Boxed Warning
Abuse and dependence:
CNS stimulants, including dexmethylphenidate, methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Capsule Extended Release 24 Hour, Oral, as hydrochloride:
Focalin XR: 5 mg [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Focalin XR: 10 mg
Focalin XR: 15 mg [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Focalin XR: 20 mg
Focalin XR: 25 mg [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Focalin XR: 30 mg
Focalin XR: 35 mg, 40 mg [contains fd&c blue #2 (indigotine)]
Generic: 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, 20 mg, 25 mg, 30 mg, 35 mg, 40 mg
Tablet, Oral, as hydrochloride:
Focalin: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg
Generic: 2.5 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Dexmethylphenidate is the more active, d-threo-enantiomer, of racemic methylphenidate. It is a CNS stimulant; blocks the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, and increases their release into the extraneuronal space.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Immediate release: Rapid; Extended release: Bimodal (with 2 peak concentrations ~4 hours apart)
Distribution
Vd: 2.65 ± 1.11 L/kg
Metabolism
Via de-esterification to inactive metabolite, d-α-phenyl-piperidine acetate (d-ritalinic acid)
Excretion
Urine (90%, primarily as inactive metabolite)
Onset of Action
Rapid, within 1 to 2 hours of an effective dose
Time to Peak
Fasting:
Immediate release: 1 to 1.5 hours; after a high-fat meal: 2.9 hours
Extended release: First peak: 1.5 hours (range: 1 to 4 hours); Second peak: 6.5 hours (range: 4.5 to 7 hours)
Duration of Action
Immediate release: 3 to 5 hours; extended release: 9 to 12 hours (Dopheide 2009)
Half-Life Elimination
Immediate release: Children: 2 to 3 hours; Adults: 3 hours
Protein Binding
Unknown; Racemic methylphenidate: 12% to 15%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Children
Children showed somewhat lower AUCs after administration of dexmethylphenidate immediate release.
Special Populations: Gender
In adults, the AUC of dexmethylphenidate immediate release was 25% to 35% higher in women compared with men. After administration of dexmethylphenidate ER, the first peak (Cmax) was 45% higher in women. Parameters for dexmethylphenidate immediate release were similar for boys and girls.
Use: Labeled Indications
ADHD: Treatment of ADHD
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to methylphenidate or any component of the formulation; concurrent use with or within 14 days following discontinuation with MAOI
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
ADHD: Patients not currently taking methylphenidate or who are on other stimulants: Oral:
Immediate release: Initial: 2.5 mg twice daily; dosage may be adjusted in increments of 2.5 to 5 mg at weekly intervals (maximum dose: 20 mg/day)
Extended release: Initial: 10 mg once daily; dosage may be adjusted in increments of 10 mg at weekly intervals (maximum dose: 40 mg/day)
Conversion to dexmethylphenidate from methylphenidate: Immediate release and extended release: Initial: One-half the total daily dose of racemic methylphenidate
Conversion from dexmethylphenidate immediate release to dexmethylphenidate extended release: Patients currently using dexmethylphenidate immediate-release may be switched to the same daily dose of dexmethylphenidate extended-release.
Dose reductions and discontinuation: Reduce dose or discontinue in patients with paradoxical aggravation of symptoms. Discontinue if no improvement is seen after one month of treatment.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD): Note: Reduce dose or discontinue in patients with paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse events. Discontinue if no improvement is seen after appropriate dosage adjustment over a 1-month period of time.
