Boxed Warning
Suicidality and antidepressant drugs:
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of doxepin or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared with placebo in adults older than 24 years; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared with placebo in adults 65 years and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Appropriately monitor patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy and observe closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the health care provider. Doxepin is not approved for use in pediatric patients.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling.
Capsule, Oral:
Generic: 10 mg, 25 mg, 50 mg, 75 mg, 100 mg, 150 mg
Concentrate, Oral:
Generic: 10 mg/mL (118 mL, 120 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Silenor: 3 mg [contains brilliant blue fcf (fd&c blue #1)]
Silenor: 6 mg [contains brilliant blue fcf (fd&c blue #1), fd&c yellow #10 (quinoline yellow)]
Generic: 3 mg, 6 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Increases the synaptic concentration of serotonin and norepinephrine in the central nervous system by inhibition of their reuptake by the presynaptic neuronal membrane (Pinder, 1977); antagonizes the histamine (H1) receptor for sleep maintenance.
Efficacy of doxepin in the off-label use of chronic urticaria is believed to be related to its potent H1 and H2 receptor antagonist activity (Kozel 2004).
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Administration with a high-fat meal increases the bioavailability of Silenor and delays the peak plasma concentration by ~3 hours
Distribution
Vd: 20.2 L/kg (Ziegler, 1978); Silenor 11,930 L
Metabolism
Hepatic via CYP2C19 and 2D6; metabolites include N-desmethyldoxepin (active)
Excretion
Urine (<3% as unchanged drug or N-desmethyldoxepin)
Onset of Action
Individual responses may vary; 4-8 weeks of treatment are needed before determining if a patient with depression is partially or nonresponsive (APA 2010); onset of anxiolytic effects may have a latency of 2-6 weeks (Bandelow 2008)
Time to Peak
Serum: Fasting: Silenor: 3.5 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Adults: Doxepin: ~15 hours; N-desmethyldoxepin: 31 to 51 hours (Hiemke 2018)
Protein Binding
~80%
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment may display higher doxepin concentrations than healthy individuals.
Use: Labeled Indications
Anxiety: Treatment of anxiety.
Depression: Treatment of depression including psychotic and bipolar depression.
Insomnia (Silenor only): Treatment of insomnia characterized by difficulty with sleep maintenance.
Use: Off Label
Chronic urticariacyes
Data from a controlled, double-blind crossover study supports the use of doxepin for the management of chronic idiopathic urticaria Greene 1985.
Based on clinical practice guidelines from the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (AAAAI); the American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology (ACAAI); and the Joint Council of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (JCAAI) for the diagnosis and management of acute and chronic urticaria, doxepin given for chronic idiopathic urticaria is effective and may be considered, particularly in patients whose symptoms remain poorly controlled with dose advancement of second-generation antihistamines and/or addition of one or more of the following: H2 antihistamines, first-generation H1 antihistamines, and/or leukotrienes. A World Allergy Organization position paper developed to supplement recent international guidelines does not mention doxepin for use in the management of chronic urticaria.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to doxepin, dibenzoxepins, or any component of the formulation; glaucoma; urinary retention; use of MAO inhibitors within 14 days
Documentation of allergenic cross-reactivity for tricyclic antidepressants is limited. However, because of similarities in chemical structure and/or pharmacologic actions, the possibility of cross-sensitivity cannot be ruled out with certainty.
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in the US labeling): During acute recovery phase following myocardial infarction; acute congestive heart failure; history of blood dyscrasias; severe hepatic disease; use in children
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Depression and/or anxiety: Oral: Initial: 25 to 50 mg as a single dose at bedtime or in divided doses; gradually increase based on response and tolerability to a usual dose of 100 to 300 mg daily (APA 2010; Bauer 2013).
Insomnia: Oral:
Tablet (Silenor): 3 to 6 mg once daily within 30 minutes of bedtime; maximum dose: 6 mg/day.
Capsule (off-label): Initial: 25 mg once daily at bedtime; may increase dose based on response and tolerability after 1 week up to 50 mg/day. Note: Doses <25 mg/day (ie, the 10-mg strength capsule) have not been evaluated for efficacy (BAP [Wilson 2010]; Hajak 2001).
Chronic urticaria (off-label use): Oral: Adults: 10 mg 3 times daily (Greene 1985) or 10 mg to 30 mg once daily at bedtime (Yadav 2009).
Discontinuation of therapy: When discontinuing antidepressant treatment that has lasted for >3 weeks, gradually taper the dose (eg, over 2 to 4 weeks) to minimize withdrawal symptoms and detect reemerging symptoms (APA 2010; WFSBP [Bauer 2015]). Reasons for a slower titration (eg, over 4 weeks) include use of a drug with a half-life <24 hours (eg, paroxetine, venlafaxine), prior history of antidepressant withdrawal symptoms, or high doses of antidepressants (APA 2010; Hirsch 2019a). If intolerable withdrawal symptoms occur, resume the previously prescribed dose and/or decrease dose at a more gradual rate (Shelton 2001). Select patients (eg, those with a history of discontinuation syndrome) on long-term treatment (>6 months) may benefit from tapering over >3 months (WFSBP [Bauer 2015]). Evidence supporting ideal taper rates is limited (Shelton 2001; WFSBP [Bauer 2015]).
