Dosage Forms
Tablet, oral:
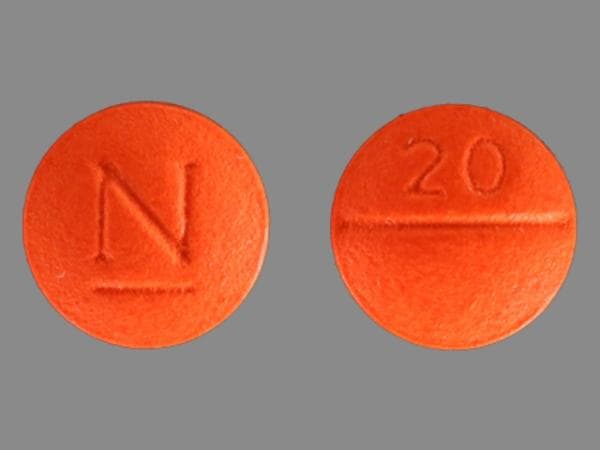
BiDil: Isosorbide dinitrate 20 mg and hydralazine hydrochloride 37.5 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
Hydralazine: Direct vasodilation of arterioles (with little effect on veins) resulting in decreased systemic resistance
Isosorbide Dinitrate: Stimulation of intracellular cyclic-GMP results in vascular smooth muscle relaxation of both arterial and venous vasculature with more prominent effects on the veins. Primarily reduces cardiac oxygen demand by decreasing preload (left ventricular end-diastolic pressure); may modestly reduce afterload. Additionally, coronary artery dilation improves collateral flow to ischemic regions.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Time to Peak
1 hour (both agents)
Half-Life Elimination
Hydralazine: 4 hours; Isosorbide dinitrate: 2 hours
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Hepatic Function Impairment
Isosorbide dinitrate concentrations increase in patients with cirrhosis.
Special Populations: Elderly
Isosorbide dinitrate, its active metabolites, and hydralazine may be eliminated more slowly in elderly patients.
Use: Labeled Indications
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): Treatment of heart failure as an adjunct to standard therapy in self-identified African-American patients. Note: Based on the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association (ACCF/AHA) guidelines for the management of heart failure, isosorbide dinitrate in combination with hydralazine is effective and recommended as additional therapy to optimal medical therapy for self-identified African-American patients with persistent NYHA class III or IV HFrEF or for patients who do not tolerate an ACE inhibitor or an ARB (ACC/AHA [Yancy 2013]). Some experts recommend isosorbide dinitrate in combination with hydralazine in addition to optimal guideline-directed medical therapy for black and nonblack patients with persistent NYHA class III or IV HFrEF, particularly for those with low output states or hypertension, or for patients who do not tolerate an ACE inhibitor, ARB, or angiotensin II-neprilysin inhibitor (Colucci 2019).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to organic nitrates or any component in the formulation; concomitant use with phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (eg, avanafil, sildenafil, tadalafil, vardenafil); concomitant use with riociguat
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF): Note: As additional therapy for persistent NYHA class III or IV HFrEF despite optimal medical therapies or for patients who cannot tolerate an ACE inhibitor, ARB, or angiotensin II-neprilysin inhibitor (ACCF/AHA [Yancy 2013]; Colucci 2019).
Oral: Initial: One tablet (containing 20 mg of isosorbide dinitrate and 37.5 mg of hydralazine) 3 times daily; titrate dose in 2 to 4 weeks to a maximum dose of 2 tablets (containing a total of 40 mg of isosorbide dinitrate and 75 mg of hydralazine) 3 times daily. Note: May also consider use of hydralazine 3 times daily and isosorbide dinitrate 3 times daily as separate components rather than this combination tablet (ACC/AHA/HFSA [Yancy 2017]; ACCF/AHA [Yancy 2013]; Meyer 2019).
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Adjustment for Toxicity
If patient experiences intolerable side effects, dose may be reduced to as little as one-half tablet 3 times daily; dose should be titrated upward as soon as tolerated.
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Protect from light.
