Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Tablet, Oral:
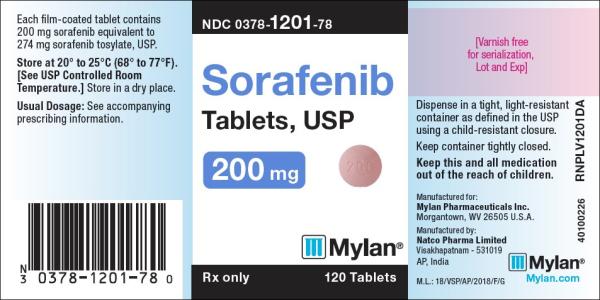
NexAVAR: 200 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Sorafenib is a multikinase inhibitor that inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by inhibiting intracellular Raf kinases (CRAF, BRAF, and mutant BRAF), and cell surface kinase receptors (VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, PDGFR-beta, cKIT, FLT-3, RET, and RET/PTC)
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Hepatic, via CYP3A4 (primarily oxidated to the pyridine N-oxide; active, minor) and UGT1A9 (glucuronidation)
Excretion
Feces (77%, 51% of dose as unchanged drug); urine (19%, as metabolites)
Time to Peak
~3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
25 to 48 hours
Protein Binding
99.5%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Race
Mean AUC in Asians is 30% lower than in white patients.
Use: Labeled Indications
Hepatocellular cancer: Treatment of unresectable hepatocellular cancer (HCC)
Renal cell cancer, advanced: Treatment of advanced renal cell cancer (RCC)
Thyroid cancer, differentiated: Treatment of locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, differentiated thyroid cancer (refractory to radioactive iodine treatment)
Use: Off Label
Angiosarcoma (recurrent or metastatic)b
Data from a phase II sarcoma study which included patients with angiosarcoma supports the use of sorafenib in the treatment of angiosarcoma Maki 2009.
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (resistant or refractory)b
Data from 2 small phase II studies support the use of sorafenib in the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), which is resistant to prior therapy with imatinib and sunitinib Kindler 2011, Park 2012. Data from a larger multicenter retrospective study also suggests sorafenib may be of benefit in the management of GIST in patients who had failed prior tyrosine kinase therapy, including imatinib and sunitinib, and in some patients who had also failed nilotinib Montemurro 2013.
Contraindications
Known severe hypersensitivity to sorafenib or any component of the formulation; use in combination with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with squamous cell lung cancer
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Note: Interrupt treatment (temporarily) in patients undergoing major surgical procedures.
Hepatocellular cancer (HCC): Oral: 400 mg twice daily; continue until no longer clinically benefiting or until unacceptable toxicity occurs (Llovet 2008).
Off-label dosing: A large retrospective analysis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma determined that a reduced initial dose (<800 mg/day) was associated with a reduced pill burden, reduced cost, and a trend toward reduced discontinuation rates while not associated with inferior overall survival rates. Most patients had Child-Pugh class A or B impairment; the average sorafenib starting dose was 367 mg/day; doses were escalated within 2 months of initiation in less than half of the patients (Reiss 2017).
Renal cell cancer (RCC), advanced: Oral: 400 mg twice daily; continue until no longer clinically benefiting or until unacceptable toxicity occurs (Escudier 2007; Escudier 2009)
Thyroid cancer, differentiated: Oral: 400 mg twice daily; continue until disease progression or until unacceptable toxicity (Brose 2014).
Angiosarcoma (off-label use): Oral: 400 mg twice daily (Maki 2009)
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) (off-label use): Oral: 400 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (Kindler 2011; Montemurro 2013; Park 2012)
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Adjustment for Toxicity
Temporary interruption and/or dosage reduction may be necessary for management of adverse drug reactions. If more than 2 dose reductions are required, discontinue treatment.
Dose reduction levels:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and renal cell carcinoma: Reduce dose to 400 mg once daily, then 200 mg once daily or 400 mg once every other day.
