Boxed Warning
Appropriate use:
This fixed combination drug is not indicated for initial therapy of hypertension. Hypertension requires therapy titrated to the individual patient. If the fixed combination represents the dosage so determined, its use may be more convenient in patient management. The treatment of hypertension is not static, but must be reevaluated as conditions in each patient warrant.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet:
Methyldopa 250 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 15 mg
Methyldopa 250 mg and hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Methyldopa stimulates central alpha-adrenergic receptors by a false transmitter that results in a decreased sympathetic outflow to the heart, kidneys, and peripheral vasculature.
Hydrochlorothiazide inhibits sodium reabsorption in the distal tubules causing increased excretion of sodium and water as well as potassium and hydrogen ions.
Use: Labeled Indications
Hypertension: Management of hypertension
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to methyldopa, hydrochlorothiazide, sulfonamide-derived drugs, or any component of the formulation; active hepatic disease (eg, acute hepatitis, active cirrhosis); hepatic disorders previously associated with use of methyldopa; concurrent use of MAO inhibitors; anuria
Note: Although the FDA approved product labeling states this medication is contraindicated with other sulfonamide-containing drug classes, the scientific basis of this statement has been challenged. See “Warnings/Precautions” for more detail.
Documentation of allergenic cross-reactivity for thiazide-related diuretics is limited. However, because of similarities in chemical structure and/or pharmacologic actions, the possibility of cross-sensitivity cannot be ruled out with certainty.
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Hypertension: Oral: Note: Dose is individualized.
Replacement therapy: Initial: Methyldopa 250 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 15 mg 2 to 3 times daily or methyldopa 250 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 25 mg twice daily or methyldopa 500 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 30 mg once daily or methyldopa 500 mg/hydrochlorothiazide 50 mg once daily.
Maximum daily dose, based on the hydrochlorothiazide content: Oral: 50 mg/day
Dosing: Geriatric
Avoid use (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
Administration
When the dose of methyldopa component is increased, consider administration in the evening to minimize daytime sedation.
Storage
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Protect from light.
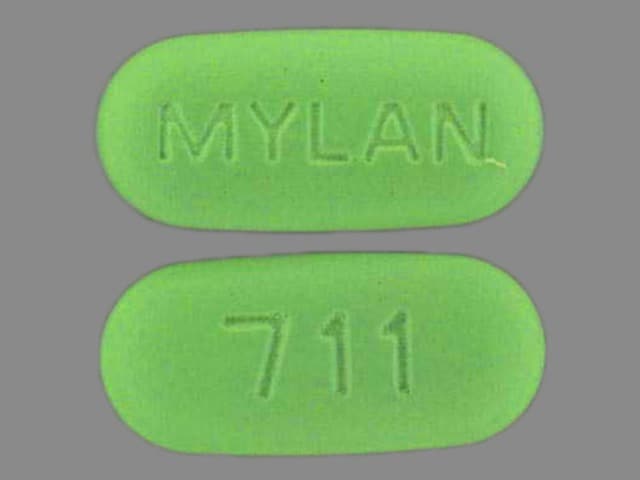
Methyldopa and Hydrochlorothiazide Images
Drug Interactions
Ajmaline: Sulfonamides may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Ajmaline. Specifically, the risk for cholestasis may be increased. Monitor therapy
Alcohol (Ethyl): May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Alfuzosin: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Allopurinol: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the potential for allergic or hypersensitivity reactions to Allopurinol. Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may increase the serum concentration of Allopurinol. Specifically, Thiazide Diuretics may increase the concentration of Oxypurinol, an active metabolite of Allopurinol. Monitor therapy
Amifostine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Amifostine. Management: When amifostine is used at chemotherapy doses, blood pressure lowering medications should be withheld for 24 hours prior to amifostine administration. If blood pressure lowering therapy cannot be withheld, amifostine should not be administered. Consider therapy modification
Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic). Avoid combination
Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical). Monitor therapy
Amphetamines: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the hypotensive effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Anticholinergic Agents: May increase the serum concentration of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Antidiabetic Agents: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Antidiabetic Agents. Monitor therapy
Antidiabetic Agents: Hyperglycemia-Associated Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Antidiabetic Agents. Monitor therapy
Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]): Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]). Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Benazepril: HydroCHLOROthiazide may enhance the hypotensive effect of Benazepril. HydroCHLOROthiazide may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Benazepril. Benazepril may decrease the serum concentration of HydroCHLOROthiazide. Monitor therapy