Children ≥6 years and Adolescents: Oral:
Patients not currently taking methylphenidate:
Immediate release: Initial: 2.5 mg twice daily; doses should be taken at least 4 hours apart; dosage may be adjusted in increments of 2.5 to 5 mg at weekly intervals; maximum daily dose: 20 mg/day; however, some patients may require and tolerate daily doses up to 50 mg/day with frequent monitoring (AACAP [Pliszka 2007]; Dopheide 2009)
Extended release: Initial: 5 mg once daily; dosage may be adjusted in increments of 5 mg/day at weekly intervals; maximum daily dose: 30 mg/day; however, some patients may require and tolerate daily doses up to 50 mg/day with frequent monitoring (AACAP [Pliszka 2007]; Dopheide 2009)
Conversion to dexmethylphenidate from methylphenidate:
Immediate release: Initial: Half the total daily dose of racemic methylphenidate; maximum daily dexmethylphenidate dose: 20 mg/day; however, some patients may require and tolerate daily doses up to 50 mg/day with frequent monitoring (AACAP [Pliszka 2007]; Dopheide 2009)
Extended release: Initial: Half the total daily dose of racemic methylphenidate; maximum daily dexmethylphenidate dose: 30 mg/day; however, some patients may require and tolerate daily doses up to 50 mg/day with frequent monitoring (AACAP [Pliszka 2007]; Dopheide 2009)
Conversion from dexmethylphenidate immediate release to dexmethylphenidate extended release: When changing from Focalin tablets to Focalin XR capsules, switch to the same daily dose using Focalin XR; maximum daily dose: 30 mg/day; however, some patients may require and tolerate daily doses up to 50 mg/day with frequent monitoring (AACAP [Pliszka 2007]; Dopheide 2009)
Administration
Extended release: Administer once daily in the morning with or without food; do not crush, chew, or divide. Capsules may be opened and contents sprinkled over a spoonful of applesauce; consume immediately and swallow without chewing; do not store for future use.
Immediate release: Administer twice daily at least 4 hours apart; may be taken with or without food.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Protect from light and moisture.
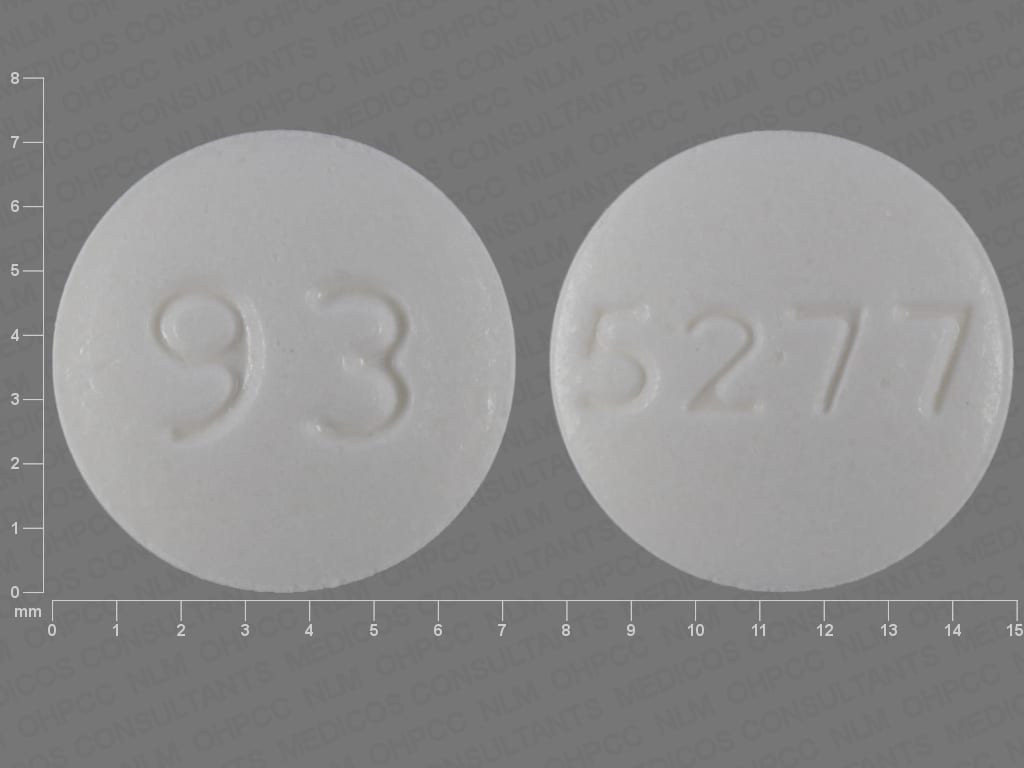
Dexmethylphenidate Images
Drug Interactions
Acebrophylline: May enhance the stimulatory effect of CNS Stimulants. Avoid combination
Amifampridine: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the neuroexcitatory and/or seizure-potentiating effect of Amifampridine. Monitor therapy
Antacids: May increase the absorption of Dexmethylphenidate. Specifically, antacids may interfere with the normal release of drug from the extended-release capsules (Focalin XR brand), which could result in both increased absorption (early) and decreased delayed absorption. Monitor therapy
Antihypertensive Agents: Dexmethylphenidate may diminish the therapeutic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
AtoMOXetine: May enhance the hypertensive effect of Sympathomimetics. AtoMOXetine may enhance the tachycardic effect of Sympathomimetics. Monitor therapy
BuPROPion: May enhance the neuroexcitatory and/or seizure-potentiating effect of Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential. Monitor therapy
Cannabinoid-Containing Products: May enhance the tachycardic effect of Sympathomimetics. Exceptions: Cannabidiol. Monitor therapy
Cocaine (Topical): May enhance the hypertensive effect of Sympathomimetics. Management: Consider alternatives to use of this combination when possible. Monitor closely for substantially increased blood pressure or heart rate and for any evidence of myocardial ischemia with concurrent use. Consider therapy modification
Doxofylline: Sympathomimetics may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Doxofylline. Monitor therapy