Thyroid cancer: Reduce dose to 600 mg/day (as 400 mg and 200 mg 12 hours apart), then 400 mg/day (200 mg twice daily), then 200 mg once daily.
Cardiovascular toxicity:
Cardiac ischemia and/or infarction (grade 2 or higher): Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
Heart failure:
Grade 3: Interrupt treatment until resolves to grade 1 or lower, then resume with the dose decreased by 1 dose level. If no resolution after 30 days of treatment interruption, discontinue treatment unless patient is deriving clinical benefit.
Grade 4: Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
Hypertension:
Grade 2 asymptomatic and diastolic pressure is 90 to 99 mm Hg: Manage with antihypertensive therapy; continue sorafenib at the same dose and monitor blood pressure closely.
Grade 2 symptomatic/persistent or grade 2 symptomatic increase by >20 mm Hg (diastolic) or >140/90 mm Hg if previously within normal limits or grade 3: Interrupt sorafenib treatment until symptoms resolve and diastolic blood pressure is <90 mm Hg; manage with antihypertensive therapy; reduce dose by 1 dose level when resumed; if needed, reduce an additional dose level.
Grade 4: Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
QT prolongation (QTc interval >500 msec or ≥60 msec increase from baseline): Interrupt treatment; correct electrolyte (magnesium potassium, calcium) abnormality; use medical judgement before restarting.
Gastrointestinal perforation (any grade): Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
Hemorrhage requiring medical intervention (grade 2 or higher): Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
Dermatologic toxicity:
Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis: Discontinue therapy if suspected.
Renal cell carcinoma and hepatocellular carcinoma:
Grade 2 (painful erythema and swelling of the hands or feet and/or discomfort affecting normal activities):
First occurrence: Continue sorafenib and consider symptomatic treatment with topical therapy. Note: If no improvement within 7 days, see dosing for second or third occurrence.
Second or third occurrence (or no improvement after 7 days of 1st occurrence): Hold treatment until resolves to grade 0 to 1; resume treatment with dose reduced by one dose level (400 mg daily or 400 mg every other day).
Fourth occurrence: Discontinue treatment.
Grade 3 (moist desquamation, ulceration, blistering, or severe pain of the hands or feet or severe discomfort that prevents working or performing daily activities):
First or second occurrence: Hold treatment until resolves to grade 0 to 1; resume treatment with dose reduced by one dose level (400 mg daily or 400 mg every other day).
Third occurrence: Discontinue treatment.
Thyroid cancer:
Grade 2 (painful erythema and swelling of the hands or feet and/or discomfort affecting normal activities):
First occurrence: Decrease dose to 600 mg daily (in divided doses). Note: If no improvement within 7 days, see dosing for second occurrence.
Second or third occurrence (or no improvement within 7 days of a reduced dose after first occurrence): Hold treatment until resolved or improved to grade 1; if resumed, decrease the dose by 1 dose level.
Fourth occurrence: Discontinue treatment.
Grade 3 (moist desquamation, ulceration, blistering, or severe pain of the hands or feet or severe discomfort that prevents working or performing daily activities):
First occurrence: Hold treatment until resolved or improved to grade 1; if resumed, decrease by 1 dose level.
Second occurrence: Hold treatment until resolved or improved to grade 1; if resumed, decrease by 2 dose levels.
Third occurrence: Discontinue treatment.
Following improvement of grade 2 or 3 dermatologic toxicity to grade 0 or 1 after at least 28 days of a reduced dose, the sorafenib dose may be increased 1 dose level from the reduced dose (~50% of patients requiring dose reduction for dermatologic toxicity may meet the criteria for increased dosing; and half of those patients may tolerate the increased dose without recurrent grade 2 or higher dermatologic toxicity).
Other non-hematologic toxicities:
Grade 2: Continue treatment as scheduled (on time); decrease dose by 1 level.
Grade 3:
First occurrence: Interrupt sorafenib treatment until resolves to grade 2 or lower, then resume with the dose decreased by 1 dose level.