Benperidol: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Beta2-Agonists: May enhance the hypokalemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Beta-Blockers: Alpha2-Agonists may enhance the AV-blocking effect of Beta-Blockers. Sinus node dysfunction may also be enhanced. Beta-Blockers may enhance the rebound hypertensive effect of Alpha2-Agonists. This effect can occur when the Alpha2-Agonist is abruptly withdrawn. Management: Closely monitor heart rate during treatment with a beta blocker and clonidine. Withdraw beta blockers several days before clonidine withdrawal when possible, and monitor blood pressure closely. Recommendations for other alpha2-agonists are unavailable. Exceptions: Levobunolol; Metipranolol. Consider therapy modification
Bile Acid Sequestrants: May decrease the absorption of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. The diuretic response is likewise decreased. Consider therapy modification
Bradycardia-Causing Agents: May enhance the bradycardic effect of other Bradycardia-Causing Agents. Monitor therapy
Brigatinib: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Brigatinib may enhance the bradycardic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Bromperidol. Bromperidol may diminish the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Avoid combination
Calcium Salts: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may decrease the excretion of Calcium Salts. Continued concomitant use can also result in metabolic alkalosis. Monitor therapy
CarBAMazepine: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CarBAMazepine. Specifically, there may be an increased risk for hyponatremia. Monitor therapy
Cardiac Glycosides: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Cardiac Glycosides. Specifically, cardiac glycoside toxicity may be enhanced by the hypokalemic and hypomagnesemic effect of thiazide diuretics. Monitor therapy
Ceritinib: Bradycardia-Causing Agents may enhance the bradycardic effect of Ceritinib. Management: If this combination cannot be avoided, monitor patients for evidence of symptomatic bradycardia, and closely monitor blood pressure and heart rate during therapy. Exceptions are discussed in separate monographs. Consider therapy modification
COMT Inhibitors: May decrease the metabolism of COMT Substrates. Monitor therapy
Corticosteroids (Orally Inhaled): May enhance the hypokalemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Corticosteroids (Systemic): May enhance the hypokalemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Cyclophosphamide: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Cyclophosphamide. Specifically, granulocytopenia may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Dexketoprofen: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Sulfonamides. Monitor therapy
Dexmethylphenidate: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Diacerein: May enhance the therapeutic effect of Diuretics. Specifically, the risk for dehydration or hypokalemia may be increased. Monitor therapy
Diazoxide: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Diazoxide. Monitor therapy
Diazoxide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Dichlorphenamide: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the hypokalemic effect of Dichlorphenamide. Monitor therapy
Dofetilide: HydroCHLOROthiazide may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Dofetilide. HydroCHLOROthiazide may increase the serum concentration of Dofetilide. Avoid combination
DULoxetine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of DULoxetine. Monitor therapy
Fexinidazole [INT]: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Fexinidazole [INT]. Avoid combination
Fexinidazole [INT]: Bradycardia-Causing Agents may enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Fexinidazole [INT]. Avoid combination
Herbs (Hypertensive Properties): May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Herbs (Hypotensive Properties): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Hypotension-Associated Agents: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Hypotension-Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products: Methyldopa may diminish the therapeutic effect of Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products. Management: Discontinue all drugs that may inhibit or interfere with catecholamine transport or uptake for at least 5 biological half-lives before iobenguane administration. Do not administer methyldopa until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose. Avoid combination
Ipragliflozin: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Specifically, the risk for intravascular volume depletion may be increased. Monitor therapy
Iron Preparations: May decrease the serum concentration of Methyldopa. Exceptions: Ferric Carboxymaltose; Ferric Derisomaltose; Ferric Gluconate; Ferric Hydroxide Polymaltose Complex; Ferric Pyrophosphate Citrate; Ferumoxytol; Iron Dextran Complex; Iron Sucrose. Consider therapy modification
Ivabradine: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Ivabradine. Monitor therapy
Ivabradine: Bradycardia-Causing Agents may enhance the bradycardic effect of Ivabradine. Monitor therapy
Lacosamide: Bradycardia-Causing Agents may enhance the AV-blocking effect of Lacosamide. Monitor therapy
Levodopa-Containing Products: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Levodopa-Containing Products. Monitor therapy
