Boxed Warning
Serious adverse reactions:
Fluoroquinolones have been associated with disabling and potentially irreversible serious adverse reactions that have occurred together, including tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and CNS effects. Discontinue levofloxacin immediately and avoid the use of fluoroquinolones in patients who experience any of these serious adverse reactions. Because fluoroquinolones have been associated with serious adverse reactions, reserve levofloxacin for use in patients who have no alternative treatment options for the following indications: uncomplicated urinary tract infection, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and acute bacterial sinusitis.
Exacerbation of myasthenia gravis:
Fluoroquinolones may exacerbate muscle weakness in patients with myasthenia gravis. Avoid levofloxacin in patients with a known history of myasthenia gravis.
Dosage Forms
Excipient information presented when available (limited, particularly for generics); consult specific product labeling. [DSC] = Discontinued product
Solution, Intravenous [preservative free]:
Generic: 250 mg/50 mL (50 mL); 500 mg/100 mL (100 mL); 750 mg/150 mL (150 mL); 25 mg/mL (20 mL, 30 mL)
Solution, Oral:
Generic: 25 mg/mL (10 mL [DSC], 20 mL [DSC], 100 mL, 200 mL, 480 mL)
Tablet, Oral:
Levaquin: 250 mg [DSC], 500 mg, 750 mg
Generic: 250 mg, 500 mg, 750 mg
Pharmacology
Mechanism of Action
As the S(-) enantiomer of the fluoroquinolone, ofloxacin, levofloxacin, inhibits DNA-gyrase in susceptible organisms thereby inhibits relaxation of supercoiled DNA and promotes breakage of DNA strands. DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II), is an essential bacterial enzyme that maintains the superhelical structure of DNA and is required for DNA replication and transcription, DNA repair, recombination, and transposition.
Pharmacokinetics/Pharmacodynamics
Absorption
Rapid and complete; levofloxacin oral tablet and solution formulations are bioequivalent
Distribution
Widely distributed in the body, including blister fluid, skin tissue, macrophages, prostate, and lung tissue; CSF concentrations ~15% of serum concentrations
Vd: (Chien 2005):
Infants ≥6 months, Children, and Adolescents ≤16 years: Mean range: 1.44 to 1.57 L/kg; reported values not statistically different between pediatric age subgroups; distribution not age-dependent
Adults: 1.27 L/kg
Metabolism
Minimally hepatic
Excretion
Urine (~87% as unchanged drug, <5% as metabolites); feces (<4%)
Clearance: IV (Chien 2005):
Infants and Children 6 months to 2 years: 0.35 ± 0.13 L/hour/kg
Children 2 to 5 years: 0.32 ± 0.08 L/hour/kg
Children 5 to 10 years: 0.25 ± 0.05 L/hour/kg
Children 10 to 12 years: 0.19 ± 0.05 L/hour/kg
Children 12 to 16 years: 0.18 ± 0.03 L/hour/kg
Adults: 0.15 ± 0.02 L/hour/kg
Time to Peak
1 to 2 hours
Half-Life Elimination
Infants ≥6 months and Children ≤5 years: ~4 hours (Chien 2005)
Children 5 to 10 years: 4.8 hours (Chien 2005)
Children 10 to 12 years: 5.4 hours (Chien 2005)
Children 12 to 16 years: 6 hours (Chien 2005)
Adults: ~6 to 8 hours
Adults, renal impairment: 27 ± 10 hours (CrCl 20 to 49 mL/minute); 35 ± 5 hours (CrCl <20 mL/minute)
Protein Binding
~24% to 38%; primarily to albumin
Use in Specific Populations
Special Populations: Renal Function Impairment
Cl is reduced and half-life prolonged in patients with CrCl less than 50 mL/minute.
Use: Labeled Indications
Treatment of community-acquired pneumonia, including multidrug-resistant strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae (MDRSP); nosocomial pneumonia; acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis; rhinosinusitis, acute bacterial (ABRS); prostatitis (chronic bacterial); urinary tract infection (uncomplicated or complicated); acute pyelonephritis; skin or skin structure infections (uncomplicated or complicated); inhalational anthrax (postexposure) to reduce incidence or disease progression; prophylaxis and treatment of plague (pneumonic and septicemic) due to Yersinia pestis
Limitations of use: Because fluoroquinolones have been associated with disabling and potentially irreversible serious adverse reactions (eg, tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, CNS effects), reserve levofloxacin for use in patients who have no alternative treatment options for acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, acute bacterial sinusitis, and uncomplicated urinary tract infections.
Use: Off Label
Anthraxyes
Based on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) expert panel meetings on prevention and treatment of anthrax in adults, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended agent for treatment of cutaneous anthrax and a recommended alternative agent for systemic anthrax.
Bite wound infection, prophylaxis or treatment (animal or human bite)yes
Based on the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines for the diagnosis and management of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), levofloxacin, in combination with metronidazole or clindamycin, is an effective and recommended alternative option for treatment of bite wounds, particularly in patients with a human bite wound who are hypersensitive to beta-lactams.
Cervicitis or urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis infectionyes
Based on the CDC sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended alternative agent in the treatment of cervicitis or urethritis due to C. trachomatis infection.
Diabetic foot infectionyes
Based on the IDSA guideline for diagnosis and treatment of diabetic foot infections, levofloxacin, in combination with clindamycin, is an effective and recommended treatment option for diabetic foot infections.
Epididymitis, acuteyes
Based on the CDC sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended agent in the treatment acute epididymitis most likely caused by sexually transmitted chlamydia, gonorrhea, and enteric organisms in men who practice insertive anal sex (in combination with ceftriaxone) or for acute epididymitis most likely caused by enteric organisms (as monotherapy).
Helicobacter pylori eradicationyes
Based on the American College of Gastroenterology clinical guideline for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori infection, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended component of a multiple-drug regimen for the treatment of H. pylori infection.
Intra-abdominal infection, complicated, community-acquiredyes
Based on the Surgical Infection Society (SIS) and IDSA guidelines for the diagnosis and management of complicated intra-abdominal infections, levofloxacin, in combination with metronidazole, is an effective and recommended treatment option for empiric therapy of complicated community-acquired intra-abdominal infections when resistance rates are less than 10% to 20%.
Neutropenia (chemotherapy-induced), antibacterial prophylaxisayes
Data from 2 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials support the use of oral levofloxacin for prophylaxis of bacterial infections in patients receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy Bucaneve 2005, Cullen 2005.
Based on the IDSA guidelines for the use of antimicrobial agents in neutropenic patients with cancer, oral levofloxacin is effective and recommended for antibiotic prophylaxis in high-risk patients with expected durations of prolonged and profound neutropenia (ANC ≤100 cells/mm3 for >7 days).
Osteomyelitiscyes
Data from a retrospective study suggest that levofloxacin may be beneficial for the treatment of osteomyelitis Senneville 2007. Clinical experience also suggests the utility of levofloxacin for the treatment of osteomyelitis Osmon 2019.
Based on the IDSA guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis, oral levofloxacin is effective and recommended for the treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis caused by susceptible gram-negative organisms.