Second or third occurrence (or no improvement within 7 days after first occurrence): Interrupt sorafenib treatment until resolves to grade 2 or lower, then resume with the dose decreased by 2 dose levels.
Fourth occurrence: Interrupt sorafenib treatment until resolves to grade 2 or lower, then resume with the dose decreased by 3 dose levels.
Grade 4: Permanently discontinue (do not resume).
Extemporaneously Prepared
An oral suspension may be prepared with tablets. Place two 200 mg tablets into a glass containing 60 mL (2 oz) water; let stand 5 minutes before stirring. Stir until tablets are completely disintegrated, forming a uniform suspension. Administer within 1 hour after preparation. Stir suspension again immediately before administration. To ensure the full dose is administered, rinse glass several times with a total of 180 mL (6 oz) water and administer residue. Note: Brown tablet coating may initially form a thin film but has no effect on the dosing accuracy.
Nexavar data on file, Bayer Healthcare Pharmaceuticals.
Administration
Administer on an empty stomach (1 hour before or 2 hours after eating).
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Protect from moisture.
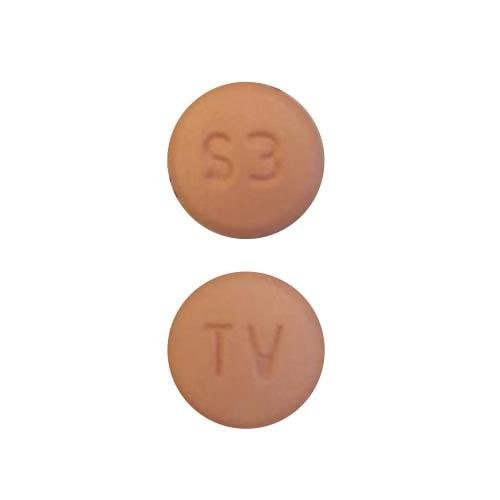
SORAfenib Images
Drug Interactions
Acetaminophen: May enhance the hepatotoxic effect of SORAfenib. SORAfenib may increase the serum concentration of Acetaminophen. Consider therapy modification
Baricitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Baricitinib. Management: Use of baricitinib in combination with potent immunosuppressants such as azathioprine or cyclosporine is not recommended. Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted. Consider therapy modification
BCG (Intravesical): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
BCG (Intravesical): Myelosuppressive Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
Bevacizumab: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of SORAfenib. Specifically, the risk for hand-foot skin reaction may be increased. Monitor therapy
Bisphosphonate Derivatives: Angiogenesis Inhibitors (Systemic) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Bisphosphonate Derivatives. Specifically, the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw may be increased. Monitor therapy
CARBOplatin: SORAfenib may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CARBOplatin. Management: Concurrent sorafenib with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with squamous cell lung cancer is contraindicated. Use in other settings is not specifically contraindicated but should be approached with added caution. Avoid combination
Chloramphenicol (Ophthalmic): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Myelosuppressive Agents. Monitor therapy
Cholic Acid: BSEP/ABCB11 Inhibitors may decrease the excretion of Cholic Acid. Avoid combination
Cladribine: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Cladribine: May enhance the myelosuppressive effect of Myelosuppressive Agents. Avoid combination
CloZAPine: Myelosuppressive Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CloZAPine. Specifically, the risk for neutropenia may be increased. Monitor therapy
Coccidioides immitis Skin Test: Immunosuppressants may diminish the diagnostic effect of Coccidioides immitis Skin Test. Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May decrease the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May increase the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Monitor therapy
Dacarbazine: SORAfenib may decrease the serum concentration of Dacarbazine. Sorafenib may also increase the concentration of dacarbazine's active metabolite. Monitor therapy
Deferiprone: Myelosuppressive Agents may enhance the neutropenic effect of Deferiprone. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of deferiprone and myelosuppressive agents whenever possible. If this combination cannot be avoided, monitor the absolute neutrophil count more closely. Consider therapy modification
Denosumab: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Specifically, the risk for serious infections may be increased. Monitor therapy
Dipyrone: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Myelosuppressive Agents. Specifically, the risk for agranulocytosis and pancytopenia may be increased Avoid combination
DOCEtaxel: SORAfenib may increase the serum concentration of DOCEtaxel. Monitor therapy