Levosulpiride: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Levosulpiride. Avoid combination
Licorice: May enhance the hypokalemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Lithium: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may decrease the excretion of Lithium. Consider therapy modification
Lormetazepam: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Mecamylamine: Sulfonamides may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Mecamylamine. Avoid combination
Methenamine: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Methenamine. Monitor therapy
Methylphenidate: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Midodrine: May enhance the bradycardic effect of Bradycardia-Causing Agents. Monitor therapy
Mirtazapine: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Alpha2-Agonists. Management: Consider avoiding concurrent use. If the combination cannot be avoided, monitor for decreased effects of alpha2-agonists if mirtazapine is initiated/dose increased, or increased effects if mirtazapine is discontinued/dose decreased. Consider therapy modification
Molsidomine: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Methyldopa. Avoid combination
Multivitamins/Fluoride (with ADE): May enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Minerals (with ADEK, Folate, Iron): May decrease the serum concentration of Methyldopa. Management: Consider separating doses of these products by 2 or more hours to minimize this interaction; however, the success of this action appears limited. Monitor for decreased therapeutic effects of methyldopa with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
Multivitamins/Minerals (with AE, No Iron): Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may increase the serum concentration of Multivitamins/Minerals (with AE, No Iron). Specifically, thiazide diuretics may decrease the excretion of calcium, and continued concomitant use can also result in metabolic alkalosis. Monitor therapy
Naftopidil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Neuromuscular-Blocking Agents (Nondepolarizing): Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the neuromuscular-blocking effect of Neuromuscular-Blocking Agents (Nondepolarizing). Monitor therapy
Nicergoline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nicorandil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nitroprusside: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Nitroprusside. Monitor therapy
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Obinutuzumab: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Management: Consider temporarily withholding blood pressure lowering medications beginning 12 hours prior to obinutuzumab infusion and continuing until 1 hour after the end of the infusion. Consider therapy modification
Opioid Agonists: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Diuretics. Opioid Agonists may diminish the therapeutic effect of Diuretics. Monitor therapy
OXcarbazepine: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of OXcarbazepine. Specifically, there may be an increased risk for hyponatremia. Monitor therapy
Pentoxifylline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Pholcodine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Pholcodine. Monitor therapy
Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Porfimer: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Porfimer. Monitor therapy
Promazine: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Promazine. Avoid combination
Prostacyclin Analogues: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Quinagolide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Reboxetine: May enhance the hypokalemic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Riluzole: Methyldopa may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Riluzole. Specifically, the risk of hepatotoxicity may be increased. Management: Consider alternatives to methyldopa in patients receiving treatment with riluzole due to the potential for additive hepatotoxicity. Consider therapy modification
Ruxolitinib: May enhance the bradycardic effect of Bradycardia-Causing Agents. Management: Ruxolitinib Canadian product labeling recommends avoiding use with bradycardia-causing agents to the extent possible. Monitor therapy
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors: May enhance the hyponatremic effect of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Serotonin/Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Alpha2-Agonists. Monitor therapy
Siponimod: Bradycardia-Causing Agents may enhance the bradycardic effect of Siponimod. Management: Avoid coadministration of siponimod with drugs that may cause bradycardia. Consider therapy modification
Sodium Phosphates: Diuretics may enhance the nephrotoxic effect of Sodium Phosphates. Specifically, the risk of acute phosphate nephropathy may be enhanced. Management: Consider avoiding this combination by temporarily suspending treatment with diuretics, or seeking alternatives to oral sodium phosphate bowel preparation. If the combination cannot be avoided, hydrate adequately and monitor fluid and renal status. Consider therapy modification