Pelvic inflammatory diseaseyes
Based on the CDC sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, levofloxacin, in combination with metronidazole, may be considered as alternative treatment in patients allergic to cephalosporins with pelvic inflammatory disease. The CDC recommends use as an alternative therapy only if standard parenteral cephalosporin therapy is not feasible, community prevalence and individual risk of quinolone-resistant gonococcal organisms is low, and if follow-up is likely. Culture sensitivity must be confirmed.
Prostatitis (acute bacterial)c
Clinical experience suggests the utility of levofloxacin in the treatment of acute bacterial prostatitis Lipsky 2010.
Prosthetic joint infectioncyes
Clinical experience suggests the utility of levofloxacin in the treatment and suppression of prosthetic joint infection caused by gram-negative bacilli Berbari 2019.
Based on the IDSA guidelines for the management of prosthetic joint infection, levofloxacin, in combination with rifampin, is an effective and recommended agent for oral phase treatment of prosthetic joint infection with staphylococci after completion of parenteral therapy.
Surgical (preoperative) prophylaxisyes
Based on the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, IDSA, SIS, and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America guidelines for antimicrobial prophylaxis in surgery, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended alternative agent for prophylaxis of certain surgical procedures (eg, gastroduodenal procedures) when a beta-lactam allergy exists.
Surgical site incisional infectionyes
Based on the IDSA guidelines for the diagnosis and management of SSTIs, levofloxacin, in combination with metronidazole, is an effective and recommended option for treatment of surgical site incisional infections occurring after surgery of the intestinal or genitourinary tract, perineum, or axilla. Systemic antibacterials are not routinely indicated for surgical site infections, but may be beneficial (in conjunction with suture removal plus incision and drainage) in patients with significant systemic response (eg, temperature >38.5ºC, heart rate >110 beats per minute, erythema/induration extending >5 cm from incision, WBC >12,000/mm3).
Travelers' diarrheayes
Based on the CDC Yellow Book, the IDSA practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of infectious diarrhea, and the American College of Gastroenterology guideline for the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of acute diarrheal infections in adults, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended treatment option for the management of travelers' diarrhea.
Tuberculosisyes
Based on the American Thoracic Society, CDC, and IDSA guidelines for the treatment of tuberculosis, levofloxacin is an effective and recommended alternative agent for treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis caused by sensitive organisms or when first-line agents are intolerable.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to levofloxacin, any component of the formulation, or other quinolones
Canadian labeling: Additional contraindications (not in US labeling): History of tendonitis or tendon rupture associated with use of any quinolone antimicrobial agent
Dosage and Administration
Dosing: Adult
Anthrax: Note: Consult public health officials for event-specific recommendations.
Inhalational exposure (postexposure prophylaxis) (alternative agent): Oral: 750 mg every 24 hours for 60 days. Note: Anthrax vaccine should also be administered to exposed individuals (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Cutaneous (without systemic involvement), treatment (off-label use): Oral: 750 mg every 24 hours for 7 to 10 days after naturally acquired infection; treat for 60 days for bioterrorism-related cases. Note: Patients with cutaneous lesions of the head or neck or extensive edema should be treated for systemic involvement (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Systemic (meningitis excluded), treatment (alternative agent) (off-label use): IV: 750 mg every 24 hours, in combination with other appropriate agents for 2 weeks or until clinically stable, whichever is longer (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Meningitis, treatment (alternative agent) (off-label use): IV: 750 mg every 24 hours, in combination with other appropriate agents for 2 to 3 weeks or until clinically stable, whichever is longer (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Note: Antitoxin should also be administered for patients with suspected systemic anthrax. Following the course of IV combination therapy for systemic anthrax infection (including meningitis), patients exposed to aerosolized spores require oral monotherapy to complete a total antimicrobial course of 60 days (CDC [Hendricks 2014]).
Bite wound infection, prophylaxis or treatment (animal or human bite) (alternative agent) (off-label use): Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily, in combination with an agent appropriate for anaerobes. Duration of therapy is 3 to 5 days for prophylaxis (IDSA [Stevens 2014]); duration of treatment for established infection is typically 5 to 14 days and varies based on patient-specific factors, including clinical response (Baddour 2019a; Baddour 2019b).
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, acute exacerbation: Oral, IV: 500 mg once daily (Amsden 2003) for 5 to 7 days (Bartlett 2019; GOLD 2018); use 750 mg once daily if Pseudomonas aeruginosa is suspected (Martinez 2005; Nicolau 2012). Note: Some experts reserve levofloxacin for patients with moderate to severe exacerbations of complicated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (eg, age ≥65 years of age, FEV1 <50% predicted, frequent exacerbations, significant comorbidities) (Bartlett 2019; Sethi 2008).
Diabetic foot infection (off-label use): Note: When used as empiric therapy, levofloxacin should be used in combination with other appropriate agents.
Mild to moderate infection: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hours (750 mg every 24 hours if P. aeruginosa is suspected) (IDSA [Lipsky 2012]; Weintrob 2019).
Moderate to severe infection (alternative agent): IV: 750 mg every 24 hours (IDSA [Lipsky 2012]; Weintrob 2019).
Epididymitis, acute (off-label use):
Patients ≥35 years of age and who are at low risk for sexually transmitted diseases (ie, likely caused by enteric organisms): Oral: 500 mg once daily for 10 days. Note: In patients <35 years of age or who are at risk of sexually transmitted diseases, fluoroquinolones are not recommended due to widespread resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to these agents (CDC [Workowski 2015]; Eyre 2019).
Men of any age who practice insertive anal sex (ie, likely caused by sexually transmitted Chlamydia trachomatis or N. gonorrhoeae, and enteric organisms): Oral: 500 mg once daily for 10 days, in combination with a single dose of ceftriaxone (CDC [Workowski 2015]; Eyre 2019; Marrazzo 2018).
Helicobacter pylori eradication (alternative agent) (off-label use): Levofloxacin triple regimen: Oral: Levofloxacin 500 mg once daily, in combination with amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, plus a standard-dose proton pump inhibitor twice daily; continue regimen for 10 to 14 days (ACG [Chey 2017]).
Intra-abdominal infection (including perforated appendix, appendiceal abscess, acute diverticulitis, acute cholecystitis), community-acquired (off-label use): Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily (SIS/IDSA [Solomkin 2010]). For empiric therapy, usually administered in combination with metronidazole. The addition of metronidazole may not be necessary for uncomplicated biliary infection of mild to moderate severity (SIS/IDSA [Solomkin 2010]; Vollmer 2019). Duration of therapy is for 4 to 7 days following adequate source control (SIS/IDSA [Solomkin 2010]); for uncomplicated appendicitis and diverticulitis managed nonoperatively, a longer duration is necessary (Barshak 2019; Pemberton 2019). Note: Empiric oral regimens may be appropriate for patients with mild to moderate infection. Other patients may be switched from IV to oral therapy at the same dose when clinically improved and able to tolerate an oral diet (SIS/IDSA [Solomkin 2010]; SIS [Mazuski 2017]).