Switching antidepressants: Evidence for ideal antidepressant switching strategies is limited; strategies include cross-titration (gradually discontinuing the first antidepressant while at the same time gradually increasing the new antidepressant) and direct switch (abruptly discontinuing the first antidepressant and then starting the new antidepressant at an equivalent dose or lower dose and increasing it gradually). Cross-titration (eg, over 1 to 4 weeks depending upon sensitivity to discontinuation symptoms and adverse effects) is standard for most switches but is contraindicated when switching to or from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). A direct switch may be an appropriate approach when switching to another agent in the same or similar class (eg, when switching between two SSRIs), when the antidepressant to be discontinued has been used for <1 week, or when the discontinuation is for adverse effects. When choosing the switch strategy, consider the risk of discontinuation symptoms, potential for drug interactions, other antidepressant properties (eg, half-life, adverse effects, pharmacodynamics), and the degree of symptom control desired (Hirsch 2019b; Ogle 2013; WFSBP [Bauer 2013]).
Switching to or from a monoamine oxidase inhibitor:
Allow 14 days to elapse between discontinuing an MAOI and initiation of doxepin.
Allow 14 days to elapse between discontinuing doxepin and initiation of an MAOI.
Dosing: Geriatric
Depression and/or anxiety: Oral: Carefully adjust the use of doxepin on a once-a-day dosage regimen in elderly patients based on the patient's condition; elderly patients generally should be started on low doses of doxepin and observed closely. Avoid doses >6 mg/day (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
Insomnia: Tablet (Silenor): Oral: 3 mg once daily within 30 minutes of bedtime; increase to 6 mg once daily if clinically needed; maximum dose: 6 mg daily. Avoid doses >6 mg/day (Beers Criteria [AGS 2019]).
Discontinuation of therapy: Refer to adult dosing.
Switching antidepressants: Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Depression and/or anxiety: Oral: Note: Controlled clinical trials have not shown tricyclic antidepressants to be superior to placebo for the treatment of depression in children and adolescents; not recommended as first line medication; may be beneficial for patients with comorbid conditions (Biramaher 2007; Dopheide 2006; Wagner 2005).
Children 7 to 11 years: Limited data available; efficacy results variable: 1 to 3 mg/kg/day in single or divided doses (Kliegman 2007)
Children ≥12 years and Adolescents: Initial: 25 to 75 mg/day at bedtime or in 2 to 3 divided doses; begin at the low end of range and gradually titrate; select patients may respond to 25 to 50 mg/day; maximum single dose: 150 mg; maximum daily dose: 300 mg/day
Discontinuation of therapy: Upon discontinuation of antidepressant therapy, gradually taper the dose to minimize the incidence of withdrawal symptoms and allow for the detection of reemerging symptoms. Evidence supporting ideal taper rates is limited. APA and NICE guidelines suggest tapering therapy over at least several weeks with consideration to the half-life of the antidepressant; antidepressants with a shorter half-life may need to be tapered more conservatively. In addition for long-term treated patients, WFSBP guidelines recommend tapering over 4 to 6 months. If intolerable withdrawal symptoms occur following a dose reduction, consider resuming the previously prescribed dose and/or decrease dose at a more gradual rate (APA 2010; Bauer 2002; Haddad 2001; NCCMH 2010; Schatzberg 2006; Shelton 2001; Warner 2006)
MAO inhibitor recommendations:
Switching to or from an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders:
Allow 14 days to elapse between discontinuing an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of doxepin.
Allow 14 days to elapse between discontinuing doxepin and initiation of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders.
Use with other MAO inhibitors (such as linezolid or IV methylene blue):
Do not initiate doxepin in patients receiving linezolid or IV methylene blue; consider other interventions for psychiatric condition.
If urgent treatment with linezolid or IV methylene blue is required in a patient already receiving doxepin and potential benefits outweigh potential risks, discontinue doxepin promptly and administer linezolid or IV methylene blue. Monitor for serotonin syndrome for 2 weeks or until 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue, whichever comes first. May resume doxepin 24 hours after the last dose of linezolid or IV methylene blue.
Reconstitution
Concentrate, oral: Must dilute with approximately 120 mL of water, whole or skimmed milk, or orange, grapefruit, tomato, prune or pineapple juice prior to administration. Do not mix with carbonated beverages (physically incompatible). Doxepin concentrate and methadone syrup can be mixed together with Gatorade, lemon or orange juice, sugar water, Tang, or water, but not with grape juice.
Administration
Depression and/or anxiety: Oral: Administer the total daily dosage in divided or once a day dosage schedule. If the once a day schedule is employed the maximum recommended dose is 150 mg once daily at bedtime. The 150 mg capsule strength is intended for maintenance therapy only and is not for initiation of treatment.