Esketamine: May enhance the hypertensive effect of CNS Stimulants. Monitor therapy
Fosphenytoin: Dexmethylphenidate may increase the serum concentration of Fosphenytoin. Monitor therapy
Guanethidine: May enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Sympathomimetics. Guanethidine may enhance the hypertensive effect of Sympathomimetics. Monitor therapy
Histamine H2 Receptor Antagonists: May increase the absorption of Dexmethylphenidate. Specifically, H2-antagonists may interfere with the normal release of drug from the extended-release capsules (Focalin XR brand), which could result in both increased absorption (early) and decreased delayed absorption. Monitor therapy
Inhalational Anesthetics: Dexmethylphenidate may enhance the hypertensive effect of Inhalational Anesthetics. Avoid combination
Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products: CNS Stimulants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products. Management: Discontinue all drugs that may inhibit or interfere with catecholamine transport or uptake for at least 5 biological half-lives before iobenguane administration. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose. Avoid combination
Ioflupane I 123: Dexmethylphenidate may diminish the diagnostic effect of Ioflupane I 123. Monitor therapy
Iohexol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iohexol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iohexol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Iomeprol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iomeprol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iomeprol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Iopamidol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iopamidol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iopamidol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors: May enhance the hypertensive effect of Dexmethylphenidate. Avoid combination
PHENobarbital: Dexmethylphenidate may increase the serum concentration of PHENobarbital. Monitor therapy
Phenytoin: Dexmethylphenidate may increase the serum concentration of Phenytoin. Monitor therapy
Primidone: Dexmethylphenidate may increase serum concentrations of the active metabolite(s) of Primidone. Specifically, phenobarbital concentrations could become elevated. Dexmethylphenidate may increase the serum concentration of Primidone. Monitor therapy
Proton Pump Inhibitors: May increase the absorption of Dexmethylphenidate. Specifically, proton pump inhibitors may interfere with the normal release of drug from the extended-release capsules (Focalin XR brand), which could result in both increased absorption (early) and decreased delayed absorption. Monitor therapy
Serotonergic Agents (High Risk): Dexmethylphenidate-Methylphenidate may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Isocarboxazid; Linezolid; Methylene Blue; Moclobemide; Phenelzine; Tranylcypromine. Monitor therapy
Solriamfetol: Sympathomimetics may enhance the hypertensive effect of Solriamfetol. Monitor therapy
Solriamfetol: CNS Stimulants may enhance the hypertensive effect of Solriamfetol. Monitor therapy
Sympathomimetics: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Sympathomimetics. Monitor therapy
Tedizolid: May enhance the hypertensive effect of Sympathomimetics. Tedizolid may enhance the tachycardic effect of Sympathomimetics. Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Dexmethylphenidate may increase the serum concentration of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
Actual frequency may be dependent upon dose and/or formulation. Also refer to Methylphenidate for adverse effects seen with other methylphenidate products.