DOXOrubicin (Conventional): SORAfenib may increase the serum concentration of DOXOrubicin (Conventional). Monitor therapy
Echinacea: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Fingolimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Fingolimod. Management: Avoid the concomitant use of fingolimod and other immunosuppressants when possible. If combined, monitor patients closely for additive immunosuppressant effects (eg, infections). Consider therapy modification
GlyBURIDE: SORAfenib may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of GlyBURIDE. Monitor therapy
Haloperidol: QT-prolonging Agents (Indeterminate Risk - Caution) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Haloperidol. Monitor therapy
Irinotecan Products: UGT1A1 Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Irinotecan Products. Specifically, concentrations of SN-38 may be increased. UGT1A1 Inhibitors may increase the serum concentration of Irinotecan Products. Avoid combination
Leflunomide: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Leflunomide. Specifically, the risk for hematologic toxicity such as pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, and/or thrombocytopenia may be increased. Management: Consider not using a leflunomide loading dose in patients receiving other immunosuppressants. Patients receiving both leflunomide and another immunosuppressant should be monitored for bone marrow suppression at least monthly. Consider therapy modification
Mesalamine: May enhance the myelosuppressive effect of Myelosuppressive Agents. Monitor therapy
Natalizumab: Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Natalizumab. Specifically, the risk of concurrent infection may be increased. Avoid combination
Neomycin: May decrease the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Monitor therapy
Nivolumab: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Nivolumab. Consider therapy modification
Obeticholic Acid: BSEP/ABCB11 Inhibitors may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Obeticholic Acid. Management: Avoid concomitant use of obeticholic acid and bile salt efflux pump (BSEP) inhibitors if possible. If concomitant therapy is necessary, monitor patients for elevated liver transaminases and elevated bilirubin. Consider therapy modification
Ocrelizumab: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
PACLitaxel (Conventional): SORAfenib may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of PACLitaxel (Conventional). Management: Concurrent sorafenib with carboplatin and paclitaxel in patients with squamous cell lung cancer is contraindicated. Use in other settings is not specifically contraindicated but should be approached with added caution. Avoid combination
Pidotimod: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pidotimod. Monitor therapy
Pimecrolimus: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Promazine: May enhance the myelosuppressive effect of Myelosuppressive Agents. Monitor therapy
Propacetamol: SORAfenib may enhance the hepatotoxic effect of Propacetamol. SORAfenib may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Propacetamol. Specifically, acetaminophen exposure may be increased. Management: Consider less frequent and/or lower daily doses of propacetamol in patients who are also taking sorafenib. Monitor for liver toxicity, particularly with higher propacetamol doses. Consider therapy modification
Proton Pump Inhibitors: May decrease the absorption of SORAfenib. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk): QT-prolonging Agents (Indeterminate Risk - Caution) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Roflumilast: May enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Siponimod: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Siponimod. Monitor therapy
Sipuleucel-T: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sipuleucel-T. Management: Evaluate patients to see if it is medically appropriate to reduce or discontinue therapy with immunosuppressants prior to initiating sipuleucel-T therapy. Consider therapy modification
Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live). Monitor therapy
St John's Wort: May decrease the serum concentration of SORAfenib. Avoid combination
Tacrolimus (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Immunosuppressants. Avoid combination
Tertomotide: Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Tertomotide. Monitor therapy
Tofacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Tofacitinib. Management: Concurrent use with antirheumatic doses of methotrexate or nonbiologic disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is permitted, and this warning seems particularly focused on more potent immunosuppressants. Consider therapy modification
Trastuzumab: May enhance the neutropenic effect of Immunosuppressants. Monitor therapy
Upadacitinib: Immunosuppressants may enhance the immunosuppressive effect of Upadacitinib. Avoid combination
Vaccines (Inactivated): Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Inactivated). Management: Vaccine efficacy may be reduced. Complete all age-appropriate vaccinations at least 2 weeks prior to starting an immunosuppressant. If vaccinated during immunosuppressant therapy, revaccinate at least 3 months after immunosuppressant discontinuation. Consider therapy modification
Vaccines (Live): Immunosuppressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Vaccines (Live). Immunosuppressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Vaccines (Live). Management: Avoid use of live organism vaccines with immunosuppressants; live-attenuated vaccines should not be given for at least 3 months after immunosuppressants. Exceptions: Smallpox and Monkeypox Vaccine (Live). Avoid combination
Warfarin: SORAfenib may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Warfarin. SORAfenib may increase the serum concentration of Warfarin. Management: Warfarin dose adjustment will likely be necessary. Increase frequency of INR monitoring during sorafenib therapy (particularly when starting or stopping therapy), and increase monitoring for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Hypertension (9% to 41%; grade 3: 3% to 4%; grade 4: <1%; grades 3/4: 10%, onset: ~3 weeks)
Central nervous system: Fatigue (37% to 46%), headache (≤10% to 17%), mouth pain (14%), voice disorder (13%), peripheral sensory neuropathy (≤13%), pain (11%)
Dermatologic: Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (21% to 69%; grade 3: 6% to 8%; grades 3/4: 19%), alopecia (14% to 67%), skin rash (including desquamation; 19% to 40%; grade 3: ≤1%; grades 3/4: 5%), pruritus (14% to 20%), xeroderma (10% to 13%), erythema (≥10%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypoalbuminemia (≤59%), weight loss (10% to 49%), hypophosphatemia (35% to 45%; grade 3: 11% to 13%; grade 4: <1%), increased thyroid stimulating hormone level (>0.5 mU/L: 41%; due to impairment of exogenous thyroid suppression), hypocalcemia (12% to 36%), increased amylase (30% to 34% [usually transient])
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea (43% to 68%; grade 3: 2% to 10%; grade 4: <1%), increased serum lipase (40% to 41% [usually transient]), abdominal pain (11% to 31%), decreased appetite (30%), anorexia (16% to 29%), stomatitis (24%), nausea (21% to 24%), constipation (14% to 16%), vomiting (11% to 16%)
Hematologic & oncologic: Lymphocytopenia (23% to 47%; grades 3/4: ≤13%), thrombocytopenia (12% to 46%; grades 3/4: 1% to 4%), increased INR (≤42%), neutropenia (≤18%; grades 3/4: ≤5%), hemorrhage (15% to 17%; grade 3: 2%), leukopenia
Hepatic: Increased serum ALT (59%; grades 3/4: 4%), increased serum AST (54%; grades 3/4: 2%), hepatic insufficiency (≤11%; grade 3: 2%; grade 4: 1%)
Infection: Infection
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Limb pain (15%), weakness (12%), myalgia
Respiratory: Dyspnea (≤14%), cough (≤13%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (11%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Ischemic heart disease (including myocardial infarction; ≤3%), cardiac failure (2%, congestive), flushing
Central nervous system: Depression, glossalgia
Dermatologic: Hyperkeratosis (7%), acne vulgaris, exfoliative dermatitis, folliculitis
Endocrine & metabolic: Hypokalemia (5% to 10%), hyponatremia, hypothyroidism
Gastrointestinal: Dysgeusia (6%), dyspepsia, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux disease, mucositis, xerostomia
Genitourinary: Erectile dysfunction, proteinuria
Hematologic & oncologic: Squamous cell carcinoma of skin (3%; grades 3/4: 3%), anemia
Hepatic: Increased serum transaminases (transient)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Muscle spasm (10%), arthralgia (≤10%), myalgia
Renal: Renal failure
Respiratory: Epistaxis (7%), flu-like symptoms, hoarseness, rhinorrhea
