Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
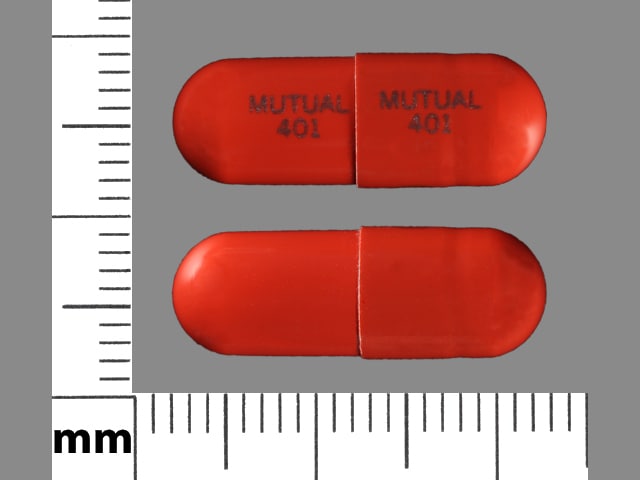
Capsule, Oral, as hydrochloride:
Tigan: 300 mg
Generic: 300 mg
Solution, Intramuscular, as hydrochloride:
Tigan: 100 mg/mL (2 mL)
Tigan: 100 mg/mL (20 mL) [contains phenol]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Acts centrally to inhibit the medullary chemoreceptor trigger zone by blocking emetic impulses to the vomiting center
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Metabolism
Via oxidation, forms metabolite trimethobenzamide N-oxide
Excretion
Urine (30% to 50%, as unchanged drug)
Onset of Action
Oral: 10 to 40 minutes; IM: 15 to 35 minutes
Time to Peak
Oral: ~45 minutes; IM: ~30 minutes
Duration of Action
Oral: 3 to 4 hours; IM: 2 to 3 hours
Half-Life Elimination
7 to 9 hours
Use: Labeled Indications
Nausea/vomiting: Treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting; treatment of nausea associated with gastroenteritis
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide or any component of the formulation; use in pediatric patients (injection only)
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Nausea/vomiting: Note: Use the lowest effective dosage based on response and tolerability.
IM: 200 mg 3 or 4 times daily
Oral: 300 mg 3 or 4 times daily
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing; reduce the dose or increase the dosing interval and adjust as needed based on patient response.
Dosing: Pediatric
Note: Use in pediatric patients is strongly discouraged due to risk of EPS, serious CNS effects, and other adverse reactions. Expert recommendations for nausea and vomiting management do not suggest trimethobenzamide as a therapeutic option; use has been replaced by newer agents with an improved safety profile (MMWR 2003; SAA [Gan 2014]). Although rectal dosing may still be referred to in pediatric textbooks, rectal formulations of trimethobenzamide are no longer available. Parenteral formulations are contraindicated in pediatric patients.