Insomnia: Oral: Administer within 30 minutes prior to bedtime. Do not take within 3 hours of food (high-fat meals delay peak levels of the tablet formulation [Silenor]).
Storage
Store at room temperature. Protect from light.
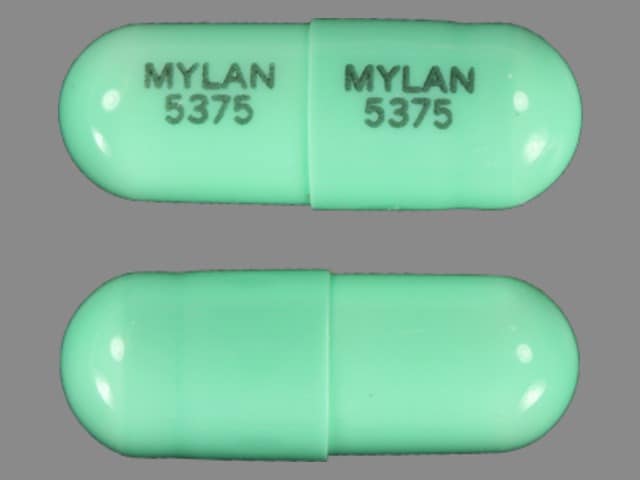
Doxepin (Systemic) Images
Drug Interactions
Abiraterone Acetate: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Avoid concurrent use of abiraterone with CYP2D6 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index whenever possible. When concurrent use is not avoidable, monitor patients closely for signs/symptoms of toxicity. Consider therapy modification
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors. Monitor therapy
Aclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Alcohol (Ethyl): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Alcohol (Ethyl). Monitor therapy
Alizapride: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Almotriptan: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Alosetron: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Alpha-/Beta-Agonists: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the vasopressor effect of Alpha-/Beta-Agonists. Management: Avoid, if possible, the use of alpha-/beta-agonists in patients receiving tricyclic antidepressants. If combined, monitor for evidence of increased pressor effects and consider reductions in initial dosages of the alpha-/beta-agonist. Consider therapy modification
Alpha1-Agonists: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the therapeutic effect of Alpha1-Agonists. Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Alpha1-Agonists. Monitor therapy
Alpha2-Agonists: Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the antihypertensive effect of Alpha2-Agonists. Management: Consider avoiding this combination. If used, monitor for decreased effects of the alpha2-agonist. Exercise great caution if discontinuing an alpha2-agonist in a patient receiving a TCA. Exceptions: Apraclonidine; Brimonidine (Ophthalmic); Lofexidine. Consider therapy modification
Alpha2-Agonists (Ophthalmic): Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Alpha2-Agonists (Ophthalmic). Monitor therapy
Altretamine: May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Amantadine: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Amifampridine: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the neuroexcitatory and/or seizure-potentiating effect of Amifampridine. Monitor therapy
Amphetamines: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Amphetamines. Tricyclic Antidepressants may potentiate the cardiovascular effects of Amphetamines. Amphetamines may enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased cardiovascular effects when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Anticholinergic Agents: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Antiemetics (5HT3 Antagonists): May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Alosetron; Ondansetron; Ramosetron. Monitor therapy
Antipsychotic Agents: Serotonergic Agents (High Risk) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Antipsychotic Agents. Specifically, serotonergic agents may enhance dopamine blockade, possibly increasing the risk for neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Antipsychotic Agents may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Monitor therapy
Aspirin: Tricyclic Antidepressants (Tertiary Amine) may enhance the antiplatelet effect of Aspirin. Monitor therapy
Asunaprevir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Consider therapy modification
Azelastine (Nasal): CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Azelastine (Nasal). Avoid combination
Barbiturates: May increase the metabolism of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Consider therapy modification
Beta2-Agonists: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Beta2-Agonists. Monitor therapy
Blonanserin: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Blonanserin. Consider therapy modification
Botulinum Toxin-Containing Products: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Brexanolone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Brexanolone. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Bromopride: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Avoid combination
Bromperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
Buprenorphine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Buprenorphine. Management: Consider reduced doses of other CNS depressants, and avoiding such drugs in patients at high risk of buprenorphine overuse/self-injection. Initiate buprenorphine at lower doses in patients already receiving CNS depressants. Consider therapy modification
BusPIRone: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cannabis: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
CarBAMazepine: May decrease the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Chloral Betaine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Chlormethiazole: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Monitor closely for evidence of excessive CNS depression. The chlormethiazole labeling states that an appropriately reduced dose should be used if such a combination must be used. Consider therapy modification
Chlorphenesin Carbamate: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cimetidine: May decrease the metabolism of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Cimetropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Cimetropium. Avoid combination
Cinacalcet: May increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Seek alternatives when possible. If these combinations are used, monitor closely for increased effects/toxicity and/or elevated serum concentrations (when testing is available) of the tricyclic antidepressant. Consider therapy modification
Citalopram: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. Citalopram may enhance the serotonergic effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and serotonin syndrome when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
CloBAZam: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CNS Depressants: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of other CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Cobicistat: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Cocaine (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Cyclobenzaprine: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
CYP2D6 Inhibitors (Moderate): May decrease the metabolism of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CYP2D6 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease the metabolism of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Consider therapy modification
Dacomitinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Avoid concurrent use of dacomitinib with CYP2D6 subtrates that have a narrow therapeutic index. Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Do not use serotonergic agents (high risk) with dapoxetine or within 7 days of serotonergic agent discontinuation. Do not use dapoxetine within 14 days of monoamine oxidase inhibitor use. Dapoxetine labeling lists this combination as contraindicated. Avoid combination
