-dealkylation (via CYPA4), and taurine conjugation
Excretion
Urine (85.4 %); feces (12.9%)
Clearance: Children 1 to 2 years: Oral solution: 1.05 ± 0.1 mL/minute/kg (Cranswick 2005); Children 6 to 11 years: Oral tablet: 0.82 ± 0.05 mL/minute/kg (Simons 2005); Adults: 0.63 mL/kg/minute
Onset of Action
1 hour (Devillier 2008)
Time to Peak
Children 1 to 2 years: Oral solution: Median: 1 hour (range: 1 to 6 hours) (Cranswick 2005); Children 6 to 11 years: Oral tablet: 1.2 ± 0.2 hours (Simons 2005); Adults: Oral solution: 0.5 hours; Tablet: 0.9 hours
Duration of Action
24 hours (Devillier 2008)
Half-Life Elimination
Children 1 to 2 years: Oral solution: 4.09 ± 0.67 hours (Cranswick 2005); Children 6 to 11 years: Oral tablet: 5.7 ± 0.2 hours (Simons 2005); Adults: ~8 to 9 hours
Protein Binding
91% to 92%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
In patients with mild, moderate, severe renal impairment, and end-stage renal disease, the AUC increased by 1.8, 3.2, 4.3, and 5.7-fold, respectively, and the half-life increased by 1.4, 2, 2.9, and 4-fold, respectively.
Special Populations: Elderly
Total body Cl was approximately 33% lower in 9 elderly subjects, compared with younger adults.
Special Populations: Gender
Half-life was slightly shorter in women than in men; however, the body weight–adjusted oral Cl in women appears to be comparable with that in men.
Use: Labeled Indications
Chronic idiopathic urticaria: Treatment of uncomplicated skin manifestations of chronic idiopathic urticaria in adults and pediatric patients 6 months and older
Perennial allergic rhinitis: Relief of symptoms associated with perennial allergic rhinitis in adults and pediatric patients 6 months to 2 years
Allergic rhinitis (OTC only): Temporary relief of symptoms due to hay fever or other respiratory allergies (including rhinitis, sneezing, itchy/watery eyes, or itching of the throat/nose) in adults and pediatric patients 2 years and older
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to levocetirizine, cetirizine, or any component of the formulation; end-stage renal disease (CrCl <10 mL/minute); hemodialysis; infants and children 6 months to 11 years of age with renal impairment
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Chronic idiopathic urticaria: Oral: 5 mg once daily (in the evening); some patients may experience relief of symptoms with 2.5 mg once daily. In one clinical trial, the titrated use of higher doses (up to 10 mg twice daily) in adults demonstrated clinical improvement (Staevska 2010).
Allergic rhinitis (OTC only): Oral: 5 mg once daily (in the evening); some patients with less severe symptoms may experience relief with 2.5 mg once daily; maximum dose: 5 mg/day
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing; dosing should begin at the lower end of the dosing range.
Dosing: Pediatric
Allergic rhinitis, perennial: Oral:
Infants ≥6 months and Children ≤5 years: 1.25 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 1.25 mg/day; Note: In children >2 years, dosing based on previous FDA approved manufacturer labeling (Xyzal prescribing information January 2016)
Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: Note: Dosing based on previous FDA approved manufacturer labeling (Xyzal prescribing information January 2016):
6 to 11 years: 2.5 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 2.5 mg/day
≥12 years: 5 mg once daily (in the evening); some patients may experience relief of symptoms with 2.5 mg once daily
Hay fever and other respiratory allergies: OTC labeling: Oral:
Children 2 to 5 years: 1.25 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 1.25 mg/day
Children 6 to 11 years: 2.5 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 2.5 mg/day
Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: 2.5 to 5 mg once daily (in the evening); dose based on symptom severity; maximum daily dose: 5 mg/day
Urticaria, chronic: Oral:
Infants ≥6 months and Children ≤5 years: 1.25 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 1.25 mg/day
Children 6 to 11 years: 2.5 mg once daily (in the evening); maximum daily dose: 2.5 mg/day
Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: 5 mg once daily (in the evening); some patients may experience relief of symptoms with 2.5 mg once daily
Administration
Administer in the evening with or without food. Use an accurate measuring device for the oral solution; a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device.