Neutropenia (chemotherapy-induced), antibacterial prophylaxis in high-risk patients anticipated to have an ANC ≤100 cells/mm3 for >7 days (off-label use): Oral: 500 or 750 mg once daily (Bucaneve 2005; Cullen 2005; IDSA [Freifeld 2011]; Lee 2018b; Wingard 2019). Some clinicians will provide antibacterial prophylaxis if ANC is anticipated to be <500 cells/mm3 for >7 days (Wingard 2019). For hematopoietic cell transplant recipients, begin at the time of stem cell infusion and continue until recovery of neutropenia or until initiation of empiric antibiotic therapy for neutropenic fever (ASBMT [Tomblyn 2009]).
Osteomyelitis (off-label use): Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily for ≥6 weeks (IDSA [Berbari 2015]; Osmon 2019; Senneville 2007).
Plague (Yersinia pestis infection): Note: Consult public health officials for event-specific recommendations:
Treatment: Limited data available: Oral, IV: 500 mg every 24 hours for 10 to 14 days (CDC 2015; Sexton 2019). Note: Some experts reserve fluoroquinolones for patients who cannot tolerate aminoglycosides or tetracyclines (Sexton 2019).
Postexposure prophylaxis (alternative agent): Oral: 500 mg once daily for 10 days (Sexton 2019).
Pneumonia:
Community-acquired pneumonia: Outpatients or inpatients (non-ICU or ICU): Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily. Duration is for a minimum of 5 days and varies based on disease severity and response to therapy; patients should be afebrile for ≥48 hours and clinically stable prior to discontinuation. Note: Use in outpatients should be reserved for patients with comorbidities, immunosuppressing conditions, or a history of antimicrobial use within previous 3 months. When used as empiric therapy of ICU inpatients, use in combination with other appropriate agent(s) (IDSA/ATS [Mandell 2007]).
Hospital-acquired or ventilator-associated pneumonia: Oral, IV: 750 mg every 24 hours for 7 days; duration may be individualized based on patient-specific factors and response to therapy. When used as empiric therapy, use in combination with other appropriate agents (IDSA/ATS [Kalil 2016]).
Prostatitis:
Acute bacterial prostatitis (off-label use): Oral, IV: 500 mg once daily for 4 to 6 weeks (Meyrier 2019a).
Chronic bacterial prostatitis: Oral: 500 mg once daily for 4 to 6 weeks (Meyrier 2019b).
Prosthetic joint infection (off-label use):
Treatment:
Gram-negative bacilli: Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily (Berbari 2019).
Staphylococcus aureus, oral continuation therapy (following pathogen-specific IV therapy in patients undergoing 1-stage exchange or debridement with retention of prosthesis): Oral: 500 to 750 mg once daily in combination with rifampin; duration is a minimum of 3 months, depending on patient-specific factors (Berbari 2019; IDSA [Osmon 2013]).
Chronic suppressive therapy for gram-negative bacilli: Oral: 500 mg once daily (Berbari 2019).
Rhinosinusitis, acute bacterial (alternative agent): Oral: 500 or 750 mg once daily for 5 to 7 days (initial therapy) or 7 to 10 days (for patients who have not responded to initial therapy) (IDSA [Chow 2012]; Patel 2019). Note: In uncomplicated acute bacterial rhinosinusitis, initial observation and symptom management without antibiotic therapy is appropriate in most patients (AAO-HNS [Rosenfeld 2015]; ACP/CDC [Harris 2016]). Fluoroquinolone use in acute sinusitis should be reserved for those who have no alternative treatment options due to serious risks associated with use compared to benefits (FDA Drug Safety Communication 2016).
Sexually transmitted infections:
Cervicitis or urethritis due to Chlamydia trachomatis (alternative agent) (off-label use): Oral: 500 mg once daily for 7 days (CDC [Workowski 2015]); consider concurrent treatment for gonorrhea based on individual risk factors or if local prevalence is elevated (>5%) (CDC [Workowski 2015]; Marrazzo 2018).
Pelvic inflammatory disease, outpatient therapy, mild to moderate disease (alternative agent) (off-label use): Patients where fluoroquinolone-resistant N. gonorrhoeae is not likely a causative agent: Oral: 500 mg once daily with metronidazole for 14 days (CDC [Workowski 2015]). Some experts consider the addition of metronidazole optional (Wiesenfeld 2019). Note: Due to concerns of fluoroquinolone resistance, use should only be considered when first-line options cannot be given or the prevalence of fluoroquinolone-resistant N. gonorrhoeae is <5% in the location where the infection was acquired (CDC [Workowski 2015]; Wiesenfeld 2019).
Skin and skin structure infection:
Purulent cellulitis or abscess (for patients with or at risk for gram-negative infection): Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily in combination with other appropriate agents. Treat for 5 to 14 days depending on severity and clinical response. Note: Systemic antibiotics are only indicated for treatment of abscess in certain instances (eg, immunocompromised patients, signs of systemic infection, large or multiple abscesses, indwelling device, high risk for adverse outcome with endocarditis) (IDSA [Stevens 2014]; Spelman 2019).
Surgical site incisional infection (off-label use):
Intestinal or genitourinary tract surgery: IV: 750 mg every 24 hours in combination with metronidazole (IDSA [Stevens 2014]).
Perineum or axilla surgery: Oral, IV: 750 mg every 24 hours in combination with metronidazole (IDSA [Stevens 2014]).
Surgical (preoperative) prophylaxis (alternative agent) (off-label use): IV: 500 mg beginning 120 minutes prior to initial surgical incision; use in combination with other appropriate agents may be warranted (procedure dependent) (ASHP/IDSA/SIS/SHEA [Bratzler 2013]). Note: Postoperative prophylaxis is not recommended for clean and clean-contaminated surgeries (CDC [Berríos-Torres 2017]).
Traveler's diarrhea, uncomplicated (empiric therapy) (off-label use): Oral: 500 mg once daily for 1 to 3 days (ACG [Riddle 2016]; Riddle 2017). If symptoms not resolved after 24 hours following single-dose therapy, continue for a total of 3 days. The 3-day therapy course is recommended in patients with fever or dysentery; enteric infection due to Shigella dysenteriae is an exception as a 5-day treatment duration appears to be superior to single-dose or 3-day regimens (ACG [Riddle 2016]). Note: Most cases are self-limited and may not warrant antimicrobial therapy. Fluoroquinolone resistance is increasing; azithromycin may be preferred, particularly in regions such as Southeast Asia or India with a high prevalence of Campylobacter (ACG [Riddle 2016]).
Tuberculosis (alternative agent) (off-label use): Note: Expert consultation for optimal regimen and duration of treatment is advised.
Drug-susceptible tuberculosis: Oral, IV: 500 mg to 1 g every 24 hours given in combination with additional appropriate antituberculosis agents (IDSA [Nahid 2016]).
Drug-resistant tuberculosis: Oral, IV: 750 mg to 1 g every 24 hours given in combination with additional appropriate antituberculosis agents. Note: In the treatment of multi-drug resistant TB, greater efficacy has been observed with 1,000 mg doses compared to 500 mg doses (Schluger 2019).