>10%:
Central nervous system: Headache (adults: 26% to 39%; children and adolescents: 25%), insomnia (children and adolescents: 5% to 17%), jitteriness (adults: 12%), anxiety (5% to 11%)
Gastrointestinal: Decreased appetite (children and adolescents: 30%), xerostomia (adults: 7% to 20%), abdominal pain (children and adolescents: 15%)
1% to 10%:
Central nervous system: Dizziness (adults: 6%), irritability (children and adolescents: 2% to 5%), depression (children and adolescents: 3%), emotional lability (children and adolescents: 3%)
Dermatologic: Pruritus (children and adolescents: 3%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (children and adolescents: 9%), dyspepsia (5% to 9%), vomiting (children and adolescents: 2% to 9%), anorexia (children and adolescents: 5% to 7%)
Respiratory: Pharyngolaryngeal pain (adults: 4% to 7%), nasal congestion (children and adolescents: 5%)
Miscellaneous: Fever (children and adolescents: 5%)
Frequency not defined:
Central nervous system: Drug abuse, drug dependence
Endocrine & metabolic: Growth suppression, weight loss
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Anaphylaxis, angioedema, hypersensitivity reactions, peripheral vascular disease, Raynaud disease, rhabdomyolysis
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Cardiovascular events: CNS stimulant treatment has been associated with sudden death in children and adolescents with preexisting structural cardiac abnormalities and sudden death, stroke, and MI have been reported in adults. Consistent with other studies, a large retrospective cohort study involving 1,200,438 children, adolescents, and young adults (aged 2 to 24 years) prescribed methylphenidate, dexmethylphenidate, dextroamphetamines, amphetamine salts, pemoline, or atomoxetine found no evidence that current use of an ADHD medication increased risk for sudden cardiac death, acute MI, or stroke (Cooper 2011). Stimulants should be avoided in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart rhythm abnormalities, coronary artery disease, Marfan syndrome, or other serious cardiac problems. Some products are contraindicated in patients with moderate or severe hypertension, angina, heart failure, arrhythmias, or recent MI. Prior to initiating stimulant, assess medical history and family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia; conduct a physical exam to assess for cardiac disease; patients should receive further evaluation if findings suggest cardiac disease, such as ECG and echocardiogram. Promptly conduct cardiac evaluation in patients who develop exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or any other symptoms of cardiac disease during stimulant treatment.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Hypersensitivity reactions including angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been observed in patients treated with methylphenidate.
- Peripheral vasculopathy: Stimulants are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud phenomenon; signs/symptoms are usually mild and intermittent, and generally improve with dose reduction or discontinuation. Peripheral vasculopathy effects have been observed at different times, at therapeutic doses, and in all age groups. Digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown have been observed rarely; monitor for digital changes during therapy and seek further evaluation (eg, rheumatology) if necessary.
- Priapism: Prolonged (>4 hours), painful, and nonpainful erections, sometimes requiring surgical intervention, have been reported with use of other stimulants (methylphenidate, atomoxetine) in pediatric and adult patients according to the manufacturers' labeling and a 2013 FDA warning; there are at least 22 published cases (Baytunca 2016; Bozkurt 2017; Chauhan 2016; Eiland 2014; Esnafoglu 2017; Mann 2017; Unver 2017). Priapism has been reported to develop after some time on the drug, often subsequent to an increase in dose but also during a period of drug withdrawal (drug holidays or discontinuation). Patients with certain hematological dyscrasias (eg, sickle cell disease), malignancies, perineal trauma, or concomitant use of alcohol, illicit drugs, or other medications associated with priapism may be at increased risk (Eiland 2014). Patients who develop abnormally sustained or frequent and painful erections should discontinue therapy and seek immediate medical attention. An emergent urological consultation should be obtained in severe cases. In patients with severe cases of priapism that were slow to resolve and/or required detumescence by aspiration, avoidance of stimulants and atomoxetine may be preferred (Eiland 2014).
- Visual disturbance: Difficulty in accommodation and blurred vision has been reported with the use of stimulants.
Disease-related concerns:
- Abuse and dependence: [US Boxed Warning]: CNS stimulants, including dexmethylphenidate, methylphenidate-containing products, and amphetamines, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy.