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Acute renal failure, anaphylaxis, angioedema, aortic dissection, amyotrophy, cardiac arrhythmia, cardiac failure, cerebral hemorrhage, cholangitis, cholecystitis, dehydration, eczema, erythema multiforme, gastritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, gastrointestinal perforation, gynecomastia, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hypersensitivity reaction (skin reaction, urticaria), hypertensive crisis, hyperthyroidism, increased serum alkaline phosphatase, increased serum bilirubin, interstitial pulmonary disease (acute respiratory distress, interstitial pneumonia, lung inflammation, pneumonitis, pulmonitis, radiation pneumonitis), jaundice, malignant neoplasm of skin (keratoacanthomas), nephrotic syndrome, ostealgia, osteonecrosis of the jaw, pancreatitis, pleural effusion, prolonged QT interval on ECG, respiratory tract hemorrhage, reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome, rhabdomyolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, thromboembolism, tinnitus, toxic epidermal necrolysis, transient ischemic attacks, tumor lysis syndrome, tumor pain
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Bleeding: Increased risk of bleeding may occur; consider permanently discontinuing with serious bleeding events (eg, requires medical intervention). Fatal bleeding events have been reported. Thyroid cancer patients with tracheal, bronchial, and esophageal infiltration should be treated with local therapy prior to administering sorafenib due to the potential bleeding risk.
- Cardiovascular events: May cause cardiac ischemia or infarction; consider discontinuation (temporary or permanent) in patients who develop these conditions. Use in patients with unstable coronary artery disease or recent myocardial infarction has not been studied. Heart failure has been reported in multiple clinical studies. In a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, sorafenib has been determined to be an agent that may exacerbate underlying myocardial dysfunction (magnitude: minor) (AHA [Page 2016]).
- Dermatologic toxicity: Hand-foot skin reaction and rash (generally grades 1 or 2) are the most common drug-related adverse events, and typically appear within the first 6 weeks of treatment; usually managed with topical treatment, treatment delays, and/or dose reductions. Consider permanently discontinuing with severe or persistent dermatological toxicities. The risk for hand-foot skin reaction increased with cumulative doses of sorafenib (Azad 2009). Severe dermatologic toxicities, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been reported; may be life-threatening. Discontinue sorafenib for suspected SJS or TEN.
The following treatments may be used to manage hand-foot skin reaction in addition to the recommended dosage modifications (Lacouture 2008): Prior to treatment initiation, a pedicure is recommended to remove hyperkeratotic areas/calluses, which may predispose to HFSR; avoid vigorous exercise/activities which may stress hands or feet. During therapy, patients should reduce exposure to hot water (may exacerbate hand-foot symptoms); avoid constrictive footwear and excessive skin friction. Patients may also wear thick cotton gloves or socks and should wear shoes with padded insoles. Grade 1 HFSR may be relieved with moisturizing creams, cotton gloves and socks (at night) and/or keratolytic creams such as urea (20% to 40%) or salicylic acid (6%). Apply topical steroid (eg, clobetasol ointment) twice daily to erythematous areas of grade 2 HFSR; topical anesthetics (eg, lidocaine 2%) and then systemic analgesics (if appropriate) may be used for pain control. Resolution of acute erythema may result in keratotic areas which may be softened with keratolytic agents.
- GI perforation: GI perforation has been reported (rare); monitor patients for signs/symptoms (abdominal pain, constipation, or vomiting); discontinue treatment if gastrointestinal perforation occurs.
- Hepatotoxicity: Sorafenib-induced hepatitis (characterized by a hepatocellular pattern of liver damage with significant increases of transaminases) which may result in hepatic failure and death has been observed. Bilirubin elevations and INR increases may also occur. Severe drug-induced liver injury (transaminase elevations >20 times ULN or with significant clinical sequelae [eg, elevated INR, ascites, transplantation or fatality]) occurred rarely. Monitor liver function tests regularly. Discontinue sorafenib if significantly increased transaminases occur without alternative explanation (eg, viral hepatitis or progressing underlying malignancy).