Urinary tract infection:
Note: Uncomplicated urinary tract infection (UTI) has traditionally been defined as infection in an otherwise healthy nonpregnant female with a normal urinary tract; UTI in other patient populations has been considered complicated. Some experts instead categorize UTI as either acute simple cystitis (mild infection limited to the bladder with no signs/symptoms of upper tract or systemic infection in a nonpregnant adult) or complicated UTI (pyelonephritis or cystitis symptoms with other signs/symptoms of systemic infection) (Hooton 2019a; Hooton 2019b).
Acute uncomplicated or simple cystitis in females:
Note: Use is discouraged due to safety concerns and significant Escherichia coli resistance; reserve for those who have no alternative treatment options (Bidell 2016; FDA Drug Safety Communication 2016; Hooton 2019a; IDSA [Gupta 2011]).
Oral: 250 mg once daily for 3 days (manufacturer's labeling).
Acute pyelonephritis or other complicated urinary tract infection:
Note: If the prevalence of fluoroquinolone resistance is >10%, an initial dose of a long-acting parenteral antimicrobial, such as ceftriaxone, ertapenem, or a consolidated 24-hour dose of an aminoglycoside is recommended for outpatients (Hooton 2019b; IDSA [Gupta 2011]).
Oral, IV: 750 mg once daily for 5 to 7 days (Hooton 2019b).
Missed dose: Administer as soon as possible if ≥8 hours until next scheduled dose; otherwise, wait until next scheduled dose.
Dosing: Geriatric
Refer to adult dosing.
Dosing: Pediatric
Note: Concentration of oral suspension may vary (commercially available or extemporaneous compounded); use caution. In pediatric patients, fluoroquinolones are not routinely first-line therapy, but after assessment of risks and benefits, can be considered a reasonable alternative for situations where no safe and effective substitute is available (eg, multidrug resistance) or in situations where the only alternative is parenteral therapy and levofloxacin offers an oral therapy option (AAP [Jackson 2016]).
General dosing, susceptible infection (AAP [Jackson 2016]): Infants ≥6 months, Children, and Adolescents:
6 months to <5 years: Oral, IV: 8 to 10 mg/kg/dose twice daily
≥5 years: Oral, IV: 10 mg/kg/dose once daily; maximum dose: 750 mg/day
Anthrax: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Limited data available in infants <6 months of age: Note: Levofloxacin is not preferred therapy for any prophylaxis or treatment regimens; use should be considered when patients are unable to tolerate first-line therapy (eg, ciprofloxacin or others depending upon disease presentation). Although longer durations of therapy are recommended in guidelines in some cases based on risk:benefit assessments (eg, up to 60 days), specific safety data for levofloxacin in pediatric patients is limited to 14 days (AAP [Bradley 2014]).
Cutaneous, without systemic involvement; treatment (AAP [Bradley 2014]): Appropriate for all strains regardless of penicillin susceptibility or if susceptibility unknown. Treatment duration: 7 to 10 days for naturally-acquired infection, and up to 60 days for biological weapon-related event.
<50 kg: Oral: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hours
Inhalational (postexposure prophylaxis) (AAP [Bradley 2014]): Reserve levofloxacin use for penicillin-resistant strains or prior to susceptibility testing. Begin therapy as soon as possible after exposure.
<50 kg: Oral (preferred), IV: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours for 60 days; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: Oral (preferred), IV: 500 mg every 24 hours for 60 days
Systemic anthrax (excluding meningitis); treatment (AAP [Bradley 2014]): Note: A fluoroquinolone is appropriate for all strains regardless of penicillin susceptibility or if susceptibility unknown; ciprofloxacin is preferred.
Initial treatment: Use in combination with a protein synthesis inhibitor (eg, clindamycin); continue therapy for at least 14 days or longer until clinical criteria for stability are met.
<50 kg: IV: 10 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: IV: 500 mg every 24 hours
Oral step-down therapy: Use in combination with a protein synthesis inhibitor (eg, clindamycin). Duration of therapy to complete treatment course is variable; some patients may require up to 60 days additional prophylaxis from onset of illness.
<50 kg: Oral: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hours
Systemic anthrax; disseminated infection including meningitis (or when meningitis cannot be ruled out):
Initial triple therapy: Use in combination with another bactericidal antimicrobial (beta-lactam or glycopeptide [depending on susceptibility]) and a protein synthesis inhibitor (eg, linezolid); continue therapy for at least 2 to 3 weeks or longer until clinical criteria for stability are met
<50 kg: IV: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: IV: 500 mg every 24 hours
Oral step-down therapy: Use in combination with a protein synthesis inhibitor (eg, clindamycin). Duration of therapy to complete treatment course is variable; some patients may require up to 60 days additional prophylaxis from onset of illness.
<50 kg: Oral: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hour
Catheter (peritoneal dialysis); exit-site or tunnel infection: Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Oral: 10 mg/kg/dose every 48 hours; maximum initial dose: 500 mg; maximum subsequent doses: 250 mg (ISPD [Warady 2012])
Chlamydia trachomatis, urogenital infections: Adolescents: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hours for 7 days (CDC [Workowski 2015])
Cystic fibrosis pulmonary exacerbation: Limited data available (Chmiel 2014): Infants ≥6 months, Children, and Adolescents:
6 months to <5 years: Oral, IV: 10 mg/kg/dose twice daily
≥5 years: Oral, IV: 10 mg/kg/dose once daily; maximum dose: 750 mg/day
Epididymitis, nongonococcal: Adolescents: Oral: 500 mg once daily for 10 days (CDC [Workowski 2015])
Mycobacterium avium Complex, severe or disseminated disease, HIV-exposed/-positive: Adolescents: Oral: 500 mg once daily in combination with other antibiotics (HHS [OI adult 2016])
Pelvic inflammatory disease: Adolescents: Oral: 500 mg once daily for 14 days with or without concomitant metronidazole; Note: Due to resistant organisms, the CDC recommends use as an alternative therapy only if standard parenteral cephalosporin therapy is not feasible and community prevalence, and individual risk of quinolone-resistant gonococcal organisms is low. Culture sensitivity must be confirmed (CDC [Workowski 2015]).
Plague (Yersinia pestis), prophylaxis or treatment: Infants ≥6 months, Children, and Adolescents: Note: Begin therapy as soon as possible after exposure:
<50 kg: Oral, IV: 8 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours for 10 to 14 days; maximum dose: 250 mg/dose
≥50 kg: Oral, IV: 500 mg every 24 hours for 10 to 14 days
Pneumonia, community-acquired (CAP) (IDSA/PIDS [Bradley 2011]): Note: May consider addition of vancomycin or clindamycin to empiric therapy if community-acquired MRSA suspected. Levofloxacin is not the preferred agent for CAP but may be used as an alternative agent when necessary.
Typical pathogens (eg, H. influenzae, S. pneumoniae): Note: Oral administration is generally reserved for mild infections or step-down therapy.