Isosorbide Dinitrate and Hydralazine Images
Drug Interactions
Alcohol (Ethyl): May enhance the vasodilatory effect of Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates). Monitor therapy
Alfuzosin: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Amifostine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Amifostine. Management: When amifostine is used at chemotherapy doses, blood pressure lowering medications should be withheld for 24 hours prior to amifostine administration. If blood pressure lowering therapy cannot be withheld, amifostine should not be administered. Consider therapy modification
Amphetamines: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]): Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Antipsychotic Agents (Second Generation [Atypical]). Monitor therapy
Aprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Barbiturates: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Benperidol: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Blood Pressure Lowering Agents: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Hypotension-Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Bosentan: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Brigatinib: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Brigatinib may enhance the bradycardic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Brimonidine (Topical): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Bromperidol: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Bromperidol. Bromperidol may diminish the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Avoid combination
Clofazimine: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Conivaptan: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
CYP3A4 Inducers (Moderate): May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inducers (Strong): May increase the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Consider an alternative for one of the interacting drugs. Some combinations may be specifically contraindicated. Consult appropriate manufacturer labeling. Consider therapy modification
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Strong): May decrease the metabolism of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Consider therapy modification
Dabrafenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Seek alternatives to the CYP3A4 substrate when possible. If concomitant therapy cannot be avoided, monitor clinical effects of the substrate closely (particularly therapeutic effects). Consider therapy modification
Dapoxetine: May enhance the orthostatic hypotensive effect of HydrALAZINE. Monitor therapy
Dapsone (Topical): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Methemoglobinemia Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Deferasirox: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Dexmethylphenidate: May diminish the therapeutic effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Diazoxide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
DULoxetine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of DULoxetine. Monitor therapy
Duvelisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Enzalutamide: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Concurrent use of enzalutamide with CYP3A4 substrates that have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided. Use of enzalutamide and any other CYP3A4 substrate should be performed with caution and close monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Erdafitinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Erdafitinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosaprepitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fosnetupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Fusidic Acid (Systemic): May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Herbs (Hypertensive Properties): May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Herbs (Hypotensive Properties): May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Hypotension-Associated Agents: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Hypotension-Associated Agents. Monitor therapy
Idelalisib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Avoid combination
Ivosidenib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Larotrectinib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Levodopa-Containing Products: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Levodopa-Containing Products. Monitor therapy
Local Anesthetics: Methemoglobinemia Associated Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Local Anesthetics. Specifically, the risk for methemoglobinemia may be increased. Monitor therapy
Lorlatinib: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Avoid concurrent use of lorlatinib with any CYP3A4 substrates for which a minimal decrease in serum concentrations of the CYP3A4 substrate could lead to therapeutic failure and serious clinical consequences. Consider therapy modification
Lormetazepam: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Methylphenidate: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
MiFEPRIStone: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Minimize doses of CYP3A4 substrates, and monitor for increased concentrations/toxicity, during and 2 weeks following treatment with mifepristone. Avoid cyclosporine, dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, fentanyl, pimozide, quinidine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus. Consider therapy modification
Mitotane: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Management: Doses of CYP3A4 substrates may need to be adjusted substantially when used in patients being treated with mitotane. Consider therapy modification
Molsidomine: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates). Monitor therapy
Molsidomine: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Naftopidil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Netupitant: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Nicergoline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nicorandil: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Nitric Oxide: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Methemoglobinemia Associated Agents. Combinations of these agents may increase the likelihood of significant methemoglobinemia. Monitor therapy
Nitroprusside: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Nitroprusside. Monitor therapy
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of HydrALAZINE. Monitor therapy
Obinutuzumab: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Management: Consider temporarily withholding blood pressure lowering medications beginning 12 hours prior to obinutuzumab infusion and continuing until 1 hour after the end of the infusion. Consider therapy modification
Palbociclib: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Pentoxifylline: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Pholcodine: Blood Pressure Lowering Agents may enhance the hypotensive effect of Pholcodine. Monitor therapy
Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors: May enhance the vasodilatory effect of Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates). Avoid combination
Prilocaine: Methemoglobinemia Associated Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Prilocaine. Combinations of these agents may increase the likelihood of significant methemoglobinemia. Management: Monitor patients for signs of methemoglobinemia (e.g., hypoxia, cyanosis) when prilocaine is used in combination with other agents associated with development of methemoglobinemia. Avoid lidocaine/prilocaine in infants receiving such agents. Monitor therapy
Prostacyclin Analogues: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Quinagolide: May enhance the hypotensive effect of Blood Pressure Lowering Agents. Monitor therapy
Rilmenidine: Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates) may enhance the hypotensive effect of Rilmenidine. Monitor therapy
Riociguat: Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates) may enhance the hypotensive effect of Riociguat. Avoid combination
Rosiglitazone: Vasodilators (Organic Nitrates) may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Rosiglitazone. Specifically, a greater risk of ischemia and other adverse effects has been associated with this combination in some pooled analyses. Monitor therapy
Sarilumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Siltuximab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Simeprevir: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Monitor therapy
Sodium Nitrite: Methemoglobinemia Associated Agents may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Sodium Nitrite. Combinations of these agents may increase the likelihood of significant methemoglobinemia. Monitor therapy
Stiripentol: May increase the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inhibitors). Management: Use of stiripentol with CYP3A4 substrates that are considered to have a narrow therapeutic index should be avoided due to the increased risk for adverse effects and toxicity. Any CYP3A4 substrate used with stiripentol requires closer monitoring. Consider therapy modification
Tocilizumab: May decrease the serum concentration of CYP3A4 Substrates (High risk with Inducers). Monitor therapy
Yohimbine: May diminish the antihypertensive effect of Antihypertensive Agents. Monitor therapy
Adverse Reactions
The following events were reported in the A-HeFT Study using the combination isosorbide dinitrate/hydralazine product. See individual drug monographs for additional information.