Darunavir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Desmopressin: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Desmopressin. Monitor therapy
Dexmethylphenidate-Methylphenidate: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Dextromethorphan: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Dimethindene (Topical): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Domperidone: QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Domperidone. Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
Doxylamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: The manufacturer of Diclegis (doxylamine/pyridoxine), intended for use in pregnancy, specifically states that use with other CNS depressants is not recommended. Monitor therapy
Dronabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Dronedarone: Doxepin-Containing Products may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Dronedarone. Avoid combination
Droperidol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider dose reductions of droperidol or of other CNS agents (eg, opioids, barbiturates) with concomitant use. Exceptions to this monograph are discussed in further detail in separate drug interaction monographs. Consider therapy modification
DULoxetine: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. DULoxetine may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations and effects if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Eletriptan: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Eluxadoline: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Eluxadoline. Avoid combination
Ergot Derivatives: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Nicergoline. Monitor therapy
Escitalopram: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. Escitalopram may enhance the serotonergic effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and serotonin syndrome when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Esketamine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Fexinidazole [INT]: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk). Avoid combination
Fexinidazole [INT]: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Fexinidazole [INT]. Avoid combination
Flunitrazepam: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Flunitrazepam. Consider therapy modification
FLUoxetine: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. FLUoxetine may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations/effects if these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
FluvoxaMINE: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. FluvoxaMINE may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations/effects if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic): Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Gastrointestinal Agents (Prokinetic). Monitor therapy
Gilteritinib: Doxepin-Containing Products may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Gilteritinib. Management: Patients with other risk factors (eg, older age, female sex, bradycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart disease, and higher drug concentrations) are likely at greater risk for these potentially life-threatening toxicities. Monitor therapy
Glucagon: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Glucagon. Specifically, the risk of gastrointestinal adverse effects may be increased. Monitor therapy
Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation): Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Glycopyrrolate (Oral Inhalation). Avoid combination
Glycopyrronium (Topical): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Guanethidine: Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Guanethidine. Monitor therapy
Haloperidol: QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Haloperidol. Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
HYDROcodone: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of HYDROcodone. Management: Avoid concomitant use of hydrocodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
HydrOXYzine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Imatinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products: Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Iobenguane Radiopharmaceutical Products. Management: Discontinue all drugs that may inhibit or interfere with catecholamine transport or uptake for at least 5 biological half-lives before iobenguane administration. Do not administer these drugs until at least 7 days after each iobenguane dose. Avoid combination
Iohexol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iohexol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iohexol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Iomeprol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iomeprol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iomeprol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Iopamidol: Agents With Seizure Threshold Lowering Potential may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Iopamidol. Specifically, the risk for seizures may be increased. Management: Discontinue agents that may lower the seizure threshold 48 hours prior to intrathecal use of iopamidol. Wait at least 24 hours after the procedure to resume such agents. In nonelective procedures, consider use of prophylactic anticonvulsants. Consider therapy modification
Ipratropium (Oral Inhalation): May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Itopride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Itopride. Monitor therapy
Kava Kava: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Lasmiditan: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Lemborexant: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Dosage adjustments of lemborexant and of concomitant CNS depressants may be necessary when administered together because of potentially additive CNS depressant effects. Close monitoring for CNS depressant effects is necessary. Consider therapy modification
Levosulpiride: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Levosulpiride. Avoid combination
Linezolid: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Lofexidine: Doxepin-Containing Products may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Lofexidine. Lofexidine may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. Doxepin-Containing Products may diminish the therapeutic effect of Lofexidine. Management: Consider avoiding this combination when possiblke. Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
Lorcaserin: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Lorcaserin may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations and effects if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Lumefantrine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Magnesium Sulfate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Metaxalone: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Methadone: Doxepin-Containing Products may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Methadone. Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
Methotrimeprazine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Methotrimeprazine. Methotrimeprazine may enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Reduce adult dose of CNS depressant agents by 50% with initiation of concomitant methotrimeprazine therapy. Further CNS depressant dosage adjustments should be initiated only after clinically effective methotrimeprazine dose is established. Consider therapy modification