Infants ≥6 months and Children <5 years: Oral, IV: 8 to 10 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Children ≥5 years and Adolescents ≤16 years: Oral, IV: 8 to 10 mg/kg/dose once every 24 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Atypical pathogens (eg, Mycoplasma pneumonia or Chlamydia ssp):
IV:
Infants ≥6 months and Children <5 years: IV: 8 to 10 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Children ≥5 years and Adolescents ≤16 years: IV: 8 to 10 mg/kg/dose once every 24 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Oral: Mild infection/step-down therapy: Adolescents with skeletal maturity: Oral: 500 mg once daily
Rhinosinusitis, acute bacterial: Note: Recommended in the following types of patients: Type I penicillin allergy, after failure of initial therapy or in patients at risk for antibiotic resistance (eg, daycare attendance, age <2 years, recent hospitalization, antibiotic use within the past month) (Chow 2012). Children and Adolescents: Oral, IV: 10 to 20 mg/kg/day divided every 12 to 24 hours for 10 to 14 days; maximum daily dose: 500 mg/day
Surgical prophylaxis: Children and Adolescents: IV: 10 mg/kg as a single dose 120 minutes prior to procedure; maximum dose: 500 mg/dose; Note: While fluoroquinolones have been associated with an increased risk of tendinitis/tendon rupture in all ages, use of these agents for single-dose prophylaxis is generally safe (Bratzler 2013).
Tuberculosis, multidrug-resistant: Limited data available: Note: Use in combination with at least 2 to 3 additional anti-TB agents (overall multidrug regimen dependent upon susceptibility profile/patterns) (Seddon 2012):
Infants and Children <5 years: Oral: 7.5 to 10 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Children ≥5 years and Adolescents: Oral: 7.5 to 10 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours; maximum daily dose: 750 mg/day
Urethritis, nongonococcal: Adolescents: Oral: 500 mg every 24 hours for 7 days (CDC [Workowski 2015])
Reconstitution
Solution for injection: Single-use vials must be further diluted in compatible solution (eg, D5W, NS) to a final concentration of 5 mg/mL prior to infusion.
Extemporaneously Prepared
Note: Commercial oral solution is available (25 mg/mL)
A 50 mg/mL oral suspension may be made with tablets and a 1:1 mixture of Ora-Plus® and strawberry syrup NF. Crush six 500 mg levofloxacin tablets in a mortar and reduce to a fine powder. Add small portions of the vehicle and mix to a uniform paste; mix while adding the vehicle in incremental proportions to almost 60 mL; transfer to a graduated cylinder, rinse mortar with vehicle, and add quantity of vehicle sufficient to make 60 mL. Label "shake well". Stable for 57 days when stored in amber plastic prescription bottles at room temperature or refrigerated.
VandenBussche HL, Johnson CE, and Fontana EM, et al, "Stability of Levofloxacin in an Extemporaneously Compounded Oral Liquid," Am J Health Syst Pharm, 1999, 56(22):2316-8.10582824
Administration
Oral: Tablets may be administered without regard to meals. Oral solution should be administered at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals. Maintain adequate hydration of patient to prevent crystalluria. Administer at least 2 hours before or 2 hours after antacids containing magnesium or aluminum, sucralfate, metal cations (eg, iron), multivitamin preparations with zinc, or didanosine chewable/buffered tablets or the pediatric powder for solution.
IV: Infuse 250 to 500 mg IV solution over 60 minutes; infuse 750 mg IV solution over 90 minutes. Too rapid of infusion can lead to hypotension. Avoid administration through an intravenous line with a solution containing multivalent cations (eg, magnesium, calcium). Maintain adequate hydration of patient to prevent crystalluria or cylindruria.
Dietary Considerations
Tablets may be taken without regard to meals. Oral solution should be administered on an empty stomach (at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after a meal).
Storage
Solution for injection:
Vial: Store at room temperature. Protect from light. Diluted solution (5 mg/mL) is stable in NS, D5W, D5NS, D5LR, D51/2NS with 20 mEq/L KCl, Plasma-Lyte 56 in D5, or sodium lactate for 72 hours when stored at room temperature; stable for 14 days when stored under refrigeration. When frozen, stable for 6 months; do not refreeze. Do not thaw in microwave or by bath immersion.
Premixed: Store at ≤25°C (77°F); do not freeze. Brief exposure to 40°C (104°F) does not adversely affect the product. Protect from light.
Tablet, oral solution: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
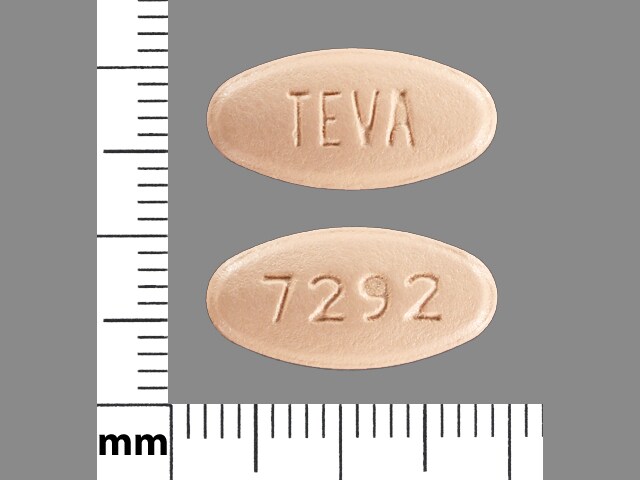
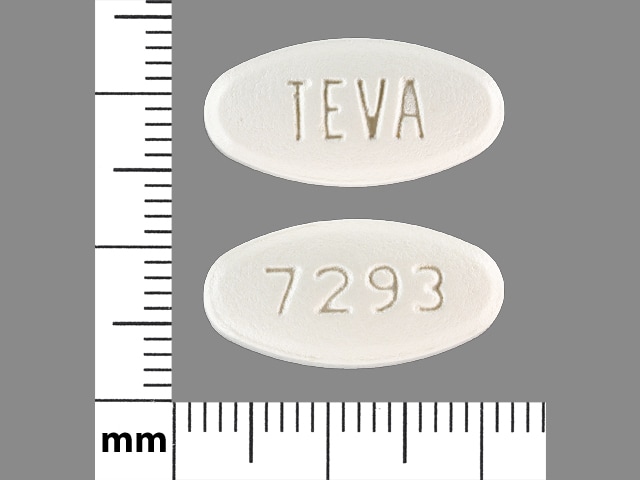
Levofloxacin (Systemic) Images
Drug Interactions
Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Systemic). Avoid combination
Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical): Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Aminolevulinic Acid (Topical). Monitor therapy
Amiodarone: Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Amiodarone. Avoid combination
Amphetamines: May enhance the cardiotoxic effect of Quinolones. Monitor therapy
Antacids: May decrease the absorption of Quinolones. Of concern only with oral administration of quinolones. Management: Avoid concurrent administration of quinolones and antacids to minimize the impact of this interaction. Recommendations for optimal dose separation vary by specific quinolone. Exceptions: Sodium Bicarbonate. Consider therapy modification
BCG (Intravesical): Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG (Intravesical). Avoid combination
BCG Vaccine (Immunization): Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of BCG Vaccine (Immunization). Monitor therapy
Blood Glucose Lowering Agents: Quinolones may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of Blood Glucose Lowering Agents. Quinolones may diminish the therapeutic effect of Blood Glucose Lowering Agents. Specifically, if an agent is being used to treat diabetes, loss of blood sugar control may occur with quinolone use. Monitor therapy
Calcium Salts: May decrease the absorption of Quinolones. Of concern only with oral administration of both agents. Exceptions: Calcium Chloride. Consider therapy modification
Cholera Vaccine: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Cholera Vaccine. Management: Avoid cholera vaccine in patients receiving systemic antibiotics, and within 14 days following the use of oral or parenteral antibiotics. Avoid combination
Corticosteroids (Systemic): May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Quinolones. Specifically, the risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture may be increased. Monitor therapy
Delamanid: QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Delamanid. Delamanid may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Avoid concomitant use of delamanid and quinolone antibiotics if possible. If coadministration is considered to be unavoidable, frequent monitoring of electrocardiograms throughout the full delamanid treatment period should occur. Consider therapy modification
Didanosine: Quinolones may decrease the serum concentration of Didanosine. Didanosine may decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Administer oral quinolones at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after didanosine. Monitor for decreased therapeutic effects of quinolones, particularly if doses cannot be separated as recommended. This does not apply to unbuffered enteric coated didanosine. Consider therapy modification
Domperidone: QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Domperidone. Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
Fexinidazole [INT]: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk). Avoid combination
Haloperidol: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Heroin: Quinolones may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Heroin. Monitor therapy
Iron Preparations: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Give oral quinolones at least several hours before (4 h for moxi- and sparfloxacin, 2 h for others) or after (8 h for moxi-, 6 h for cipro/dela-, 4 h for lome-, 3 h for gemi-, and 2 h for levo-, nor-, oflox-, pefloxacin, or nalidixic acid) oral iron. Exceptions: Ferric Carboxymaltose; Ferric Derisomaltose; Ferric Gluconate; Ferric Hydroxide Polymaltose Complex; Ferric Pyrophosphate Citrate; Ferumoxytol; Iron Dextran Complex; Iron Sucrose. Consider therapy modification