- Hypertension: May cause hypertension (generally mild-to-moderate), especially in the first 6 weeks of treatment; monitor. Use caution in patients with underlying or poorly-controlled hypertension. Consider discontinuing (temporary or permanent) in patients who develop severe or persistent hypertension while on appropriate antihypertensive therapy.
- QT prolongation: QT prolongation has been observed; may increase the risk for ventricular arrhythmia. Avoid use in patients with congenital long QT syndrome. Monitor electrolytes and ECG in patients with heart failure, bradyarrhythmias, and concurrent medications know to prolong the QT interval. Correct electrolyte (calcium, magnesium, potassium) imbalances. Interrupt treatment for QTc interval >500 msec or for ≥60 msec increase from baseline.
- Thyroid impairment: Sorafenib impairs exogenous thyroid suppression. TSH level elevations were commonly observed in the thyroid cancer study; monitor TSH levels monthly and as clinically necessary, and adjust thyroid replacement as needed.
- Wound healing complications: May complicate wound healing; temporarily withhold treatment for patients undergoing major surgical procedures. The appropriate timing to resume sorafenib after major surgery has not been determined.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information. The incidence of hand-foot skin reaction is increased in patients treated with sorafenib plus bevacizumab in comparison to those treated with sorafenib monotherapy (Azad 2009).
Monitoring Parameters
CBC with differential, electrolytes (magnesium, potassium, calcium), phosphorus, lipase and amylase levels; liver function tests; pregnancy test (females of reproductive potential prior to initiating sorafenib treatment); blood pressure (baseline, weekly for the first 6 weeks, then periodic); monitor for hand-foot skin reaction and other dermatologic toxicities; monitor ECG in patients at risk for prolonged QT interval; signs/symptoms of bleeding, GI perforation, and heart failure. Monitor adherence.
Thyroid function testing:
Patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Monitor TSH monthly.
Patients with RCC and HCC (Hamnvik 2011):
Preexisting levothyroxine therapy: Obtain baseline TSH levels, then monitor every 4 weeks until levels and levothyroxine dose are stable, then monitor every 2 months
Without preexisting thyroid hormone replacement: TSH at baseline, then every 4 weeks for 4 months, then every 2 to 3 months
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Based on the mechanism of action and findings from animal reproduction studies, adverse effects on pregnancy would be expected. Sorafenib inhibits angiogenesis, which is a critical component of fetal development.
Evaluate pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating sorafenib treatment. Females of reproductive potential should use an effective nonhormonal method of contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the final sorafenib dose. Males with female partners of reproductive potential should use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last sorafenib dose.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat cancer.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Dry skin
- Hair loss
- Lack of appetite
- Itching
- Weight loss
- Muscle spasm
- Muscle pain
- Mouth irritation
- Change in taste
- Mouth sores
- Acne
- Flushing
- Runny nose
- Joint pain
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Infection
- Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin.
- Bleeding like vomiting blood or vomit that looks like coffee grounds; coughing up blood; blood in the urine; black, red, or tarry stools; bleeding from the gums; abnormal vaginal bleeding; bruises without a reason or that get bigger; or any severe or persistent bleeding.
- Electrolyte problems like mood changes, confusion, muscle pain or weakness, abnormal heartbeat, seizures, lack of appetite, or severe nausea or vomiting.
- Kidney problems like unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain.
- Thyroid problems like change in weight without trying, anxiety, agitation, feeling very weak, hair thinning, depression, neck swelling, trouble focusing, inability handling heat or cold, menstrual changes, tremors, or sweating.
- Depression
- Sexual dysfunction
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive weight gain
- Sweating a lot
- Vision changes
- Fast heartbeat
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Chest pain
- Severe headache
- Severe abdominal pain
- Severe nausea
- Severe vomiting
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Swelling of arms or legs
- Painful extremities
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Burning or numbness feeling
- Redness or irritation of palms of hands or soles of feet
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in mouth, throat, nose, or eyes.
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.