Storage
Xyzal: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
Xyzal (OTC): Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F)
Levocetirizine Images
Drug Interactions
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Aclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Alcohol (Ethyl): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Alcohol (Ethyl). Monitor therapy
Alizapride: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Amantadine: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Amezinium: Antihistamines may enhance the stimulatory effect of Amezinium. Monitor therapy
Amphetamines: May diminish the sedative effect of Antihistamines. Monitor therapy
Anticholinergic Agents: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Azelastine (Nasal): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Azelastine (Nasal). Avoid combination
Benzylpenicilloyl Polylysine: Antihistamines may diminish the diagnostic effect of Benzylpenicilloyl Polylysine. Management: Suspend systemic H1 antagonists for benzylpenicilloyl-polylysine skin testing and delay testing until systemic antihistaminic effects have dissipated. A histamine skin test may be used to assess persistent antihistaminic effects. Consider therapy modification
Betahistine: Antihistamines may diminish the therapeutic effect of Betahistine. Monitor therapy
Blonanserin: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Blonanserin. Consider therapy modification
Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Brexanolone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Brexanolone. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Bromopride: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
Buprenorphine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Buprenorphine. Management: Consider reduced doses of other CNS depressants, and avoiding such drugs in patients at high risk of buprenorphine overuse/self-injection. Initiate buprenorphine at lower doses in patients already receiving CNS depressants. Consider therapy modification
Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cannabis: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Chloral Betaine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Chlormethiazole: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Monitor closely for evidence of excessive CNS depression. The chlormethiazole labeling states that an appropriately reduced dose should be used if such a combination must be used. Consider therapy modification
Chlorphenesin Carbamate: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cimetropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Cimetropium. Avoid combination
CNS Depressants: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Dimethindene (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Doxylamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: The manufacturer of Diclegis (doxylamine/pyridoxine), intended for use in pregnancy, specifically states that use with other CNS depressants is not recommended. Monitor therapy
Dronabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Droperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider dose reductions of droperidol or of other CNS agents (eg, opioids, barbiturates) with concomitant use. Exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Consider therapy modification
Eluxadoline: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Eluxadoline. Avoid combination
Esketamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Flunitrazepam: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Flunitrazepam. Consider therapy modification
Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic): Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
Glucagon: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Glucagon. Specifically, the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects may be increased. Monitor therapy
Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation): Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation). Avoid combination
Glycopyrronium (Topical): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Hyaluronidase: Antihistamines may diminish the therapeutic effect of Hyaluronidase. Management: Patients receiving antihistamines (particularly at larger doses) may not experience the desired clinical response to standard doses of hyaluronidase. Larger doses of hyaluronidase may be required. Consider therapy modification
HYDROcodone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of HYDROcodone. Management: Avoid concomitant use of hydrocodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
HydrOXYzine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Ipratropium (Oral Inhalation): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Itopride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Itopride. Monitor therapy
Kava Kava: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Lemborexant: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Dosage adjustments of lemborexant and of concomitant CNS depressants may be necessary when administered together because of potentially additive CNS depressant effects. Close monitoring for CNS depressant effects is necessary. Consider therapy modification
Levosulpiride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Levosulpiride. Avoid combination
Lofexidine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Drugs listed as exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Monitor therapy
Magnesium Sulfate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Methotrimeprazine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Methotrimeprazine. Methotrimeprazine may enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Reduce adult dose of CNS depressant agents by 50% with initiation of concomitant methotrimeprazine therapy. Further CNS depressant dosage adjustments should be initiated only after clinically effective methotrimeprazine dose is established. Consider therapy modification
MetyroSINE: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of MetyroSINE. Monitor therapy
Mianserin: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Minocycline (Systemic): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Mirabegron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Mirabegron. Monitor therapy
Nabilone: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Nitroglycerin: Anticholinergic Agents may decrease the absorption of Nitroglycerin. Specifically, anticholinergic agents may decrease the dissolution of sublingual nitroglycerin tablets, possibly impairing or slowing nitroglycerin absorption. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Opioid Agonists. Management: Avoid concomitant use of opioid agonists and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Orphenadrine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Orphenadrine. Avoid combination
Oxatomide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Oxomemazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
OxyCODONE: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of OxyCODONE. Management: Avoid concomitant use of oxycodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Paraldehyde: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Paraldehyde. Avoid combination