Lactobacillus and Estriol: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus and Estriol. Monitor therapy
Lanthanum: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Administer oral quinolone antibiotics at least one hour before or four hours after lanthanum. Consider therapy modification
Magnesium Salts: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Administer oral quinolones several hours before (4 h for moxi/pe/spar-, 2 h for others) or after (8 h for moxi-, 6 h for cipro/dela-, 4 h for lome/pe-, 3 h for gemi-, and 2 h for levo-, nor-, or ofloxacin or nalidixic acid) oral magnesium salts. Consider therapy modification
Methadone: Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Methadone. Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
Methylphenidate: May enhance the cardiotoxic effect of Quinolones. Monitor therapy
Multivitamins/Minerals (with ADEK, Folate, Iron): May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Specifically, polyvalent cations in multivitamin products may decrease the absorption of orally administered quinolone antibiotics. Management: Interactions can be minimized by administering the oral quinolone at least 2 hours before, or 6 hours after, the dose of a multivitamin that contains polyvalent cations (i.e., calcium, iron, magnesium, selenium, zinc). Consider therapy modification
Multivitamins/Minerals (with AE, No Iron): May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Specifically, minerals in the multivitamin/mineral product may impair absorption of quinolone antibiotics. Management: Interactions can be minimized by administering the oral quinolone at least 2 hours before, or 6 hours after, the dose of a multivitamin that contains polyvalent cations (i.e., calcium, iron, magnesium, selenium, zinc). Consider therapy modification
Mycophenolate: Quinolones may decrease the serum concentration of Mycophenolate. Specifically, quinolones may decrease concentrations of the active metabolite of mycophenolate. Monitor therapy
Nadifloxacin: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Quinolones. Avoid combination
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents: May enhance the neuroexcitatory and/or seizure-potentiating effect of Quinolones. Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Agents may increase the serum concentration of Quinolones. Monitor therapy
Ondansetron: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Pentamidine (Systemic): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Pimozide: May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Agents (Moderate Risk). Avoid combination
Porfimer: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Porfimer. Monitor therapy
Probenecid: May decrease the excretion of Quinolones. Specifically, probenecid may decreased the renal excretion of quinolone antibiotics. Probenecid may increase the serum concentration of Quinolones. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antidepressants (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Antipsychotics (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Antipsychotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Pimozide. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Class IA Antiarrhythmics (Highest Risk): Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Class IA Antiarrhythmics (Highest Risk). Avoid combination
QT-prolonging Class IC Antiarrhythmics (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Class IC Antiarrhythmics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Class III Antiarrhythmics (Highest Risk): Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Class III Antiarrhythmics (Highest Risk). Avoid combination
QT-prolonging Kinase Inhibitors (Highest Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic). Management: Consider alternatives to this drug combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Consider therapy modification
QT-prolonging Kinase Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Kinase Inhibitors (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Miscellaneous Agents (Highest Risk): Levofloxacin-Containing Products (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Miscellaneous Agents (Highest Risk). Management: Consider alternatives to this combination. If combined, monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Delamanid. Consider therapy modification
QT-prolonging Miscellaneous Agents (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Exceptions: Domperidone. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Moderate CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk): May enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of other QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
QT-prolonging Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk): QT-prolonging Quinolone Antibiotics (Moderate Risk) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of QT-prolonging Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors (Moderate Risk). Management: Monitor for QTc interval prolongation and ventricular arrhythmias when these agents are combined. Patients with additional risk factors for QTc prolongation may be at even higher risk. Monitor therapy
Quinapril: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Separate doses of quinapril and oral quinolones by at least 2 hours in order to reduce the risk of interaction. Monitor for reduced efficacy of the quinolone if these products are used concomitantly. Consider therapy modification
Sevelamer: May decrease the absorption of Quinolones. Management: Administer oral quinolones at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after sevelamer. Consider therapy modification
Sodium Picosulfate: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Sodium Picosulfate. Management: Consider using an alternative product for bowel cleansing prior to a colonoscopy in patients who have recently used or are concurrently using an antibiotic. Consider therapy modification
Strontium Ranelate: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: In order to minimize any potential impact of strontium ranelate on quinolone antibiotic concentrations, it is recommended that strontium ranelate treatment be interrupted during quinolone therapy. Avoid combination
Sucralfate: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Avoid concurrent administration of quinolones and sucralfate to minimize the impact of this interaction. Recommendations for optimal dose separation vary by specific quinolone. Consider therapy modification
Tacrolimus (Systemic): LevoFLOXacin (Systemic) may enhance the QTc-prolonging effect of Tacrolimus (Systemic). LevoFLOXacin (Systemic) may increase the serum concentration of Tacrolimus (Systemic). Monitor therapy
Typhoid Vaccine: Antibiotics may diminish the therapeutic effect of Typhoid Vaccine. Only the live attenuated Ty21a strain is affected. Management: Vaccination with live attenuated typhoid vaccine (Ty21a) should be avoided in patients being treated with systemic antibacterial agents. Use of this vaccine should be postponed until at least 3 days after cessation of antibacterial agents. Consider therapy modification
Varenicline: Quinolones may increase the serum concentration of Varenicline. Management: Monitor for increased varenicline adverse effects with concurrent use of levofloxacin or other quinolone antibiotics, particularly in patients with severe renal impairment. International product labeling recommendations vary. Consult appropriate labeling. Monitor therapy
Verteporfin: Photosensitizing Agents may enhance the photosensitizing effect of Verteporfin. Monitor therapy
Vitamin K Antagonists (eg, warfarin): Quinolones may enhance the anticoagulant effect of Vitamin K Antagonists. Monitor therapy
Zinc Salts: May decrease the serum concentration of Quinolones. Management: Give oral quinolones at least several hours before (4 h for moxi- and sparfloxacin, 2 h for others) or after (8 h for moxi-, 6 h for cipro/dela-, 4 h for lome-, 3 h for gemi-, and 2 h for levo-, nor-, pe- or ofloxacin or nalidixic acid) oral zinc salts. Exceptions: Zinc Chloride. Consider therapy modification
Test Interactions
Some quinolones may produce a false-positive urine screening result for opioids using commercially-available immunoassay kits. This has been demonstrated most consistently for levofloxacin and ofloxacin, but other quinolones have shown cross-reactivity in certain assay kits. Confirmation of positive opioid screens by more specific methods should be considered.