Methylene Blue: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Methylene Blue. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Metoclopramide: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Seek alternatives to this combination when possible. Monitor patients receiving metoclopramide with tricyclic antidepressants for signs of extrapyramidal symptoms, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and serotonin syndrome. Consider therapy modification
MetyroSINE: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of MetyroSINE. Monitor therapy
MetyroSINE: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Mianserin: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Monitor therapy
Minocycline (Systemic): May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Mirabegron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Mirabegron. Monitor therapy
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (Antidepressant): May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Nabilone: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Nefazodone: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Nefazodone. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Nicorandil: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the hypotensive effect of Nicorandil. Monitor therapy
Nitroglycerin: Anticholinergic Agents may decrease the absorption of Nitroglycerin. Specifically, anticholinergic agents may decrease the dissolution of sublingual nitroglycerin tablets, possibly impairing or slowing nitroglycerin absorption. Monitor therapy
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (COX-2 Selective): Tricyclic Antidepressants (Tertiary Amine) may enhance the antiplatelet effect of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (COX-2 Selective). Monitor therapy
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (Nonselective): Tricyclic Antidepressants (Tertiary Amine) may enhance the antiplatelet effect of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents (Nonselective). Monitor therapy
Ondansetron: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Ondansetron may enhance the serotonergic effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and serotonin syndrome when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation or serotonin syndrome may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Opioid Agonists: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Opioid Agonists. Management: Avoid concomitant use of opioid agonists and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Orphenadrine: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Orphenadrine. Avoid combination
Oxatomide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Oxitriptan: Serotonergic Agents (High Risk) may enhance the serotonergic effect of Oxitriptan. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Oxomemazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Avoid combination
OxyCODONE: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of OxyCODONE. Management: Avoid concomitant use of oxycodone and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Panobinostat: May increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Paraldehyde: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Paraldehyde. Avoid combination
PARoxetine: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. PARoxetine may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations/effects if these agents are combined. Consider therapy modification
Peginterferon Alfa-2b: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Peginterferon Alfa-2b may increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Pentamidine (Systemic): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Perampanel: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Patients taking perampanel with any other drug that has CNS depressant activities should avoid complex and high-risk activities, particularly those such as driving that require alertness and coordination, until they have experience using the combination. Consider therapy modification
Perhexiline: CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors) may increase the serum concentration of Perhexiline. Perhexiline may increase the serum concentration of CYP2D6 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Pimozide: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk). Avoid combination
Piribedil: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Piribedil. Monitor therapy
Pitolisant: Tricyclic Antidepressants may diminish the therapeutic effect of Pitolisant. Avoid combination
Potassium Chloride: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Chloride. Management: Patients on drugs with substantial anticholinergic effects should avoid using any solid oral dosage form of potassium chloride. Avoid combination
Potassium Citrate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the ulcerogenic effect of Potassium Citrate. Avoid combination
Pramipexole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Pramipexole. Monitor therapy
Pramlintide: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. These effects are specific to the GI tract. Consider therapy modification
Protease Inhibitors: May increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Agents (Highest Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Doxepin-Containing Products. Management: Consider alternatives to this combination. Patients with other risk factors (eg, older age, female sex, bradycardia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, heart disease, and higher drug concentrations) are likely at greater risk for these toxicities. Exceptions: Dronedarone; Methadone. Consider therapy modification
QT-prolonging Antipsychotics (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Pimozide. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Class IC Antiarrhythmics (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Kinase Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Kinase Inhibitors (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Gilteritinib. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Miscellaneous Agents (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Miscellaneous Agents (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Domperidone; Lofexidine. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk). Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Monitor therapy
Ramosetron: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the constipating effect of Ramosetron. Monitor therapy
Ramosetron: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Rasagiline: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Revefenacin: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Revefenacin. Avoid combination
ROPINIRole: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of ROPINIRole. Monitor therapy
Rotigotine: CNS Depressants may enhance the sedative effect of Rotigotine. Monitor therapy
Rufinamide: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of CNS Depressants. Specifically, sleepiness and dizziness may be enhanced. Monitor therapy