Perampanel: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Patients taking perampanel with any other drug that has CNS depressant activities should avoid complex and high-risk activities, particularly those such as driving that require alertness and coordination, until they have experience using the combination. Consider therapy modification
Piribedil: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Piribedil. Monitor therapy
Pitolisant: Antihistamines may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pitolisant. Avoid combination
Potassium Chloride: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Chloride. Management: Patients on drugs with substantial anticholinergic effects should avoid using any solid oral dosage form of potassium chloride. Avoid combination
Potassium Citrate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Citrate. Avoid combination
Pramipexole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Pramipexole. Monitor therapy
Pramlintide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. These effects are specific to the GI tract. Consider therapy modification
Ramosetron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Ramosetron. Monitor therapy
Revefenacin: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
ROPINIRole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of ROPINIRole. Monitor therapy
Rotigotine: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Rotigotine. Monitor therapy
Rufinamide: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Specifically, sleepiness and dizziness may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Secretin: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Secretin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of anticholinergic agents and secretin. Discontinue anticholinergic agents at least 5 half-lives prior to administration of secretin. Consider therapy modification
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors: CNS Depressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors. Specifically, the risk of psychomotor impairment may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Sodium Oxybate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider alternatives to combined use. When combined use is needed, consider minimizing doses of one or more drugs. Use of sodium oxybate with alcohol or sedative hypnotics is contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Suvorexant: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Suvorexant. Management: Dose reduction of suvorexant and/or any other CNS depressant may be necessary. Use of suvorexant with alcohol is not recommended, and the use of suvorexant with any other drug to treat insomnia is not recommended. Consider therapy modification
Tapentadol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Avoid concomitant use of tapentadol and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Tetrahydrocannabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Thalidomide: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Thalidomide. Avoid combination
Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics: Anticholinergic Agents may increase the serum concentration of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Tiotropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Tiotropium. Avoid combination
Topiramate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Topiramate. Monitor therapy
Trimeprazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Umeclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Zolpidem: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Zolpidem. Management: Reduce the Intermezzo brand sublingual zolpidem adult dose to 1.75 mg for men who are also receiving other CNS depressants. No such dose change is recommended for women. Avoid use with other CNS depressants at bedtime; avoid use with alcohol. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
>10%: Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (infants: 13%; children: 4%)
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Drowsiness (3% to 6%), fatigue (adolescents and adults: 4%)
Gastrointestinal: Constipation (infants: 7%), vomiting (4%), xerostomia (adolescents and adults: 2% to 3%)
Otic: Otitis media (children: 3%)
Respiratory: Nasopharyngitis (adolescents and adults: 4% to 6%), cough (children: 3%), epistaxis (children: 2%), pharyngitis (adolescents and adults: 2%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (children: 4%)
Frequency not defined: Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Aggressive behavior, agitation, anaphylaxis, angioedema, arthralgia, blurred vision, depression, dizziness, dysgeusia, dyspnea, dysuria, edema, febrile seizures, fixed drug eruption, hallucination, hepatitis, hypersensitivity reaction, increased appetite, increased serum bilirubin, increased serum transaminases, insomnia, movement disorder (including dystonia and oculogyric crisis), myalgia, nausea, nightmares, palpitations, paresthesia, pruritus, seizure, skin rash, suicidal ideation, syncope, tachycardia, tremor, urinary retention, urticaria, vertigo, visual disturbances, weight gain
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- CNS depression: May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks which require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
- Pruritus: Rebound pruritus may occur within several days after stopping cetirizine, usually after long-term (eg, months to years) use.
Disease-related concerns:
- Renal impairment: Levocetirizine is excreted primarily by the kidneys; use with caution in adults with mild to severe renal impairment; dosage adjustments may be needed. Use is contraindicated in end-stage renal disease (CrCl <10 mL/minute), patients undergoing hemodialysis, and in infants and children 6 months to 11 years of age with renal impairment.
- Urinary retention: Urinary retention may occur; use with caution in patients with increased risk of urinary retention (including spinal cord lesions or prostatic hyperplasia); discontinue if urinary retention occurs.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Elderly: Use with caution in the elderly.
Monitoring Parameters
Creatinine clearance (prior to treatment for dosing adjustment)
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Guidelines for the use of antihistamines in the treatment of allergic rhinitis or urticaria in pregnancy are generally the same as in nonpregnant females. Second generation antihistamines may be used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and urticaria during pregnancy; however, information related to the use of levocetirizine in pregnancy is limited and other medications may be preferred (Wallace 2008; Zuberbier 2018).
Levocetirizine is the active enantiomer of cetirizine; refer to the cetirizine monograph for additional information.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to ease allergy signs.
- It is used to treat hives.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Loss of strength and energy
- Fatigue
- Stuffy nose
- Sore throat
- Nosebleed
- Dry mouth
- Cough
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Ear pain
- Difficult urination
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.