Terlipressin: May enhance the bradycardic effect of Bradycardia-Causing Agents. Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: May enhance the bradycardic effect of Bradycardia-Causing Agents. Monitor therapy
Topiramate: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the hypokalemic effect of Topiramate. Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may increase the serum concentration of Topiramate. Management: Monitor for increased topiramate levels/adverse effects (e.g., hypokalemia) with initiation/dose increase of a thiazide diuretic. Closely monitor serum potassium concentrations with concomitant therapy. Topiramate dose reductions may be necessary. Consider therapy modification
Toremifene: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Toremifene. Monitor therapy
Tricyclic Antidepressants: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Alpha2-Agonists. Management: Consider avoiding this combination. If used, monitor for decreased effects of the alpha2-agonist. Exercise great caution if discontinuing an alpha2-agonist in a patient receiving a TCA. Consider therapy modification
Valsartan: HydroCHLOROthiazide may enhance the hypotensive effect of Valsartan. Valsartan may increase the serum concentration of HydroCHLOROthiazide. Monitor therapy
Verteporfin: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Verteporfin. Monitor therapy
Vitamin D Analogs: Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics may enhance the hypercalcemic effect of Vitamin D Analogs. Monitor therapy
Yohimbine: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Test Interactions
See individual agents.
Adverse Reactions
See individual agents.
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Electrolyte disturbances: Hypokalemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hypomagnesemia, and hyponatremia can occur with hydrochlorothiazide.
- Gout: In certain patients with a history of gout, a familial predisposition to gout, or chronic renal failure, gout can be precipitated by hydrochlorothiazide. This risk may be increased with doses ≥25 mg (Gurwitz 1997).
- Hematologic effects: Rare cases of reversible granulocytopenia and thrombocytopenia have been reported with methyldopa. May rarely produce hemolytic anemia; positive Coombs' test occurs in 10% to 20% of patients usually occurring between 6 and 12 months of therapy; perform CBC periodically. If Coombs'-positive hemolytic anemia occurs during therapy, discontinue use and do not reinitiate; Coombs’ test may not revert back to normal for weeks to months following discontinuation.
- Hepatic effects: Methyldopa may rarely produce liver disorders including fatal hepatic necrosis; use with caution in patients with previous liver disease or dysfunction. Periodically monitor liver function during the first 6-12 weeks of therapy or when unexplained fever occurs; discontinue use if fever, abnormal liver function tests, or jaundice is present.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions may occur with hydrochlorothiazide. Risk is increased in patients with a history of allergy or bronchial asthma.
- Neuromuscular effects: Patients with severe bilateral cerebrovascular disease have exhibited involuntary choreoathetotic movements with methyldopa (rare); discontinue use if these symptoms develop.
- Ocular effects: Hydrochlorothiazide may cause acute transient myopia and acute angle-closure glaucoma, typically occurring within hours to weeks following initiation; discontinue therapy immediately in patients with acute decreases in visual acuity or ocular pain. Additional treatments may be needed if uncontrolled intraocular pressure persists. Risk factors may include a history of sulfonamide or penicillin allergy.
- Photosensitivity: Photosensitization may occur with hydrochlorothiazide.
- Sedation: Usually transient, sedation may occur with initiation or whenever the methyldopa dose is increased.
- Sulfonamide (“sulfa”) allergy: The FDA-approved product labeling for many medications containing a sulfonamide chemical group includes a broad contraindication in patients with a prior allergic reaction to sulfonamides. There is a potential for cross-reactivity between members of a specific class (eg, two antibiotic sulfonamides). However, concerns for cross-reactivity have previously extended to all compounds containing the sulfonamide structure (SO2NH2). An expanded understanding of allergic mechanisms indicates cross-reactivity between antibiotic sulfonamides and nonantibiotic sulfonamides may not occur or at the very least this potential is extremely low (Brackett 2004; Johnson 2005; Slatore 2004; Tornero 2004). In particular, mechanisms of cross-reaction due to antibody production (anaphylaxis) are unlikely to occur with nonantibiotic sulfonamides. T-cell-mediated (type IV) reactions (eg, maculopapular rash) are less well understood and it is not possible to completely exclude this potential based on current insights. In cases where prior reactions were severe (Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN), some clinicians choose to avoid exposure to these classes.