Safinamide: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Secretin: Anticholinergic Agents may diminish the therapeutic effect of Secretin. Management: Avoid concomitant use of anticholinergic agents and secretin. Discontinue anticholinergic agents at least 5 half-lives prior to administration of secretin. Consider therapy modification
Selegiline: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Avoid combination
Serotonergic Agents (High Risk, Miscellaneous): Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk, Miscellaneous). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Serotonergic Non-Opioid CNS Depressants: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Serotonergic Non-Opioid CNS Depressants. Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Non-Opioid CNS Depressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and CNS depression when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Serotonergic Opioids (High Risk): Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Serotonergic Opioids (High Risk). Serotonergic Opioids (High Risk) may enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity and CNS depression. Consider therapy modification
Serotonin 5-HT1D Receptor Agonists (Triptans): May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Exceptions: Almotriptan; Eletriptan. Monitor therapy
Serotonin/Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes when these agents are combined. Exceptions: DULoxetine. Monitor therapy
Sertraline: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Sertraline may increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) and increased TCA concentrations/effects if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Sodium Oxybate: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Consider alternatives to combined use. When combined use is needed, consider minimizing doses of one or more drugs. Use of sodium oxybate with alcohol or sedative hypnotics is contraindicated. Consider therapy modification
Sodium Phosphates: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Sodium Phosphates. Specifically, the risk of seizure and/or loss of consciousness may be increased in patients with significant sodium phosphate induced fluid/electrolyte abnormalities. Monitor therapy
St John's Wort: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. St John's Wort may decrease the serum concentration of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Sulfonylureas: Cyclic Antidepressants may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of Sulfonylureas. Monitor therapy
Suvorexant: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Suvorexant. Management: Dose reduction of suvorexant and/or any other CNS depressant may be necessary. Use of suvorexant with alcohol is not recommended, and the use of suvorexant with any other drug to treat insomnia is not recommended. Consider therapy modification
Syrian Rue: May enhance the serotonergic effect of Serotonergic Agents (High Risk). This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) when these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Tapentadol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Management: Avoid concomitant use of tapentadol and benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants when possible. These agents should only be combined if alternative treatment options are inadequate. If combined, limit the dosages and duration of each drug. Consider therapy modification
Tetrahydrocannabinol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Thalidomide: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Thalidomide. Avoid combination
Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics: Anticholinergic Agents may increase the serum concentration of Thiazide and Thiazide-Like Diuretics. Monitor therapy
Thyroid Products: May enhance the arrhythmogenic effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Thyroid Products may enhance the stimulatory effect of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Tiotropium: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the anticholinergic effect of Tiotropium. Avoid combination
Topiramate: Anticholinergic Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Topiramate. Monitor therapy
Tricyclic Antidepressants: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of other Tricyclic Antidepressants. Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of other Tricyclic Antidepressants. Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of other Tricyclic Antidepressants. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor closely for increased TCA adverse effects, including serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity, CNS depression, and anticholinergic effects. Monitor therapy
Trimeprazine: May enhance the CNS depressant effect of CNS Depressants. Monitor therapy
Umeclidinium: May enhance the anticholinergic effect of Anticholinergic Agents. Avoid combination
Valproate Products: May increase the serum concentration of Tricyclic Antidepressants. Monitor therapy
Vilazodone: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Vilazodone. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Vortioxetine: Tricyclic Antidepressants may enhance the serotonergic effect of Vortioxetine. This could result in serotonin syndrome. Management: Monitor for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome/serotonin toxicity (eg, hyperreflexia, clonus, hyperthermia, diaphoresis, tremor, autonomic instability, mental status changes) if these agents are combined. Monitor therapy
Yohimbine: Tricyclic Antidepressants may increase the serum concentration of Yohimbine. Monitor therapy
Zolpidem: CNS Depressants may enhance the CNS depressant effect of Zolpidem. Management: Reduce the Intermezzo brand sublingual zolpidem adult dose to 1.75 mg for men who are also receiving other CNS depressants. No such dose change is recommended for women. Avoid use with other CNS depressants at bedtime; avoid use with alcohol. Consider therapy modification
Adverse Reactions
Actual frequency may be dependent on diagnosis.
Cardiovascular: Hypertension (chronic insomnia patients ≤3%), edema, flushing, hypotension, tachycardia
Central nervous system: Sedation (chronic insomnia patients 6% to 9%), dizziness (chronic insomnia patients ≥1%), ataxia, chills, confusion, disorientation, drowsiness, extrapyramidal reaction, fatigue, hallucination, headache, numbness, paresthesia, seizure, tardive dyskinesia
Dermatologic: Alopecia, diaphoresis (excessive), pruritus, skin photosensitivity, skin rash
Endocrine & metabolic: Altered serum glucose, change in libido, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, SIADH, weight gain
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (chronic insomnia patients 2%), gastroenteritis (chronic insomnia patients ≤2%), anorexia, aphthous stomatitis, constipation, diarrhea, dysgeusia, dyspepsia, vomiting, xerostomia
Genitourinary: Breast hypertrophy, testicular swelling, urinary retention
Hematologic & oncologic: Agranulocytosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia
Hepatic: Jaundice
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Tremor, weakness
Ophthalmic: Blurred vision
Otic: Tinnitus
Respiratory: Upper respiratory tract infection (chronic insomnia patients 4%), exacerbation of asthma