>10%:
Cardiovascular: Chest pain (16%)
Central nervous system: Headache (50%), dizziness (32%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Weakness (14%)
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Hypotension (8%), palpitations (4%), ventricular tachycardia (4%), tachycardia (2%)
Central nervous system: Paresthesia (4%), drowsiness (1%), malaise (1%)
Dermatologic: Alopecia (1%), diaphoresis (1%)
Endocrine & metabolic: Hyperglycemia (4%), hyperlipidemia (3%), hypercholesterolemia (1%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (10%), vomiting (4%), cholecystitis (1%)
Hypersensitivity: Angioedema (1%), hypersensitivity reaction (1%)
Neuromuscular & skeletal: Arthralgia (1%), myalgia (1%), tendon disease (1%)
Ophthalmic: Amblyopia (3%)
Respiratory: Bronchitis (8%), rhinitis (4%), sinusitis (4%)
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Drug-induced lupus-like syndrome: Hydralazine may cause a drug-induced lupus-like syndrome (more likely on larger doses, longer duration).
- Fluid/sodium retention: Hydralazine-induced fluid and sodium retention may require addition or increased dosage of diuretics.
- Hypotension/bradycardia: Severe hypotension can occur; paradoxical bradycardia and increased angina pectoris can accompany hypotension. Use with caution in volume or salt depletion and/or moderate hypotension; use with extreme caution with inferior wall MI and suspected right ventricular infarctions. Symptomatic hypotension, particularly with upright posture, may occur with even small doses.
- Intracranial pressure increased: Nitrates may precipitate or aggravate increased intracranial pressure and subsequently may worsen clinical outcomes in patients with neurologic injury (eg, intracranial hemorrhage, traumatic brain injury) (Rangel-Castilla 2008).
- Peripheral neuritis: Hydralazine has been associated with peripheral neuritis (eg, paresthesia, numbness, and tingling), possibly due to an antipyridoxine effect. Pyridoxine therapy should be initiated with onset of such symptoms.
Disease-related concerns:
- Cardiovascular disease: Use with caution in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD); tachycardia and hypotension (due to hydralazine) may potentiate myocardial ischemia and angina, especially in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM): Avoid use in patients with HCM with outflow tract obstruction; nitrates may reduce preload, exacerbating obstruction and cause hypotension or syncope and/or worsening of heart failure (ACCF/AHA [Gersh, 2011]).
- Pulmonary hypertension: Use with caution in pulmonary hypertension; may cause hypotension.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Tolerance: When nitrates are used in combination with hydralazine for HF, tolerance to nitrate therapy is less of a concern (Gogia 1995).
Monitoring Parameters
Blood pressure (standing and sitting/supine), heart rate; CBC and antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers (if symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus occur)
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Hydralazine crosses the placenta (ESC [Regitz-Zagrosek 2018]).
See individual monographs for additional information.
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat heart failure (weak heart).
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Headache
- Loss of strength and energy
- Nausea
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Lupus like rash on the cheeks or other body parts, sunburn easy, muscle or joint pain, chest pain or shortness of breath, or swelling in the arms or legs.
- Severe dizziness
- Passing out
- Chest pain
- Fast heartbeat
- Burning or numbness feeling
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.