Adverse Reactions
1% to 10%:
Cardiovascular: Chest pain (1%), edema (1%)
Central nervous system: Headache (6%), insomnia (4%), dizziness (3%)
Dermatologic: Skin rash (2%), pruritus (1%)
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (7%), diarrhea (5%), constipation (3%), abdominal pain (2%), dyspepsia (2%), vomiting (2%)
Genitourinary: Vaginitis (1%)
Infection: Candidiasis (1%)
Local: Injection site reaction (1%)
Respiratory: Dyspnea (1%)
<1%, postmarketing, and/or case reports: Abnormal dreams, abnormal electroencephalogram, abnormal gait, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, acute renal failure, ageusia, agitation, agranulocytosis, altered sense of smell, anaphylactic shock, anaphylaxis, anemia, angioedema, anorexia, anosmia, anxiety, aplastic anemia, arthralgia, blurred vision, bronchospasm, cardiac arrhythmia, casts in urine, Clostridioides difficile associated diarrhea, Clostridioides difficile colitis, confusion, crystalluria, decreased visual acuity, delirium, depression, dermatological disorders, diplopia, disorientation, disturbance in attention, drowsiness, dysgeusia, elevation in serum levels of skeletal-muscle enzymes, encephalopathy (rare), eosinophilia, epistaxis, erythema multiforme, esophagitis, exacerbation of myasthenia gravis, fever, fixed drug eruption, gastritis, gastroenteritis, genital candidiasis, glossitis, granulocytopenia, hallucination, hemolytic anemia, hepatic failure, hepatic insufficiency, hepatitis, hepatotoxicity (idiosyncratic) (Chalasani 2014), hyperglycemia, hyperkalemia, hyperkinetic muscle activity, hypersensitivity angiitis, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, hypersensitivity reaction, hypertonia, hypoacusis, hypoglycemia, hypotension, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, increased INR, increased intracranial pressure, increased liver enzymes, increased serum alkaline phosphatase, interstitial nephritis, jaundice, leukopenia, memory impairment, multiorgan failure, muscle injury, muscular paralysis (musculospiral) (Pan 2017), myalgia, nervousness, nightmares, nonimmune anaphylaxis, palpitations, pancreatitis, pancytopenia, paranoid ideation, paresthesia, peripheral neuropathy (may be irreversible), phlebitis, phototoxicity, prolonged prothrombin time, prolonged QT interval on ECG, psychosis, renal function abnormality, restlessness, rhabdomyolysis, rupture of tendon, scotoma, seizure, serum sickness, skeletal pain, skin photosensitivity, sleep disorder, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, stomatitis, suicidal ideation, suicidal tendencies, syncope, tachycardia, tendonitis, thrombocytopenia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura, tinnitus, torsades de pointes, toxic epidermal necrolysis, toxic psychosis, tremor, urticaria, uveitis, vasodilation, ventricular arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia, vertigo, visual disturbance, voice disorder
Warnings/Precautions
Concerns related to adverse effects:
- Altered cardiac conduction: Fluoroquinolones may prolong QTc interval; avoid use in patients with a history of QTc prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, or concurrent administration of other medications known to prolong the QT interval (including Class Ia and Class III antiarrhythmics, cisapride, erythromycin, antipsychotics, and tricyclic antidepressants).
- Aortic aneurysm and dissection: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with aortic aneurysm ruptures or dissection within 2 months following use, particularly in elderly patients. Fluoroquinolones should not be used in patients with a known history of aortic aneurysm or those at increased risk, including patients with peripheral atherosclerotic vascular diseases, hypertension, genetic disorders involving blood vessel changes (eg, Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome), and elderly patients, unless no other treatment options are available. Longer treatment duration (eg, >14 days) may increase risk (Lee 2018a).
- Glucose regulation: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with disturbances in glucose regulation, including hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia. These events have occurred most often in patients receiving concomitant oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin. Severe cases of hypoglycemia, including coma and death, have been reported. Diabetic patients should be monitored closely for signs/symptoms of disordered glucose regulation. Discontinue if a hypoglycemic reaction occurs and immediately initiate appropriate therapy.
- Hepatotoxicity: Unrelated to hypersensitivity, severe hepatotoxicity (including acute hepatitis and fatalities) has been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk. Discontinue therapy immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatitis occur.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred with quinolone therapy. The spectrum of these reactions can vary widely; reactions may present as typical allergic symptoms (eg, itching, urticaria, rash, edema) after a single dose, or may manifest as severe idiosyncratic dermatologic (eg, Stevens-Johnson, toxic epidermal necrolysis), vascular (eg, vasculitis), pulmonary (eg, pneumonitis), renal (eg, nephritis), hepatic (eg, hepatic failure, necrosis), and/or hematologic (eg, anemia, cytopenias) events, usually after multiple doses. Prompt discontinuation of drug should occur if skin rash or other symptoms arise.
- Phototoxicity: Avoid excessive sunlight and take precautions to limit exposure (eg, loose-fitting clothing, sunscreen); may cause moderate to severe phototoxicity reactions. Discontinue use if photosensitivity occurs.
- Serious adverse reactions: [US Boxed Warning]: Fluoroquinolones are associated with disabling and potentially irreversible serious adverse reactions that may occur together, including tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, and CNS effects. Discontinue levofloxacin immediately and avoid use of fluoroquinolones in patients who experience any of these serious adverse reactions. Patients of any age or without preexisting risk factors have experienced these reactions; may occur within hours to weeks after initiation.
- CNS effects: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with an increased risk of CNS effects including seizures, increased intracranial pressure (including pseudotumor cerebri), lightheadedness, dizziness, and tremors. May occur following the first dose; discontinue immediately and avoid further use of fluoroquinolones in patients who experience these reactions. Use with caution in patients with known or suspected CNS disorder, or risk factors that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with an increased risk of peripheral neuropathy; may occur soon after initiation of therapy and may be irreversible; discontinue if symptoms of sensory or sensorimotor neuropathy occur. Avoid use in patients who have previously experienced peripheral neuropathy.