Nausea and vomiting, opioid induced: Limited data available (Kliegman 2016): Children and Adolescents:
<15 kg: Oral: 100 mg every 6 hours as needed
≥15 kg: Oral: 200 mg every 6 hours as needed
Administration
IM: Administer IM only; not recommended for IV use. Inject deep into upper outer quadrant of gluteal muscle.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions are permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Trimethobenzamide Images
Drug Interactions
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Aclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Alcohol (Ethyl): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of Trimethobenzamide. Monitor therapy
Amantadine: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Anticholinergic Agents: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Cannabinoid-Containing Products: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the tachycardic effect of Cannabinoid-Containing Products. Exceptions: Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Chloral Betaine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Cimetropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Cimetropium. Avoid combination
Eluxadoline: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Eluxadoline. Avoid combination
Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic): Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
Glucagon: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Glucagon. Specifically, the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects may be increased. Monitor therapy
Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation): Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation). Avoid combination
Glycopyrronium (Topical): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Ipratropium (Oral Inhalation): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Itopride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Itopride. Monitor therapy
Levosulpiride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Levosulpiride. Avoid combination
Mianserin: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Mirabegron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Mirabegron. Monitor therapy
Nitroglycerin: Anticholinergic Agents may decrease the absorption of Nitroglycerin. Specifically, anticholinergic agents may decrease the dissolution of sublingual nitroglycerin tablets, possibly impairing or slowing nitroglycerin absorption. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Opioid Agonists. Specifically, the risk for constipation and urinary retention may be increased with this combination. Monitor therapy
Oxatomide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Potassium Chloride: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Chloride. Management: Patients on drugs with substantial anticholinergic effects should avoid using any solid oral dosage form of potassium chloride. Avoid combination
Potassium Citrate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Citrate. Avoid combination
Pramlintide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. These effects are specific to the GI tract. Consider therapy modification
Ramosetron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Ramosetron. Monitor therapy
Revefenacin: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
Secretin: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Secretin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of anticholinergic agents and secretin. Discontinue anticholinergic agents at least 5 half-lives prior to administration of secretin. Consider therapy modification
Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics: Anticholinergic Agents may increase the serum concentration of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Tiotropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Tiotropium. Avoid combination
Topiramate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Topiramate. Monitor therapy
Umeclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Adverse Reactions
Frequency not defined.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension (IV administration)
Central nervous system: Coma, depression, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, extrapyramidal reaction, headache, opisthotonos, Parkinsonian-like symptoms, seizure
Dermatologic: Allergic skin reaction
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea
Hematologic & oncologic: Hematologic disease
Hepatic: Jaundice
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reaction
Local: Burning sensation at injection site, erythema at injection site, pain at injection site, swelling at injection site
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Muscle cramps
Ophthalmic: Blurred vision
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- CNS effects: CNS serious adverse effects (eg, coma, mood depression, disorientation, seizure) have been reported. Consider reducing the daily dosage by increasing the dosing interval or discontinuing use if serious CNS reactions occur. May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks which require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving). Recent or concomitant use of other medications causing CNS depression or adverse events may increase the risk of serious CNS reactions.
- Extrapyramidal symptoms: May cause extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), primarily acute dystonic reactions (ie, sudden onset of muscular spasms usually in the head/neck or opisthotonos); other EPS (akathisia, restlessness, akinesia, other parkinsonian-like symptoms [eg, tremor]), laryngospasm, dysphagia, oculogyric crisis) may also occur. If EPS occurs, reduce the daily dosage by increasing the dosing interval or discontinue therapy, depending on the severity of symptoms. Treat acute dystonic reactions with anticholinergics. Avoid use in patients receiving concomitant therapy (eg, antipsychotics) that cause EPS.
- Hepatotoxicity: Use may potentially cause hepatotoxicity. If hepatic impairment occurs during therapy, discontinue use.
- Skin reactions: Allergic-type skin reactions have been reported with use; discontinue with signs of sensitization.
Disease-related concerns:
- Hepatic impairment: Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; clearance is predominantly renal; dosage reduction recommended in patients with CrCl ≤70 mL/minute/1.73 m2.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Pediatric: Injection is contraindicated in children. Oral formulation is not recommended for use in pediatrics due to risk of EPS, serious CNS effects, and other potential adverse effects associated with use.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Masking effects: EPS and other CNS effects that may result from use may mask signs of an undiagnosed primary disease (eg, encephalopathy, metabolic imbalance, Reye syndrome). If CNS symptoms occur, evaluate the risks vs. benefits of continuing therapy.
Monitoring Parameters
Renal function in elderly patients and patients with reduced renal function.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Although use for the treatment of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy has been reported (Milkovich 1976; Pretorius 1961), use of other agents is preferred (ACOG 189 2018).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat upset stomach and throwing up.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Diarrhea
- Fatigue
- Headache
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Tremors
- Difficulty moving
- Rigidity
- Abnormal movements
- Muscle spasm
- Muscle cramps
- Difficulty swallowing
- Difficulty speaking
- Agitation
- Change in balance
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Blurred vision
- Depression
- Seizures
- Confusion
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.