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abdominal pain, abnormal dreams, abnormal gait, acne rosacea, adenocarcinoma (lung, stage I), adjustment disorder, ageusia, altered blood pressure (inadequately controlled), anemia, angle-closure glaucoma, anxiety, arthralgia, atrioventricular block, back injury, back pain, blepharospasm, bone fracture, breast cyst, bronchitis, cerebrovascular accident, change in appetite, chest pain, confusion, cough, decreased heart rate, decreased lacrimation, decreased neutrophils, decreased performance on neuropsychometrics, decreased range of motion (joints), depression, dermatitis, diplopia, disturbance in attention, dysmenorrhea, dyspnea, dysuria, ECG abnormality (ST-T segment, QRS complex, QRS axis), erythema, eye infection, eye pain, eye redness, falling, feeling of heaviness, folliculitis, fungal infection, gastroesophageal reflux disease, gum line erosion, hematochezia, hematoma, hemoglobinuria, herpes zoster, hot flash, hyperbilirubinemia, hyperhidrosis, hyperkalemia, hypermagnesemia, hypersensitivity, hypoacusis, hypokalemia, increased serum ALT, increased serum transaminases, influenza, joint sprain, laceration, laryngitis, lethargy, limb pain, lip blister, lower respiratory tract infection, malignant melanoma, migraine, mood elevation, motion sickness, muscle cramps, myalgia, nasal congestion, nasopharyngeal disorder, neck pain, nightmares, nocturia, onychomycosis, otalgia, pallor, palpitations, perforated tympanic membrane, peripheral edema, pharyngitis, pharyngolaryngeal pain, pneumonia, rales, rhinorrhea, sinus congestion, sinusitis, skin irritation, sleep paralysis, somnambulism (complex sleep-related behavior [sleep-driving, cooking or eating food, making phone calls]), staphylococcal cellulitis, syncope, tenosynovitis, tooth infection, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection, vasodepressor syncope, ventricular premature contractions, viral infection, wheezing
Warnings/Precautions
Major psychiatric warnings:
- Suicidal thinking/behavior: [US Boxed Warning]: Antidepressants increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults (18 to 24 years of age) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders; consider risk prior to prescribing. Short-term studies did not show an increased risk in patients >24 years of age and showed a decreased risk in patients ≥65 years. Closely monitor patients for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior, particularly during the initial 1 to 2 months of therapy or during periods of dosage adjustments (increases or decreases); the patient's family or caregiver should be instructed to closely observe the patient and communicate condition with healthcare provider. A medication guide concerning the use of antidepressants should be dispensed with each prescription. Doxepin is not approved for use in pediatric patients.
- The possibility of a suicide attempt is inherent in major depression and may persist until remission occurs. Worsening depression and severe abrupt suicidality that are not part of the presenting symptoms may require discontinuation or modification of drug therapy. Use caution in high-risk patients during initiation of therapy.
- Risk of suicidal behavior may be increased regardless of doxepin dose; antidepressant doses of doxepin are 10- to 100-fold higher than doses for insomnia.
- Prescriptions should be written for the smallest quantity consistent with good patient care. The patient's family or caregiver should be alerted to monitor patients for the emergence of suicidality and associated behaviors such as anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, impulsivity, akathisia, hypomania, and mania; patients should be instructed to notify their healthcare provider if any of these symptoms or worsening depression or psychosis occur.
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Anticholinergic effects: May cause anticholinergic effects (constipation, xerostomia, blurred vision, urinary retention); use with caution in patients with decreased gastrointestinal motility, paralytic ileus, urinary retention, BPH, xerostomia, or visual problems. The degree of anticholinergic blockade produced by this agent is high relative to other antidepressants (APA 2010).
- CNS depression: May cause CNS depression, which may impair physical or mental abilities; patients must be cautioned about performing tasks that require mental alertness (eg, operating machinery or driving).
- Fractures: Bone fractures have been associated with antidepressant treatment. Consider the possibility of a fragility fracture if an antidepressant-treated patient presents with unexplained bone pain, point tenderness, swelling, or bruising (Rabenda 2013; Rizzoli 2012).
- Ocular effects: May cause mild pupillary dilation which in susceptible individuals can lead to an episode of narrow-angle glaucoma. Consider evaluating patients who have not had an iridectomy for narrow-angle glaucoma risk factors.
- Orthostatic hypotension: May cause orthostatic hypotension (risk is moderate relative to other antidepressants); use with caution in patients at risk of this effect or in those who would not tolerate transient hypotensive episodes (cerebrovascular disease, cardiovascular disease, hypovolemia, or concurrent medication use which may predispose to hypotension/bradycardia) (APA 2010).
- QT prolongation: May cause QT prolongation.
- SIADH and hyponatremia: Antidepressant agents have been associated with the development of SIADH and hyponatremia, predominately in elderly patients. Other risk factors include volume depletion, concurrent use of diuretics, female gender, low body weight, and severe physical illness. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) have a lower risk for hyponatremia in comparison to SSRIs (De Picker 2014).
- Sleep-related activities: An increased risk for hazardous sleep-related activities such as sleep-driving; cooking and eating food, making phone calls, and having sex while asleep have also been noted; amnesia may also occur. Discontinue treatment in patients who report any sleep-related episodes.
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with a history of cardiovascular disease (including previous MI, stroke, tachycardia, or conduction abnormalities); the risk conduction abnormalities with this agent is moderate relative to other antidepressants (APA 2010). In a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, doxepin has been determined to be an agent that may exacerbate underlying myocardial dysfunction (magnitude: moderate) (AHA [Page 2016]).
- Diabetes: Use with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus; may alter glucose regulation (APA 2010).
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution in patients with hepatic impairment; higher doxepin concentrations may occur.
- Mania/hypomania: May precipitate a shift to mania or hypomania in patients with bipolar disorder. Monotherapy in patients with bipolar disorder should be avoided. Patients presenting with depressive symptoms should be screened for bipolar disorder, including details regarding family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. Doxepin is not FDA approved for the treatment of bipolar depression.