Disease-related concerns:
- Bariatric surgery: Dehydration: Avoid diuretics in the immediate postoperative period after bariatric surgery; electrolyte disturbances and dehydration may occur. Diuretics may be resumed, if indicated, once oral fluid intake goals are met (Ziegler 2009).
- Diabetes: Use hydrochlorothiazide with caution in patients with prediabetes or diabetes mellitus; may see a change in glucose control.
- Hepatic impairment: Use hydrochlorothiazide with caution in patients with severe hepatic dysfunction. In progressive or severe liver disease, avoid electrolyte and acid/base imbalances that might lead to hepatic encephalopathy/coma.
- Hypercalcemia: Thiazide diuretics may decrease renal calcium excretion; consider avoiding use in patients with hypercalcemia.
- Hypercholesterolemia: Use hydrochlorothiazide with caution in patients with moderate or high cholesterol concentrations.
- Hypokalemia: Use hydrochlorothiazide with caution in patients with hypokalemia; correct before initiating therapy.
- Parathyroid disease: Thiazide diuretics reduce calcium excretion; pathologic changes in the parathyroid glands with hypercalcemia and hypophosphatemia have been observed with prolonged use; should be discontinued prior to testing for parathyroid function.
- Renal impairment: Cumulative effects of hydrochlorothiazide may develop, including azotemia, in patients with impaired renal function. Avoid hydrochlorothiazide in severe renal disease (ineffective); may precipitate azotemia. The active metabolites of methyldopa accumulate in uremia.
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Hydrochlorothiazide can cause SLE exacerbation or activation.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: [US Boxed Warning]: Fixed-dose therapy is not indicated as the initial treatment for hypertension.
Monitoring Parameters
Blood pressure; serum electrolytes, BUN, creatinine; CBC; liver enzymes (periodically during the first 6 to 12 weeks or when unexplained fever occurs); Coombs test (direct) (may obtain prior to initiation and at 6 and 12 months).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
C
Pregnancy Considerations
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this combination. See individual agents.
Patient Education
- Discuss specific use of drug and side effects with patient as it relates to treatment. (HCAHPS: During this hospital stay, were you given any medicine that you had not taken before? Before giving you any new medicine, how often did hospital staff tell you what the medicine was for? How often did hospital staff describe possible side effects in a way you could understand?)
- Patient may experience headache, constipation, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, or lack of appetite. Have patient report immediately to prescriber signs of lupus (rash on the cheeks or other body parts, sunburn easy, muscle or joint pain, chest pain or shortness of breath, or swelling in the arms or legs), signs of infection, signs of high blood sugar (confusion, fatigue, increased thirst, increased hunger, passing a lot of urine, flushing, fast breathing, or breath that smells like fruit), signs of fluid and electrolyte problems (mood changes, confusion, muscle pain or weakness, abnormal heartbeat, severe dizziness, passing out, fast heartbeat, increased thirst, seizures, loss of strength and energy, lack of appetite, unable to pass urine or change in amount of urine passed, dry mouth, dry eyes, nausea, or vomiting), signs of liver problems (dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin), signs of kidney problems (unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain), signs of pancreatitis (severe abdominal pain, severe back pain, severe nausea, or vomiting), severe dizziness, passing out, severe loss of strength and energy, bruising, bleeding, sexual dysfunction, abnormal movements, burning or numbness feeling, shortness of breath, excessive weight gain, swelling of arms or legs, agitation, skin changes, vision changes, or eye pain (HCAHPS).
- Educate patient about signs of a significant reaction (eg, wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat). Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Patient should consult prescriber for additional questions.
Intended Use and Disclaimer: Should not be printed and given to patients. This information is intended to serve as a concise initial reference for health care professionals to use when discussing medications with a patient. You must ultimately rely on your own discretion, experience, and judgment in diagnosing, treating, and advising patients.