- Cardiovascular disorders: CNS stimulants may increase heart rate (mean increase 3 to 6 bpm) and blood pressure (mean increase 2 to 4 mg Hg). Use with caution in patients with hypertension, heart failure, recent MI, ventricular arrhythmia, and other cardiovascular conditions that might be exacerbated by increases in blood pressure or heart rate.
- Psychiatric disorders: Use with caution in patients with preexisting psychosis (may exacerbate symptoms of behavior and thought disorder) or bipolar disorder (may induce mixed/manic episode). New-onset psychosis or mania may occur with stimulant use. Patients should be screened for bipolar disorder and risk factors for developing a manic episode prior to treatment (eg, comorbid or history of depressive symptoms; family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, or depression); consider discontinuation if psychotic or manic symptoms (eg, delusional thinking, hallucinations, mania) occur. May be associated with aggressive behavior or hostility in children (causal relationship not established); monitor for development or worsening of these behaviors. Patients with ADHD are at increased risk for suicidal ideation and suicide attempt; however, neither increased risk nor a causal relationship with methylphenidate and attempted suicide has been observed in large cohort trials (Huang 2018; Man 2017). Monitor for suicide-related behavior.
- Seizure disorder: Limited information exists regarding stimulant use in seizure disorder. Whereas patients with ADHD are at an increased risk for seizure activity compared to the general population, a retrospective study using drug claims data showed that the use of stimulant medications was associated with a lower risk (Cortese 2013; Wiggs 2018). Manufacturers of some stimulants recommend discontinuing therapy if seizures occur.
- Tourette syndrome/tics: Use with caution in patients with Tourette syndrome or other tic disorders. Stimulants may exacerbate tics (motor and phonic) and Tourette syndrome; however, evidence demonstrating increased tics is limited. Evaluate for tics and Tourette syndrome prior to therapy initiation (AACAP [Murphy 2013; Pliszka 2007]).
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Pediatric: Use of stimulants has been associated with appetite suppression, weight loss, and slowing of growth rate; monitor growth rate, height, and weight during treatment. Treatment interruption may be necessary in patients who are not increasing in height or gaining weight as expected.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Discontinuation of therapy: Abrupt discontinuation, rapid dose reduction, or administration of an antagonist may result in withdrawal symptoms including dysphoric mood, fatigue, vivid, unpleasant dreams, insomnia or hypersomnia, increased appetite, and psychomotor retardation or agitation.
Monitoring Parameters
Cardiac evaluation should be completed at baseline and on any patient who develops exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, and any symptom of cardiac disease during treatment with stimulants. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate (baseline, following dose increases and periodically during treatment); growth rate (height and weight) and appetite in children; weight in adults; signs of peripheral vasculopathy (eg, digital changes); sleep and behavioral changes. Assess for risk of abuse prior to prescribing and signs of misuse, abuse, or addiction throughout treatment (NICE 2018).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Dexmethylphenidate is the more active d-threo enantiomer of racemic methylphenidate; refer to the methylphenidate monograph for additional information.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat attention deficit problems with hyperactivity.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Fatigue
- Anxiety
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Throat pain
- Abdominal pain
- Heartburn
- Weight loss
- Lack of appetite
- Trouble sleeping
- Dry mouth
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Severe cerebrovascular disease like change in strength on one side is greater than the other, trouble speaking or thinking, change in balance, or vision changes.
- Serotonin syndrome like dizziness, severe headache, agitation, sensing things that seem real but are not, fast heartbeat, abnormal heartbeat, flushing, tremors, sweating a lot, change in balance, severe nausea, or severe diarrhea.
- Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin.
- Infection
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Joint pain
- Purple patches on skin or mouth
- Slow heartbeat
- Fast heartbeat
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Severe headache
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Vision changes
- Seizures
- Tremors
- Abnormal movements
- Sweating a lot
- Agitation
- Burning or numbness feeling in extremities
- Change in color of hands or feet from pale to blue or red
- Temperature sensitivity
- Wounds on fingers or toes
- Erection that lasts more than 4 hours
- Unable to pass urine
- Change in amount of urine passed
- Muscle pain
- Muscle weakness
- Sex drive changes
- Depression like thoughts of suicide, anxiety, emotional instability, or confusion.
- Mood changes
- Sensing things that seem real but are not
- Behavioral changes
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.