- Respiratory disease: Use with caution in patients with respiratory compromise or sleep apnea; use of Silenor is generally not recommended in patients with severe sleep apnea.
- Seizure disorder: Use with caution in patients at risk of seizures, including those with a history of seizures, head trauma, brain damage, alcoholism, or concurrent therapy with medications which may lower seizure threshold (APA 2010).
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Elderly: May cause confusion and oversedation in elderly patients.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: Symptomatic treatment of insomnia should be initiated only after careful evaluation of potential causes of sleep disturbance. Failure of sleep disturbance to resolve after 7-10 days may indicate psychiatric and/or medical illness.
- Discontinuation syndrome: Abrupt discontinuation or interruption of antidepressant therapy has been associated with a discontinuation syndrome. Symptoms arising may vary with antidepressant however commonly include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, lightheadedness, dizziness, diminished appetite, sweating, chills, tremors, paresthesias, fatigue, somnolence, and sleep disturbances (eg, vivid dreams, insomnia). Less common symptoms include electric shock-like sensations, cardiac arrhythmias (more common with tricyclic antidepressants), myalgias, parkinsonism, arthralgias, and balance difficulties. Psychological symptoms may also emerge such as agitation, anxiety, akathisia, panic attacks, irritability, aggressiveness, worsening of mood, dysphoria, mood lability, hyperactivity, mania/hypomania, depersonalization, decreased concentration, slowed thinking, confusion, and memory or concentration difficulties. Greater risks for developing a discontinuation syndrome have been associated with antidepressants with shorter half-lives, longer durations of treatment, and abrupt discontinuation. For antidepressants of short or intermediate half-lives, symptoms may emerge within 2-5 days after treatment discontinuation and last 7-14 days (APA 2010; Fava 2006; Haddad 2001; Shelton 2001; Warner 2006).
- Electroconvulsive therapy: May increase the risks associated with electroconvulsive therapy; consider discontinuing, when possible, prior to ECT treatment (APA 2010).
- Surgery: Recommended by some manufacturers to discontinue TCAs prior to elective surgery; risks exist for drug interactions with anesthesia and for cardiac arrhythmias. However, definitive drug interactions have not been widely reported in the literature and continuation of TCAs is generally recommended as long as precautions are taken to reduce the significance of any adverse events that may occur. Norepinephrine should be considered the vasopressor of choice for TCA-related hypotension (Pass 2004). Therapy should not be abruptly discontinued in patients receiving high doses for prolonged periods.
Monitoring Parameters
ECG, heart rate, and blood pressure (in patients with preexisting cardiac disease or at increased risk for QT-prolonging effects); electrolytes (potassium, magnesium, and sodium concentrations at baseline and as clinically indicated); liver function tests (baseline; as clinically indicated); suicidal ideation (baseline and with dose changes); blood glucose (baseline and as clinically indicated); weight and BMI (at baseline; periodic intervals) (APA 2010).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor
C
Pregnancy Considerations
Tricyclic antidepressants may be associated with irritability, jitteriness, and convulsions (rare) in the neonate (Yonkers 2009).
The ACOG recommends that therapy for depression during pregnancy be individualized; treatment should incorporate the clinical expertise of the mental health clinician, obstetrician, primary health care provider, and pediatrician (ACOG 2008). According to the American Psychiatric Association (APA), the risks of medication treatment should be weighed against other treatment options and untreated depression. For women who discontinue antidepressant medications during pregnancy and who may be at high risk for postpartum depression, the medications can be restarted following delivery (APA 2010). Treatment algorithms have been developed by the ACOG and the APA for the management of depression in women prior to conception and during pregnancy (Yonkers 2009). Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are not the preferred initial therapy for depression in pregnancy; if a TCA is needed, doxepin is not the recommended agent (Larsen 2015).
Pregnant women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy are encouraged to enroll in the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants (NPRAD). Women 18 to 45 years of age or their health care providers may contact the registry by calling 844-405-6185. Enrollment should be done as early in pregnancy as possible.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat low mood (depression).
- It is used to treat anxiety.
- It is used to treat sleep problems.
- It may be given to you for other reasons. Talk with the doctor.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Taste changes
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Lack of appetite
- Mouth irritation
- Mouth sores
- Weight gain
- Sweating a lot
- Flushing
- Hair loss
- Dry mouth
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Depression like thoughts of suicide, anxiety, agitation, irritability, panic attacks, mood changes, behavioral changes, or confusion
- High blood sugar like confusion, fatigue, increased thirst, increased hunger, passing a lot of urine, flushing, fast breathing, or breath that smells like fruit
- Low blood sugar like dizziness, headache, fatigue, feeling weak, shaking, fast heartbeat, confusion, increased hunger, or sweating
- Fast heartbeat
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Not able to pass urine
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Anxiety
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Chills
- Sore throat
- Enlarged breasts
- Nipple discharge
- Testicle swelling
- Noise or ringing in the ears
- Yellow skin or eyes
- Severe headache
- Vision changes
- Worsening of asthma
- Eye pain
- Eye irritation
- Eyelid swelling
- Sexual dysfunction
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.