- Psychiatric reactions: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with an increased risk of psychiatric reactions, including toxic psychosis, hallucinations, or paranoia; may also cause nervousness, agitation, delirium, attention disturbances, insomnia, anxiety, nightmares, memory impairment, confusion, depression, and suicidal thoughts or actions. Use with caution in patients with a history of or risk factor for depression. Reactions may occur following the first dose; discontinue if reaction occurs and institute appropriate therapy.
- Tendinitis/tendon rupture: Fluoroquinolones have been associated with an increased risk of tendonitis and tendon rupture in all ages; risk may be increased with concurrent corticosteroids, solid organ transplant recipients, and in patients >60 years of age, but has also occurred in patients without these risk factors. Rupture of the Achilles tendon has been reported most frequently; but other tendon sites (eg, rotator cuff, biceps, hand) have also been reported. Inflammation and rupture may occur bilaterally. Cases have been reported within hours or days of initiation, and up to several months after discontinuation of therapy. Strenuous physical activity, renal failure, and previous tendon disorders may be independent risk factor for tendon rupture. Discontinue at first sign of tendon pain, swelling, inflammation or rupture. Avoid use in patients with a history of tendon disorders or who have experienced tendinitis or tendon rupture.
- Superinfection: Prolonged use may result in fungal or bacterial superinfection, including Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) and pseudomembranous colitis; CDAD has been observed >2 months postantibiotic treatment.
Disease-related concerns:
- Myasthenia gravis: [US Boxed Warning]: May exacerbate muscle weakness related to myasthenia gravis; avoid use in patients with known history of myasthenia gravis. Cases of severe exacerbations, including the need for ventilatory support and deaths have been reported.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution in patients with renal impairment; dosage adjustment required. May increase risk of tendon rupture.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Use with caution in patients with rheumatoid arthritis; may increase risk of tendon rupture.
Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Drug-drug interactions: Potentially significant interactions may exist, requiring dose or frequency adjustment, additional monitoring, and/or selection of alternative therapy. Consult drug interactions database for more detailed information.
Special populations:
- Elderly: Adverse effects (eg, hepatotoxicity, tendon rupture, QT changes, aortic dissection) may be increased in the elderly.
- G6PD deficiency: Hemolytic reactions may (rarely) occur with quinolone use in patients with latent or actual G6PD deficiency.
- Pediatric: Safety of use in pediatric patients for >14 days of therapy has not been studied; increased incidence of musculoskeletal disorders (eg, arthralgia, tendon rupture) has been observed in children.
Dosage form specific issues:
- Benzyl alcohol and derivatives: Some dosage forms may contain benzyl alcohol; large amounts of benzyl alcohol (≥99 mg/kg/day) have been associated with a potentially fatal toxicity ("gasping syndrome") in neonates; the "gasping syndrome" consists of metabolic acidosis, respiratory distress, gasping respirations, CNS dysfunction (including convulsions, intracranial hemorrhage), hypotension, and cardiovascular collapse (AAP ["Inactive" 1997]; CDC 1982); some data suggests that benzoate displaces bilirubin from protein binding sites (Ahlfors 2001); avoid or use dosage forms containing benzyl alcohol with caution in neonates. See manufacturer's labeling.
Other warnings/precautions:
- Appropriate use: [US Boxed Warning]: Reserve use of levofloxacin for treatment of acute bacterial sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, or uncomplicated urinary tract infection for patients who have no alternative treatment options because of the risk of disabling and potentially serious adverse reactions (eg, tendinitis and tendon rupture, peripheral neuropathy, CNS effects).
Monitoring Parameters
Evaluation of organ system functions (renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic) is recommended periodically during therapy; the possibility of crystalluria should be assessed; WBC and signs of infection, altered mental status, signs and symptoms of tendonitis; signs and symptoms of disordered glucose regulation
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Considerations
Levofloxacin crosses the placenta and can be detected in the amniotic fluid and cord blood (Ozyüncü 2010a; Ozyüncü 2010b). Information specific to levofloxacin use during pregnancy is limited (Padberg 2014).
Patient Education
What is this drug used for?
- It is used to treat bacterial infections.
Frequently reported side effects of this drug
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
Other side effects of this drug: Talk with your doctor right away if you have any of these signs of:
- Kidney problems like unable to pass urine, blood in the urine, change in amount of urine passed, or weight gain.
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis like red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin (with or without fever); red or irritated eyes; or sores in mouth, throat, nose, or eyes.
- Tendon inflammation or rupture like pain, bruising, or swelling in the back of the ankle, shoulder, hand, or other joints.
- Depression like thoughts of suicide, anxiety, emotional instability, or confusion.
- Liver problems like dark urine, fatigue, lack of appetite, nausea, abdominal pain, light-colored stools, vomiting, or yellow skin.
- High blood sugar like confusion, fatigue, increased thirst, increased hunger, passing a lot of urine, flushing, fast breathing, or breath that smells like fruit.
- Low blood sugar like dizziness, headache, fatigue, feeling weak, shaking, fast heartbeat, confusion, increased hunger, or sweating.
- Noise or ringing in the ears
- Chest pain
- Fast heartbeat
- Abnormal heartbeat
- Passing out
- Dizziness
- Severe loss of strength and energy
- Muscle pain
- Muscle weakness
- Difficulty focusing
- Trouble with memory
- Trouble sleeping
- Agitation
- Restlessness
- Vision changes
- Sensing things that seem real but are not
- Anxiety
- Nightmares
- Confusion
- Behavioral changes
- Mood changes
- Seizures
- Severe headache
- Shortness of breath
- Bruising
- Bleeding
- Tremors
- Abnormal gait
- Vaginal pain, itching, and discharge
- Thrush
- Chills
- Severe or persistent abdominal pain
- Severe or persistent chest pain
- Severe or persistent back pain
- Nerve problems like sensitivity to heat or cold; decreased sense of touch; burning, numbness, or tingling; pain, or weakness in the arms, hands, legs, or feet.
- Clostridioides (formerly Clostridium) difficile-associated diarrhea like abdominal pain or cramps, severe diarrhea or watery stools, or bloody stools.
- Signs of a significant reaction like wheezing; chest tightness; fever; itching; bad cough; blue skin color; seizures; or swelling of face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Note: This is not a comprehensive list of all side effects. Talk to your doctor if you have questions.
Consumer Information Use and Disclaimer: This information should not be used to decide whether or not to take this medicine or any other medicine. Only the healthcare provider has the knowledge and training to decide which medicines are right for a specific patient. This information does not endorse any medicine as safe, effective, or approved for treating any patient or health condition. This is only a brief summary of general information about this medicine. It does NOT include all information about the possible uses, directions, warnings, precautions, interactions, adverse effects, or risks that may apply to this medicine. This information is not specific medical advice and does not replace information you receive from the healthcare provider. You must talk with the healthcare provider for complete information about the risks and benefits of using this medicine.